Method and system for automatic address allocation in a network and network protocol therefor
a network and address technology, applied in the field of telecommunications networks, can solve the problems of time-consuming and error-prone manual task of configuring each node with the associated address, installation and maintenance of additional hardware in the network and software, and the financial cost of additional hardware and software, so as to facilitate the use of network resources more efficiently
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
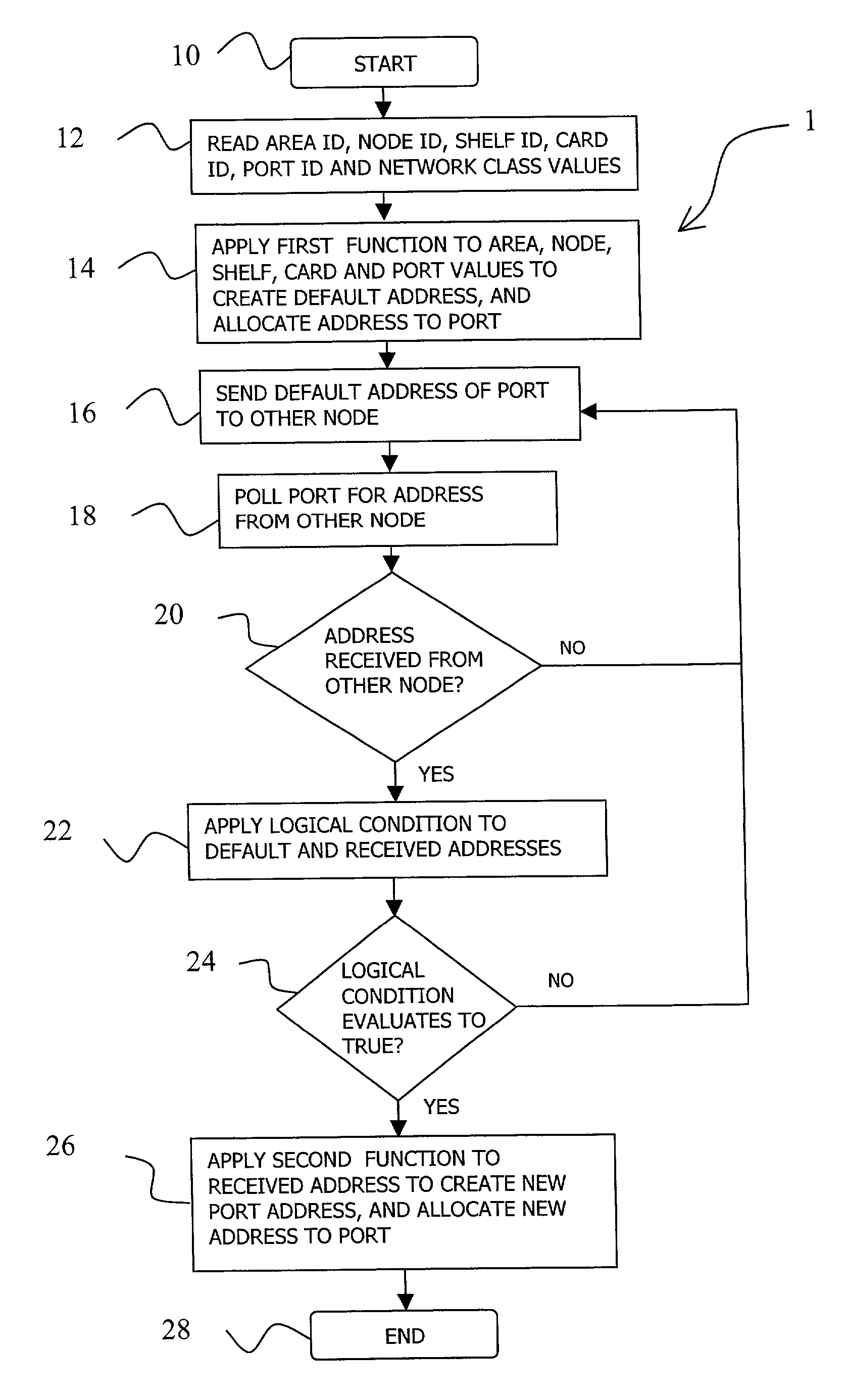
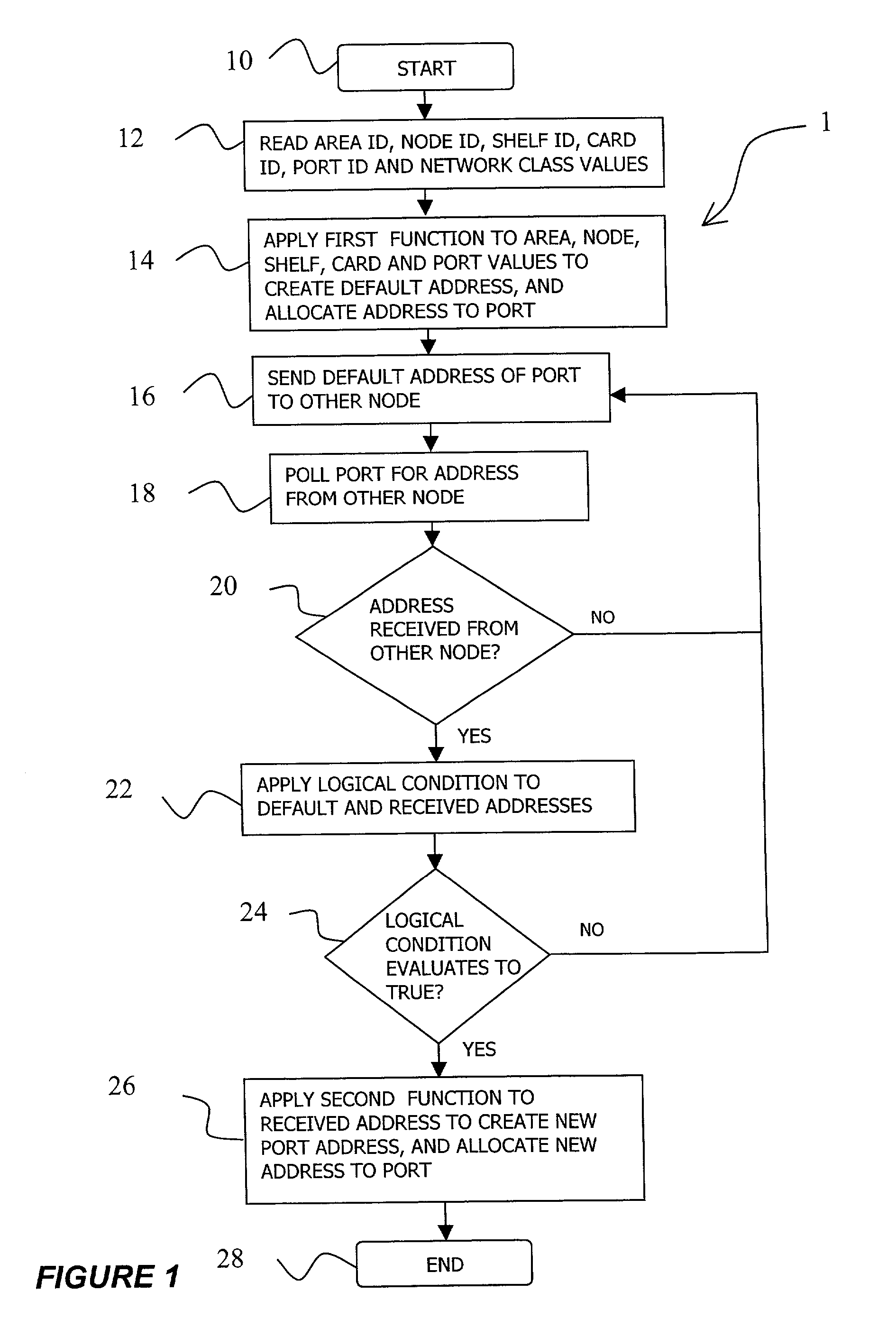
[0042]A method for automatic allocation of unique addresses to ports of the devices in a network according to a first embodiment of the invention is illustrated in FIG. 1 by flowchart 1. At the start of the method (box 10), a network administrator adds a new device to the network, e.g. a new node, powers up the node, provisions it with various cards, and configures the node with values for an area identifier, node identifier, and with an IP network type class value of “A”, “B” or “C”. The choice of the network class is performed before the network is created, and prior to the addition of any nodes to the network in function of the number of nodes that will be installed in the network. The definition of Class “A”, “B” and “C” networks is given in RFC 791, “INTERNET PROTOCOL, DARPA INTERNET PROGRAM, PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION”, published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), September 1981. A Class “A”, or / 8 network, is assigned to few networks in the Internet, where the network...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com