Method for joint-mining of coalbed gas and coal
a coalbed gas and coal-fired technology, applied in the field of new processes, can solve the problems of increasing geostress and gas pressure, difficulty in realizing and difficulty in achieving scale and industrial development in other directions at present, so as to improve the seepage rate of coalbed gas, and improve the permeability of coal seams after heated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
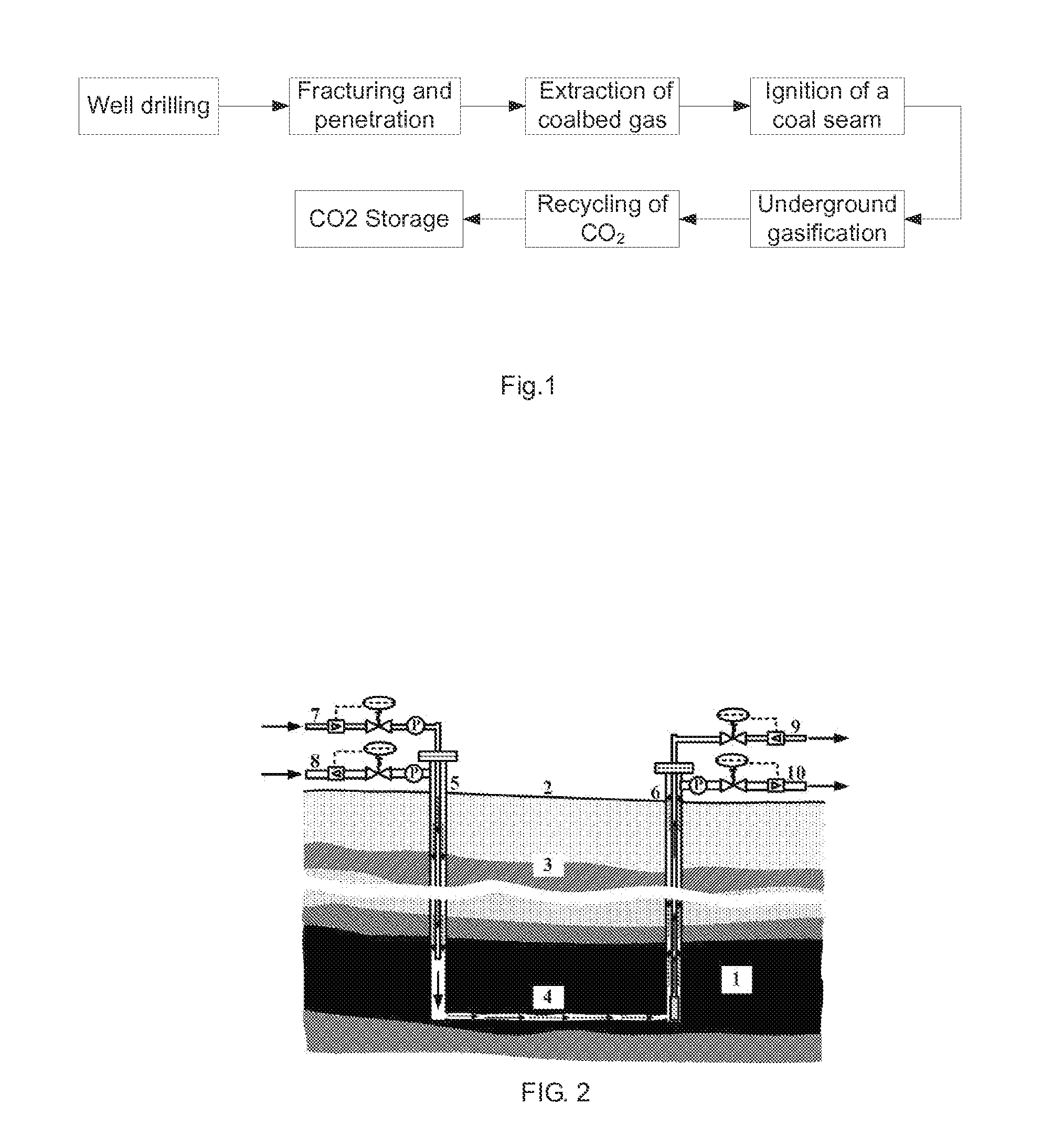
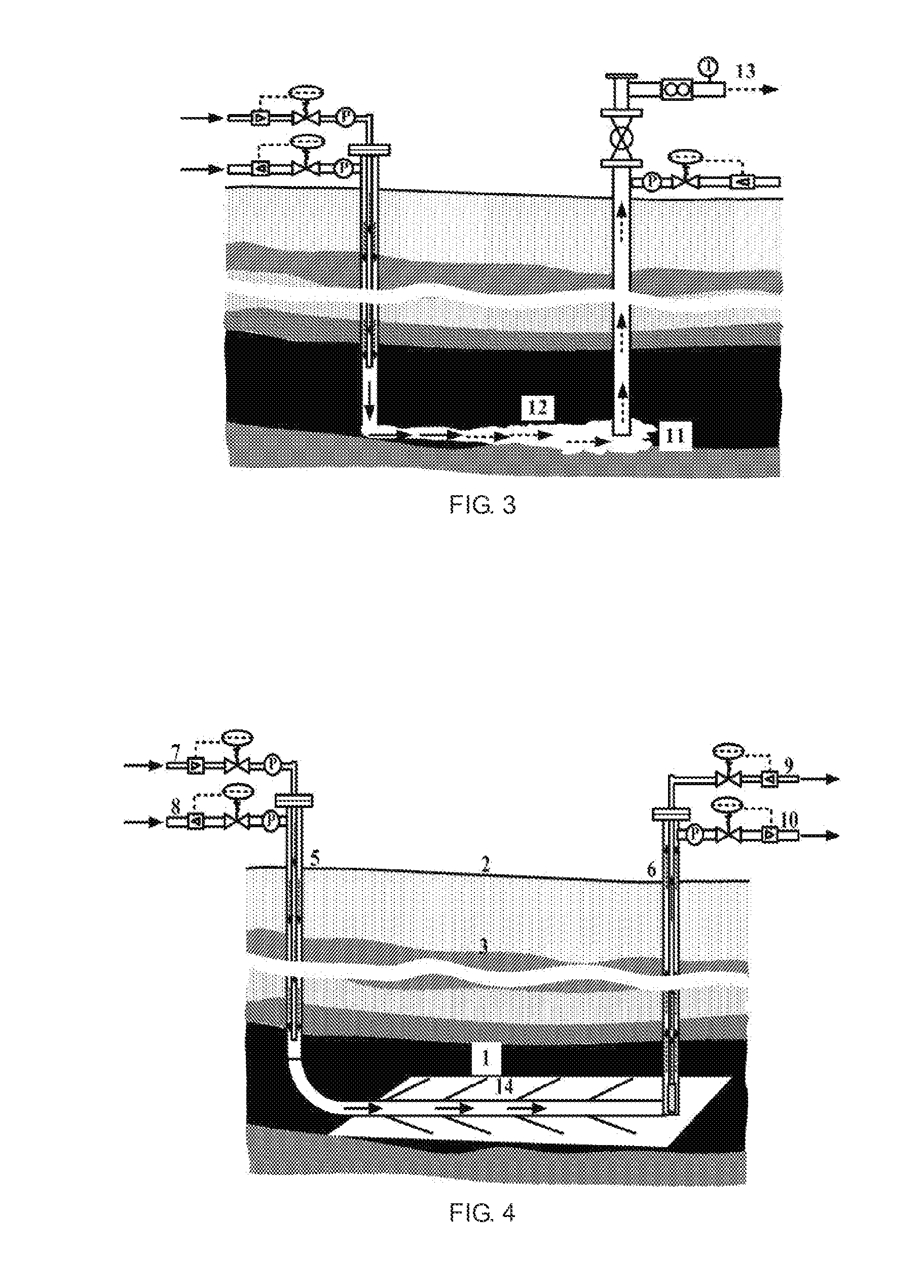
[0095]This embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 2 and FIG. 3. FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a method for joint-mining of coalbed gas and coal according to the present invention, wherein a coal seam between boreholes is injected with CO2, i.e. by cold state fracturing, for extraction of coalbed gas. FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of the method for joint-mining of coalbed gas and coal, wherein a fire zone is established to heat a fracture and then expanded it to form a gasification passage for synchronous displacement of coalbed gas. As shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, boreholes are arranged according to the range of a coal seam to be gasified in this embodiment. The number of the boreholes is determined according to the reserves of the coal seam and the production scale of gas. However, to implement the present invention, at least one injection borehole and one production borehole should be included. The specific implementation is as below.
[0096]Referring to FIG. 2 and FI...
