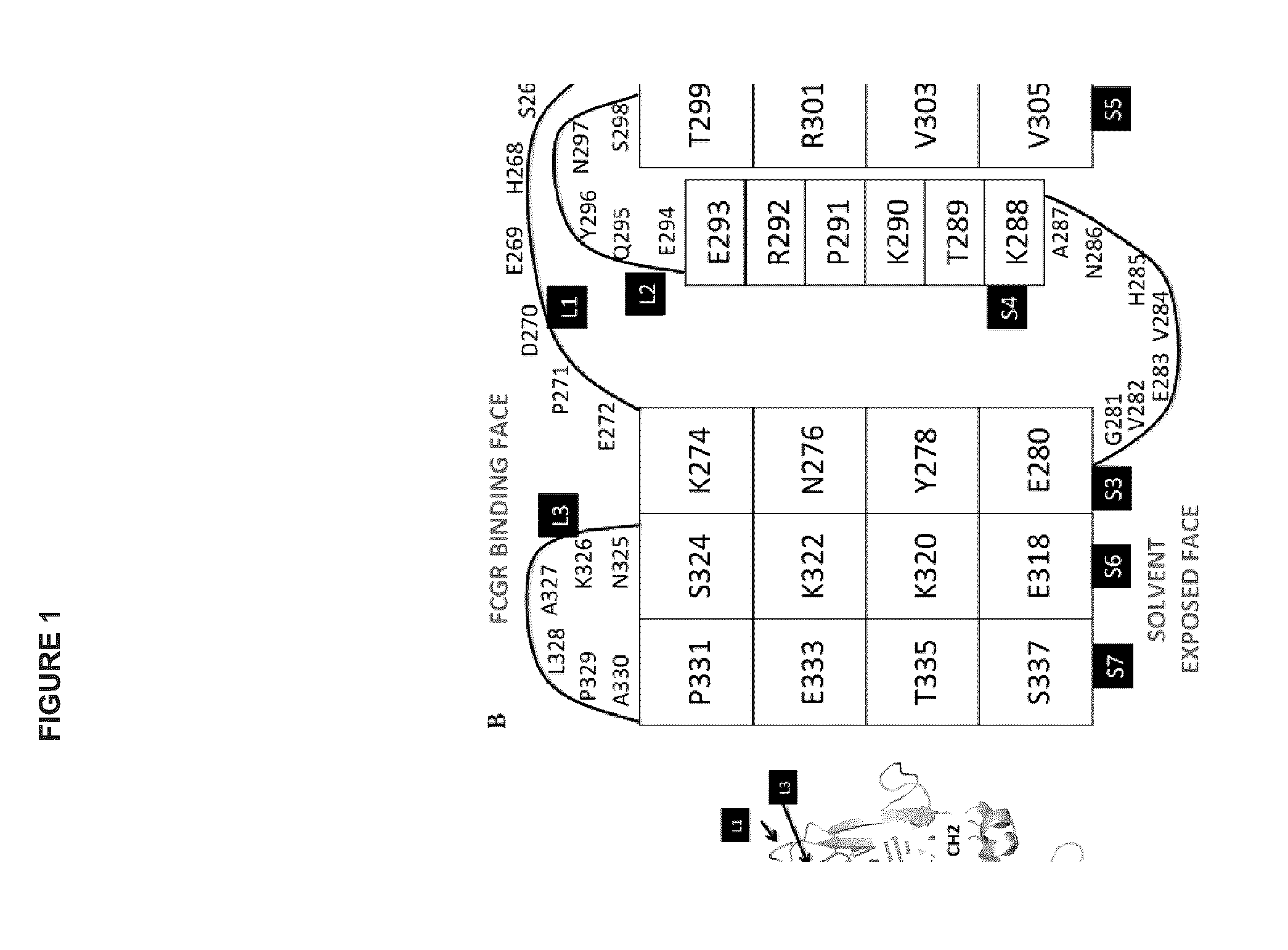
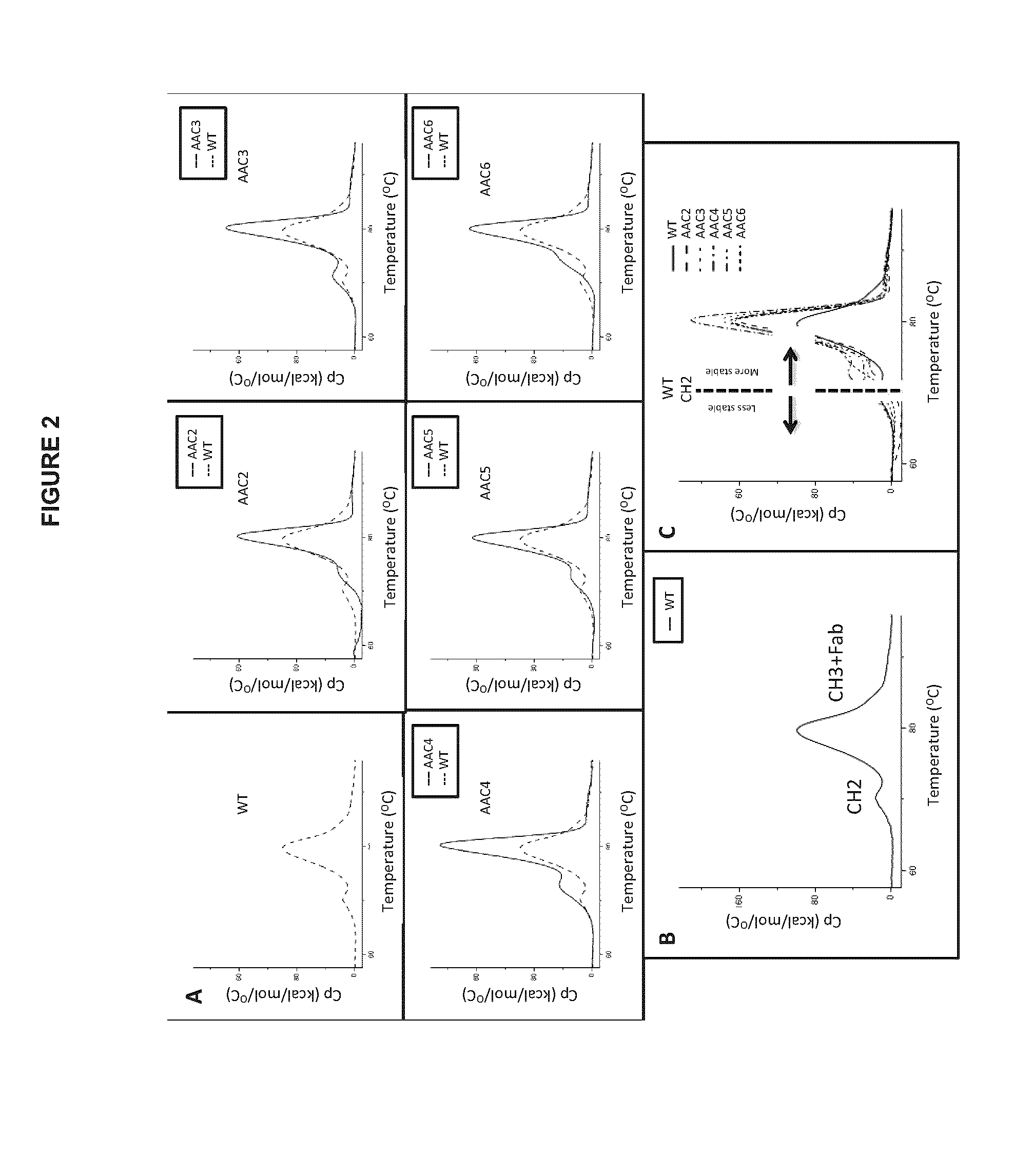
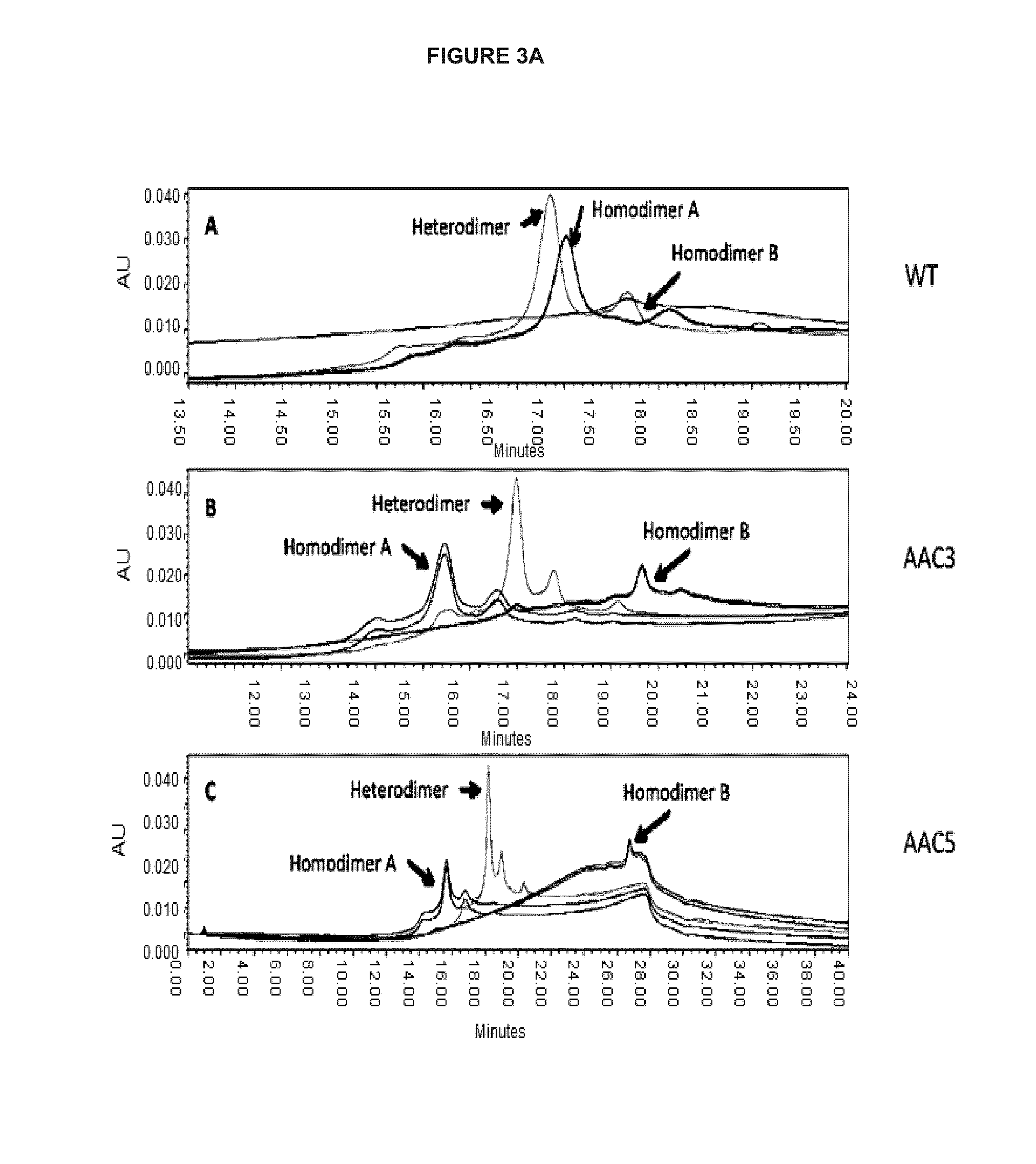
Heteromultimers with reduced or silenced effector function
a heterodimer and effector function technology, applied in the field of therapeutic antibody design, to achieve the effect of reducing the effector function of an antibody construct and reducing binding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation and Expression of Antibody Constructs (Heteromultimers)
[0234]The following antibody constructs were prepared. All antibody constructs were based on the sequence of the wild-type anti-Her2 antibody trastuzumab (see FIG. 5, SEQ ID NO:2 for wild-type trastuzumab Heavy chain amino acid sequence, SEQ ID NO:3 for wild-type trastuzumab light chain sequence) with the following added modifications in the heavy chain CH3 domain introduced in order to promote the formation of a heterodimer Fc domain with increased stability as compared to a CH3 domain that does not comprise amino acid mutations.
Chain A: T350V / L351Y / S400E / F405A / Y407V, and
Chain B: T350V / T366L / N390R / K392M / T394W
