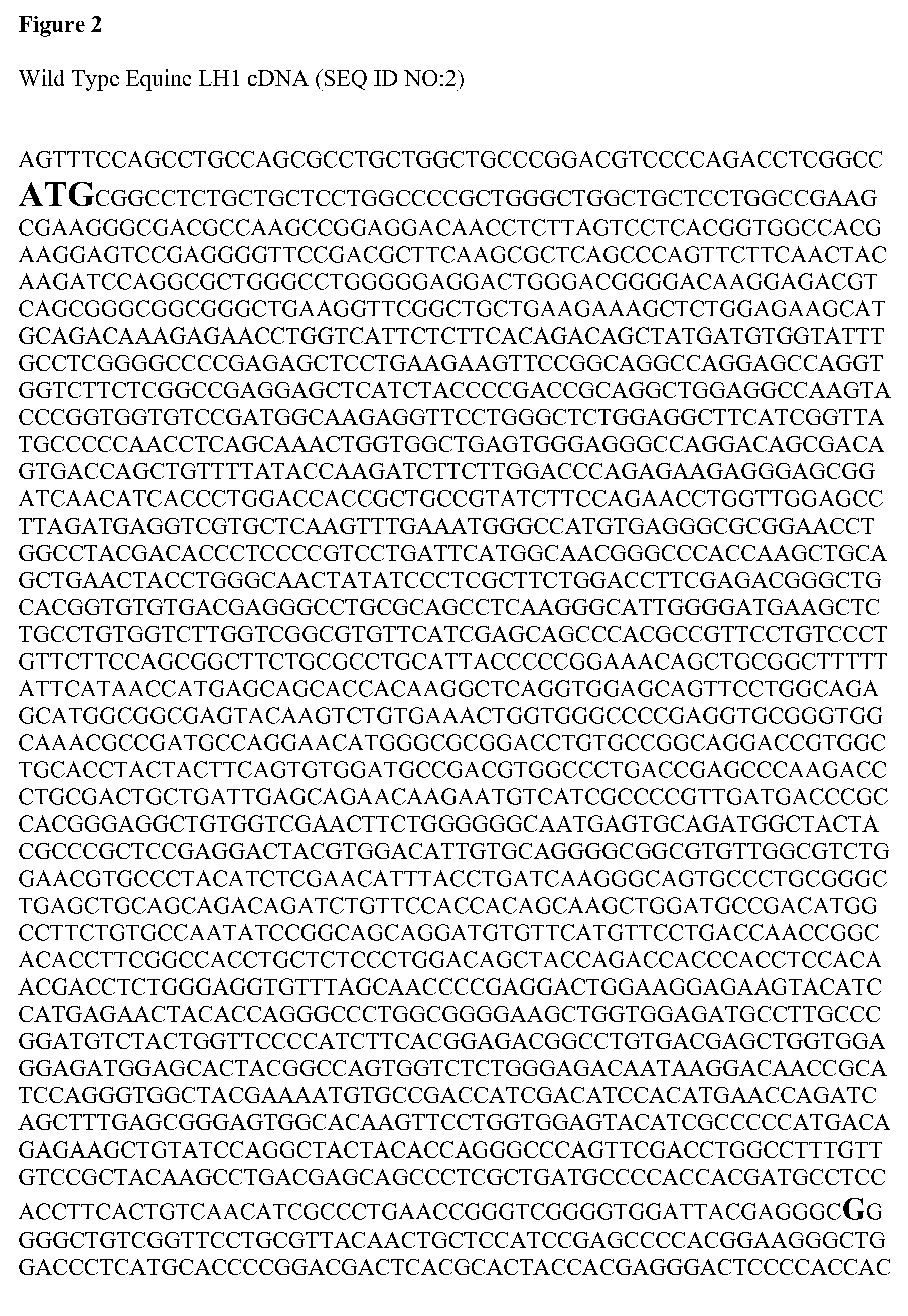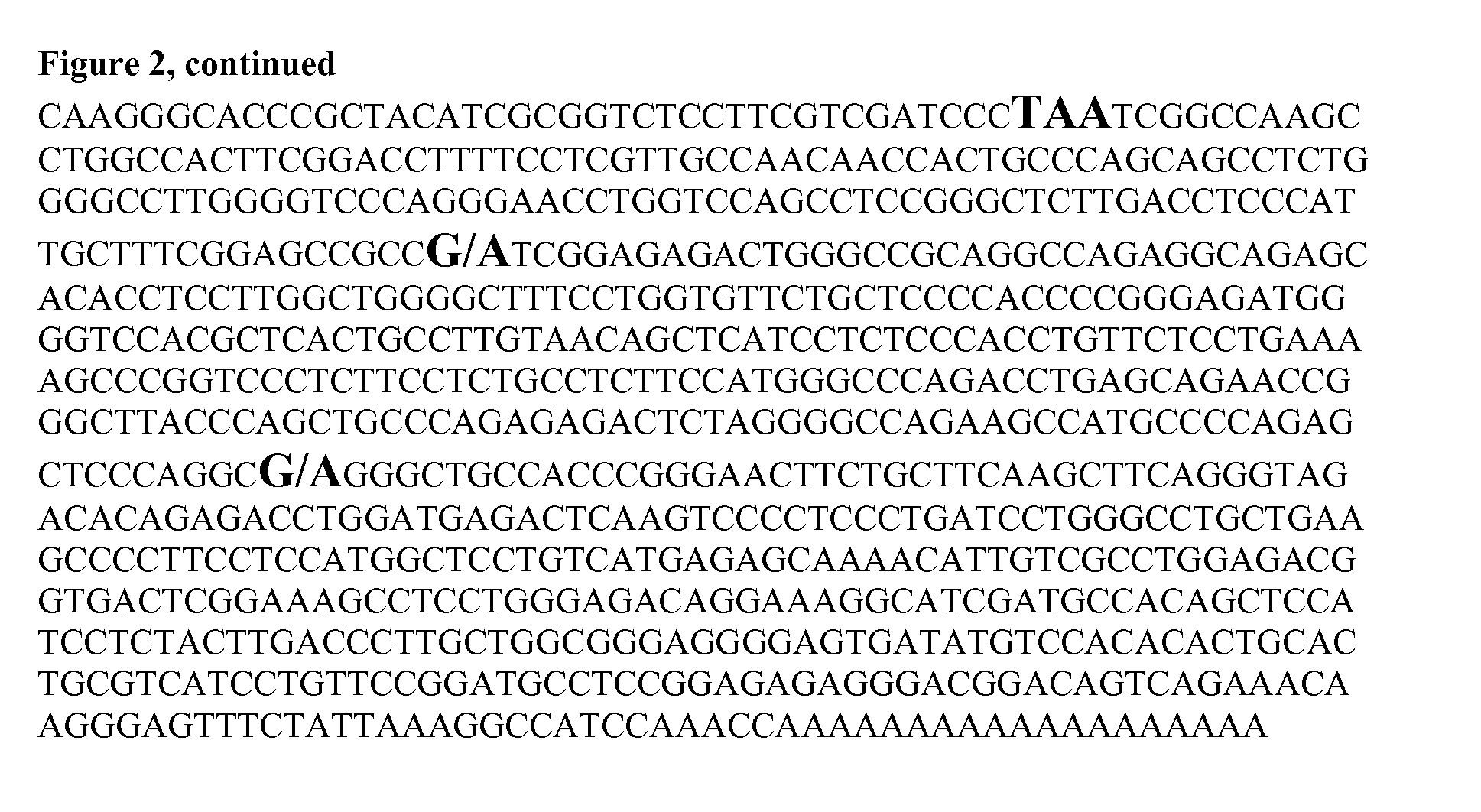Identification of the causative mutation for inherited connective tissue disorders in equines and methods for testing for same
a technology of connective tissue disorders and mutations, applied in the field of detecting point mutations in genes associated with fragile foal syndrome type 1 and other directions, can solve problems such as hyperextensibility of all skin types
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0038]This Example demonstrates a 100% correlation between homozygosity (AA) for the causative mutation and the disease phenotype. The disease phenotype is recognizable on clinical examination and is characterized by the presence at birth of soft skin lacking adequate tensile strength to withstand even normal environmental contact. The skin is hyperextensible (lacking normal recoil when traction is applied / released) over the whole body, especially the head, neck, thorax and limbs. Over the first hours to days of life, focal seromas, hematomas, and lacerations / ulcerations result from incidental environmental contact. Such lesions are predominantly found over pressure points such as fetlocks (metacarpal-phalangeal joints), carpi (knees), and tarsi (hocks), but may occur anywhere on the body (including oral cavity and perineum). Limb joints, particularly the fetlocks) are lax and hyperextensible, and affected foals cannot typically stand normally. The ears are typically bent or floppy....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| freezing temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com