Predicting performance of gas condensate reservoirs
a technology of gas condensate and reservoir, which is applied in the direction of instruments, surveying, and accessories of wellbore/wells, can solve the problems of significant productivity reduction, difficult to accurately forecast the gas condensate productivity, and significant reduction in gas phase production from gas condensate wells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
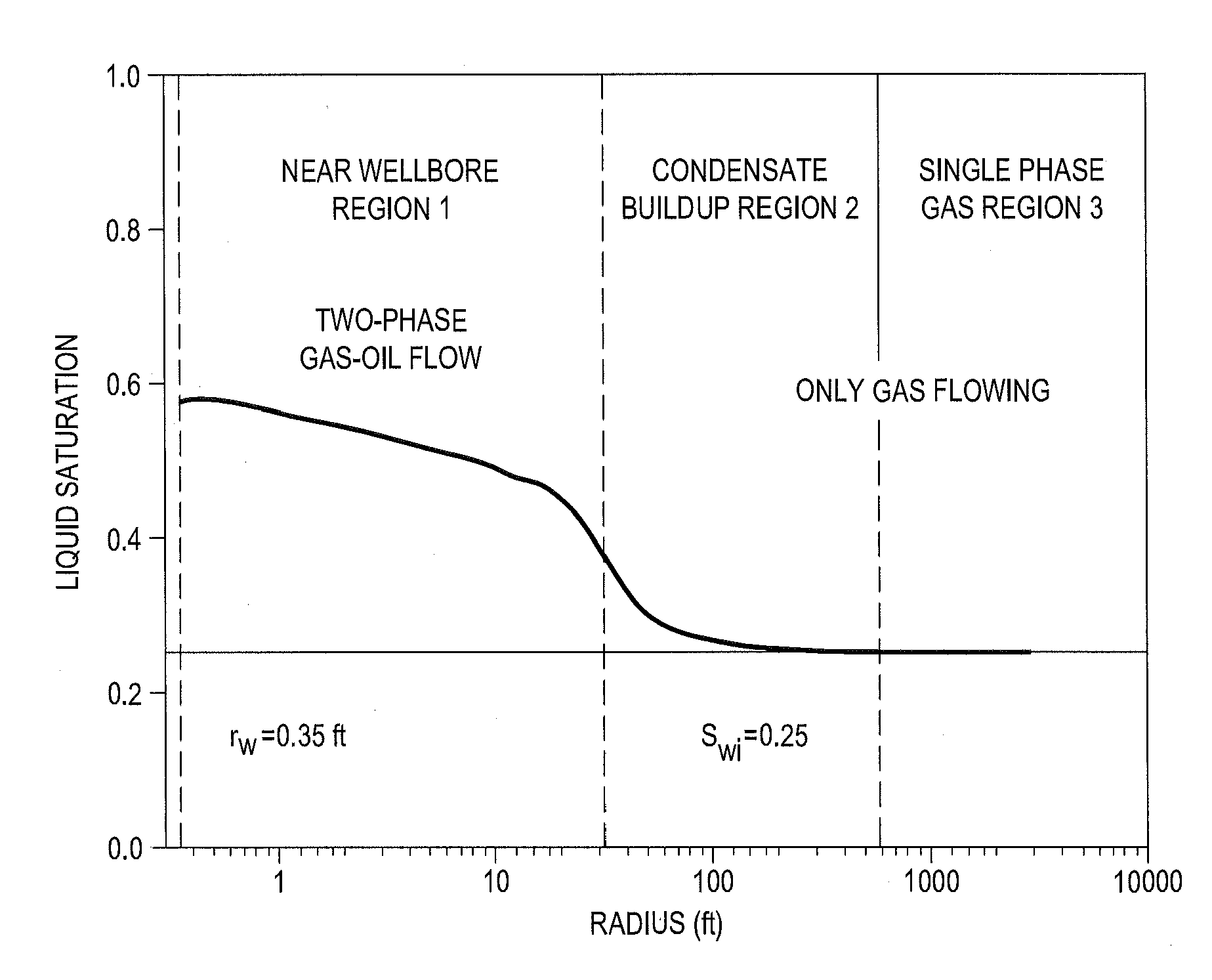
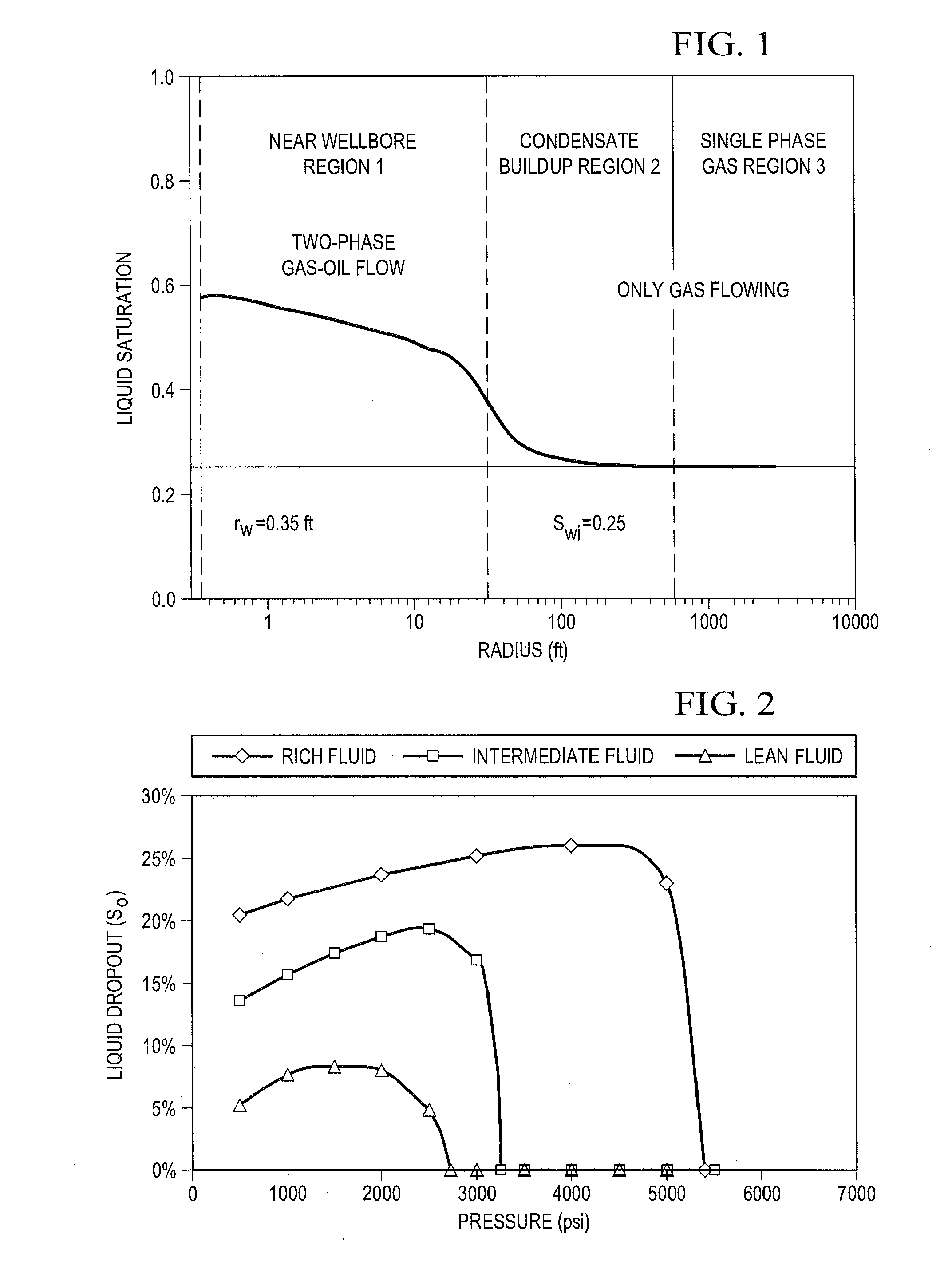
[0052]In the drawings, FIG. 1 schematically indicates flow behavior of a gas condensate well in three regions. Region 1 represents an inner near-wellbore region, as shown in FIG. 1, where both condensate and gas are mobile. It is the most important region for calculating condensate well productivity, as most of the pressure drop occurs in Region 1. The flowing composition (GOR) within Region I is constant throughout and a semi-steady state regime exists. This means that the single phase gas entering Region 1 has the same composition as the produced well stream mixture. The dew point of the producing well stream mixture equals the reservoir pressure at the outer edge of Region 1.
[0053]Region 2 is the region where the condensate saturation is building up. The condensate is immobile, and only gas is flowing. The loss in productivity due to liquid build-up is mostly influenced by the value of gas relative permeability (krg) near the well when compared with the value of krg in the reserv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com