[0235]This construct, with the above modifications is referred to as v791. All sequences described herein are numbered using the EU numbering system.
[0236]Additional variants were constructed based on v791, with amino acid modifications in the hinge region and or CH2 domain of the heavy chain as shown in Table A...
example 2
Asymmetric Antibody Constructs Based on Trastuzumab do not Bind to FcγR
[0240]The ability of the asymmetric antibody constructs to bind to FcγRIIaH, FcγRIIaR, FcγRIIb FcγRIIIaF, FcγRIIIaV, and FcγRIa was assessed by surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
[0241]Affinity of FcγRs to antibody Fc was measured by SPR using a PrateOn XPR36 at 25° C. with 10 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 3.4 mM EDTA, and 0.05% Tween 20 at pH 7.4. Recombinant HER-2 was captured on the activated GLM sensorchip by injecting 4.0 μg / mL in 10 mM NaOAc (pH 4.5) at 25 μL / min until approx. 3000 resonance units (RUs) were immobilized with the remaining active groups quenched. 40 μg / mL of purified HER-2 / neu-based antibodies were indirectly captured when injected at 25 μL / min for 240 s (resulting in approx. 500RUs) following a buffer injection to establish a stable baseline. FcγRs were injected at 60 μL / min for 120 s with a 180 s dissociation phase to obtain a set of binding sensograms. Resultant kD values were determined from bindi...
example 3
Asymmetric Antibody Constructs Based on Trastuzumab do not Bind to C1q
[0244]The ability of the asymmetric antibody constructs to bind to C1q was tested as follows. Human C1q was purchased from GenWay Biotech (San Diego, Calif.). SPR chip immobilization of antibodies was as described in Example 2. 30 nM C1q injected over mAb variants captured onto a HER2 SPR surface using standard protocols as also described in Example 2. The results are shown in Table C below.
TABLE CResults of C1q binding assayVariantC1q1WTyesControl / 1051NBAAC1partialAAC2NBAAC3NBAAC4NBAAC5NBAAC6NBAAC7NBAAC8NB1C1q is a hexamer of heterotrimers witha potential stoichiomentry mAb:C1q of 6:1. The binding kinetics were very complex, and a proper Kd could not be determined. Receptor was tested at 30 nM. ‘partial’ means diminished binding, ‘NB’ means no detectable binding
[0245]All of the variants showed undetectable binding to C1q, except for AAC1 which showed decreased, but detectable binding to C1q.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com