embodiment 2
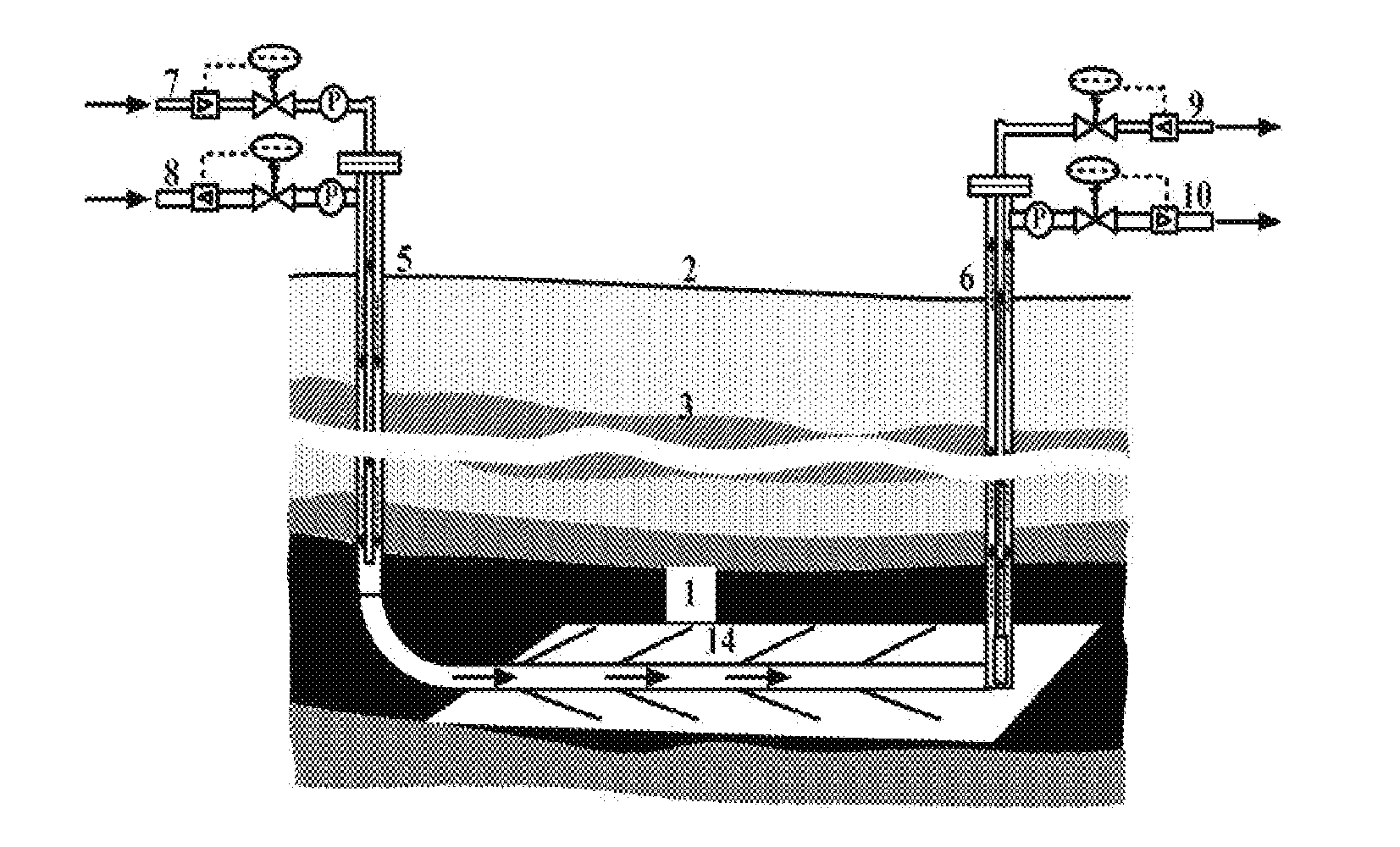
[0110]In Embodiment 2, the extraction rate of the coalbed gas is quickened by a pinnate branch horizontal drilling technology, and the natural fractures and cleats of the coal seam are communicated by a multilateral well technology, thereby increasing the exposed area of the coal seam and facilitating the implementation of the subsequent gasification. This embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 4 and FIG. 5. FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of the method for joint-mining of coalbed gas and coal according to the present invention, wherein the extraction of coalbed gas is performed by pinnate branch horizontal drilling. FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of the method for joint-mining of coalbed gas and coal. The specific implementation is as below.
[0111]A vertical borehole as a production borehole 6 is constructed from the ground 2 to the coal seam 1 through overlying strata 3. A vertical borehole as an injection borehole 5 is constructed at a certain distance away from the prod...
embodiment 3
[0120]Embodiment 3 is basically the same as Embodiment 2, except for a different that an original passage for drainage and gas extraction is established by directionally horizontal drilling technology and the horizontal well 15 is formed with an arrangement mode of a U-shape structure. The horizontal well is vertical to a direction of a primary fracture of a coal seal, a vertical well, i.e., a production borehole 6, is used for drainage while gas extraction is performed by an injection borehole 5. At the end of the original extraction of coalbed gas, a fire zone is established in the production borehole 6, the passage starts being heated, and the synchronous displacement of coalbed gas is performed to implement the gasification of the coal seam between the boreholes. This embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 6 and FIG. 7. FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a method for joint-mining of coalbed gas and coal according to the present invention, where the extraction of coalb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com