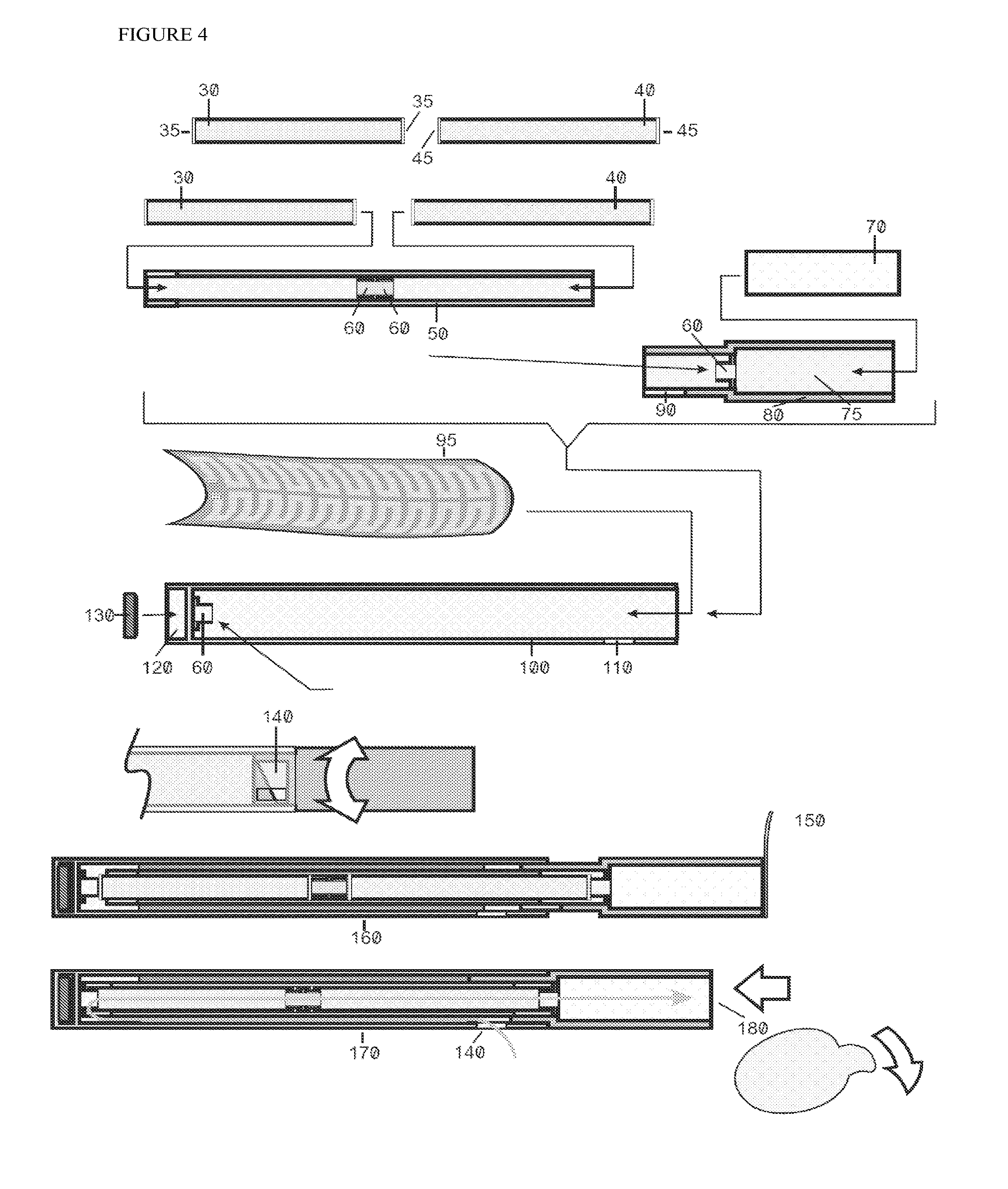
Device and method for delivery of a medicament
a delivery device and medicament technology, applied in the direction of drug compositions, tobacco, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of medicaments, limited use of pulmonary delivery, and limited use of medicaments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment # 3
[0181]EXPERIMENT #3: Evaluation of Leading Acid Candidates Under Ambient Temperature
[0182]Objective:
[0183]The objective of this experiment was to assess which of the leading acid candidates selected from the experiment described above will deliver the greatest amount of nicotine under ambient conditions.
[0184]Experimental Design:
[0185]The current experiment was carried out as described in the previous experiment except that the glass chambers were not immersed in a heated water bath, but sampled at ambient temperature. Individual experiments were carried out using the selected acid candidates: 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, Pyruvic acid, 2-Oxovaleric acid, 4-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, 3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid and 2-Oxooctanoic acid. For each experiment a different acid was placed in Chamber A as in the previous experiment with nicotine free base in Chamber B. A nicotine free base control experiment was also conducted as in the previous experiment.
[0186]Results:
[0187]The following tab...
experiment # 4
[0190]EXPERIMENT #4: Assessment of Leading Acid Candidates from the Previous 70° C. and Ambient Temperature Experiments (Experiment 2 and 3 Respectively) Utilizing the Prior Art Design for Aerosol Generation
[0191]Objective:
[0192]The objective of this experiment was to compare the prior art configuration to the sequential orientation of acid and base to determine which yields higher nicotine delivery. The two leading acid candidates which generated similar nicotine delivery at 70° C. and one acid candidate which delivered the highest amount of nicotine under ambient temperature (from Experiments #2-3) were tested under 70° C. and ambient conditions, respectively.
[0193]Experimental Design:
[0194]In this experiment, two identical rectangular glass chambers exactly like those used in Experiment #2 were employed. Chamber A contained 200 μL of the leading acid and chamber B contained 200 μL of nicotine free base. The two chambers were connected via a “Y” shaped glass connector which was th...
experiment # 5
[0199]EXPERIMENT #5: Effectiveness of a Sequential Arrangement of an Acid Reservoir and a Base Reservoir to Provide an Acid Over Base Environment in the Development of an Aerosol Plume with Sufficient Concentrations of Nicotine
[0200]Objective:
[0201]The objective of this experiment was to determine the influence of the arrangement of the acid and base reservoirs in sequence allowing the acid vapors to be lifted into the nicotine free base chamber and over the nicotine to generate a plume cloud with sufficient quantities of nicotine free base. Pyruvic acid was selected for use in this experiment.
[0202]Experimental Design:
[0203]The experimental design was the same as in Experiment #2. This experiment was divided into two parts, A and B. The first part, A, involved the assessment of the use of 200 pi, each of nicotine free base and pyruvic acid in separate chambers collected over 3 samples (20 puffs per sample). The second part of the experiment (part B) involved a comparison of the abo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com