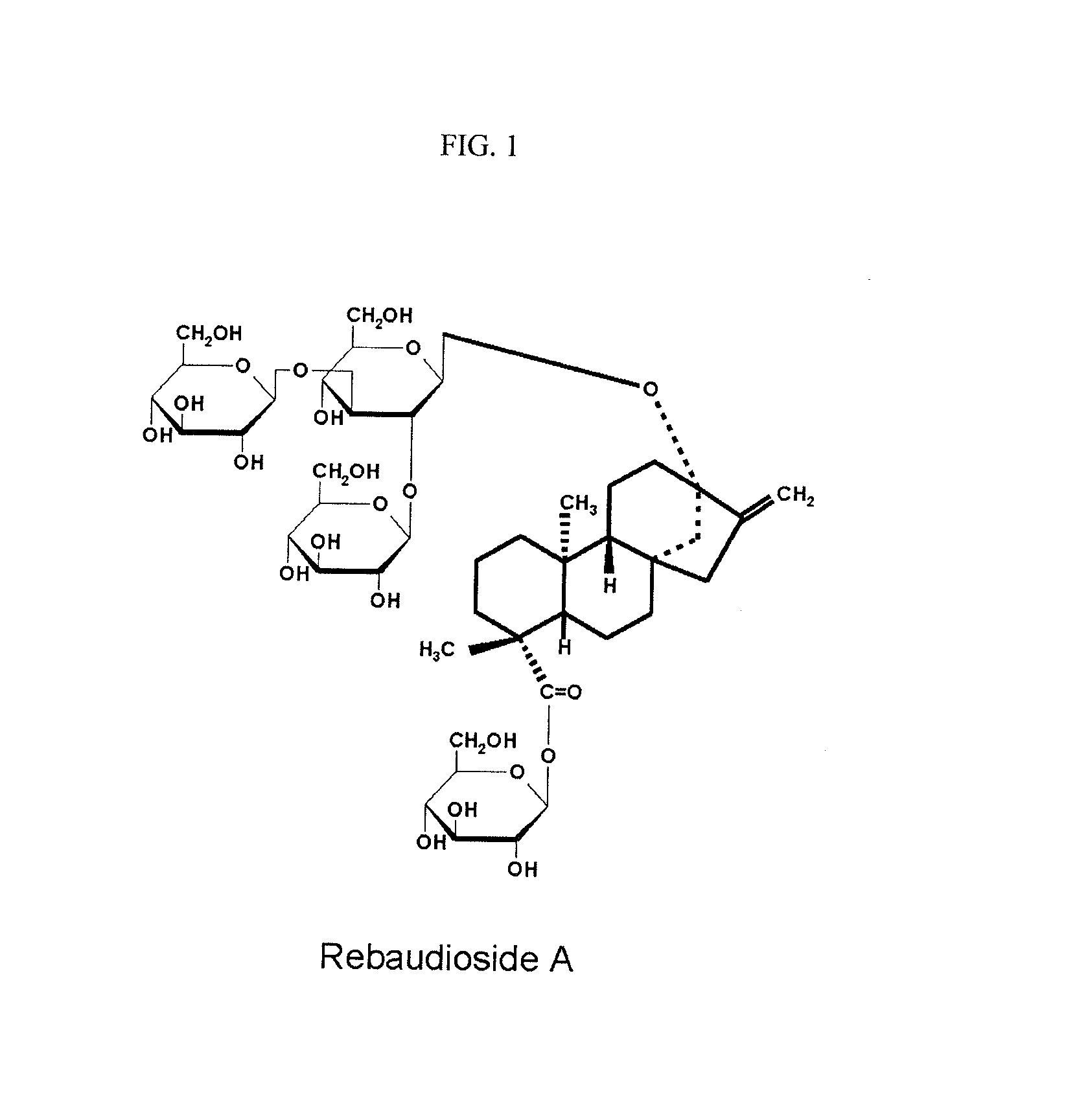
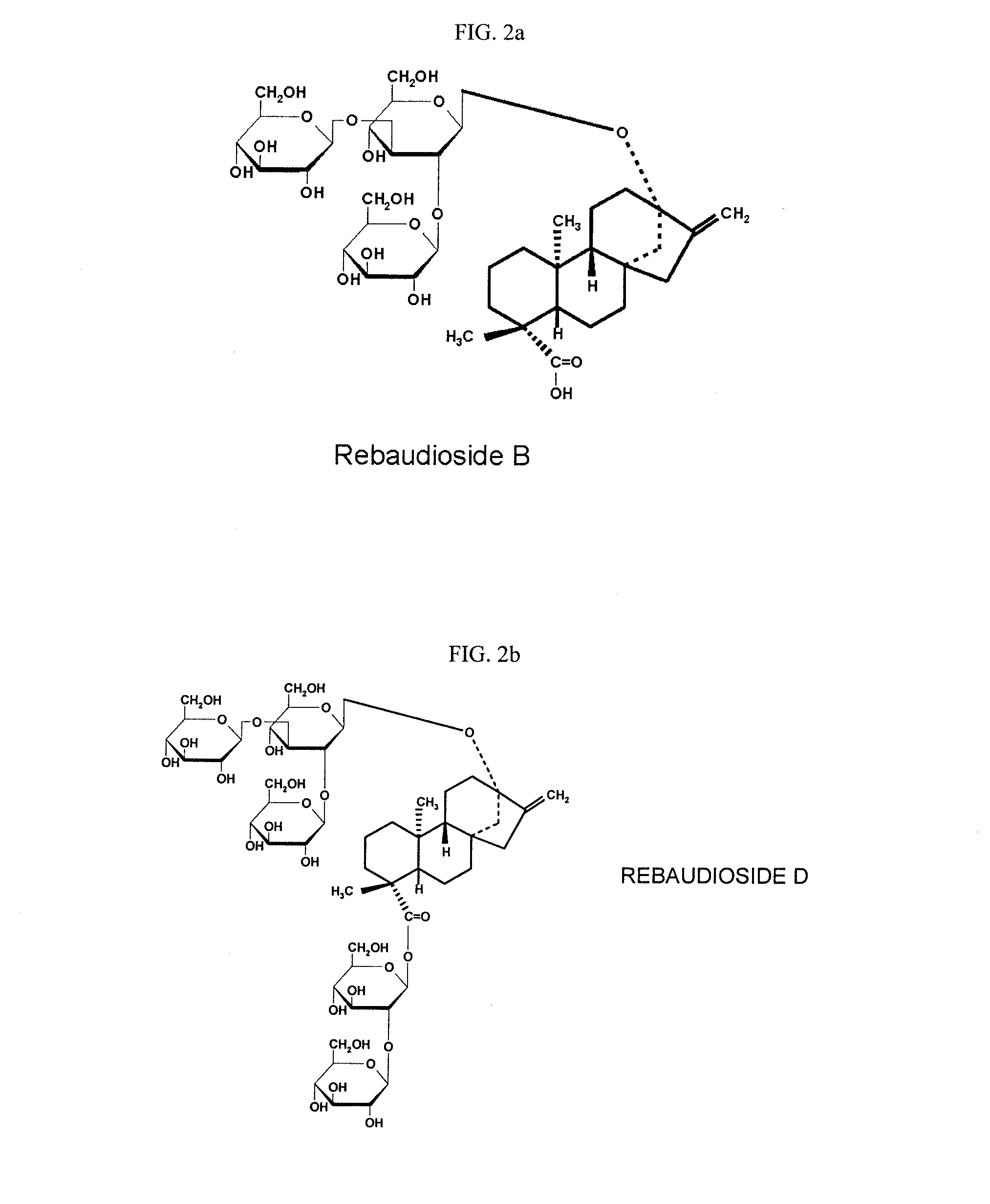
Stevia composition
a technology of stevia and composition, applied in the field of stevia composition, can solve the problems of sugareners such as dulcin, sodium cyclamate and saccharin being banned or restricted, glycosides still possessing non-sweet taste attributes,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Reb D and Reb B Soluble Composition
[0075]70 g of rebaudioside D with 98.1% purity (dry weight basis), having water solubility of 0.03% and 30 g of rebaudioside B with 99.0% purity (dry weight basis), and having water solubility of 0.01%, both produced by PureCircle Sdn Bhd (Malaysia), were mixed with 400 g water and incubated in thermostatted oil bath. The temperature was increased at 1° C. per minute to 121° C. The mixture was maintained at 121° C. for 1 hour and then the temperature was decreased to 80° C., at 1° C. per minute, and the obtained solution was spray dried using YC-015 laboratory spray drier (Shanghai Pilotech Instrument & Equipment Co. Ltd., China) operating at 175° C. inlet and 100° C. outlet temperature. Solution was maintained at 80° C. to prevent premature crystallization. About 90 g of amorphous powder was obtained with 1% solubility.
example 2
Effect of Stevia Composition on Solubility in Water
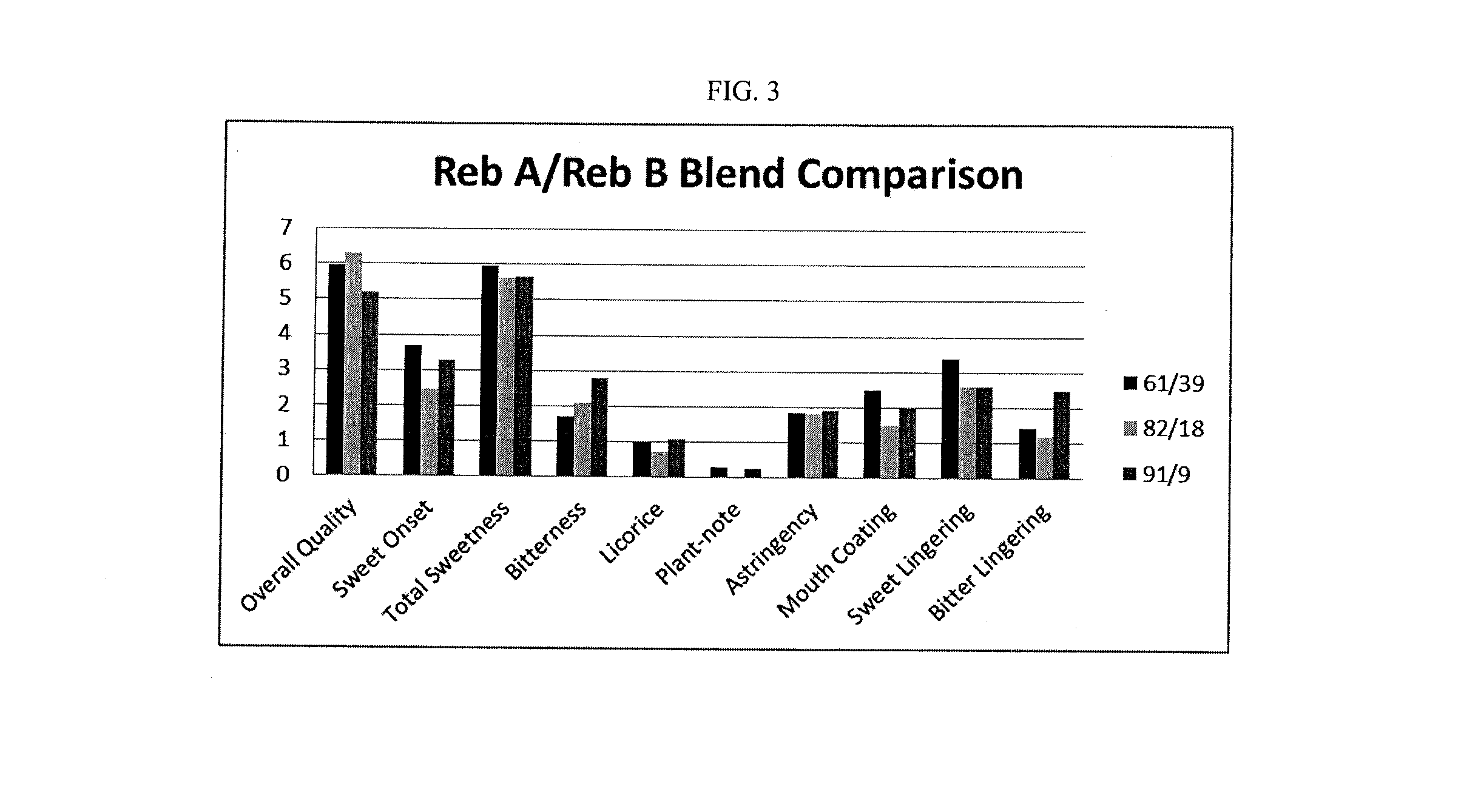
[0076]Solubility were evaluated for Reb A, Reb B, mechanical blends of Reb A and Reb B powders of different ratios, and mixtures of Reb A and Reb B prepared according to process described in EXAMPLE 1. Reb A and Reb B showed solubility around 1% and 0.1% at room temperature and increased solubility on heating to a higher temperature. Table 1 shows the solubility of different ingredients and their blends.
TABLE 1Reb A / Reb B blends (wt / wt ratio of Reb Bto total glycosides)PurePureBlend made by processSolubilityRebRebMechanical blendof inventionin waterAB10%16%26%10%16%26%0.5% YesNo*No*No*No*YesYesYes1%YesNo*No*No*No*YesYesYes2%NoNo*No*No*No*YesYesYes5%NoNo*No*No*No*YesYesYes*Suspension was opaque and particles settled down when mixing was stopped
example 3
Sweetness Factor (SF) Determination
[0077]The sweetness factors for different sweetener from all major groups were measured by tasting several concentrations of each sweetener in water by a trained panel. From the sensory test data, the concentration (%) that corresponds to the 5% sucrose equivalent (SE) sweetness were estimated and listed in Table 2. The sweetness equivalent (SE) of high intensity sweeteners (HIS) varies according to the target sugar equivalent sweetness levels, that are tested as shown in Table 3. Table 3 also shows the sweetness factors of Reb A, Reb B and a test sample (Reb A / B) with a blend of Reb A and Reb B at 84:16 ratio.
TABLE 2Sweetness factors of selected sweetenersCalculatedSweetener GroupSweetenerUsage Level, %SFSteviol GlycosideReb A (97%)0.0172291Reb D (97%)0.0172291Reb B (98%)0.0397126Other Natural HISMogroside V (70%)0.0212236GlycosylatedGlucosylated Steviol0.055690Terpenoid sweetenerGlycosidesSynthetic HISSucralose0.0083602Sugar AlcoholErythritol7.49...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com