Random sampling as a built-in function for database administration and replication
a database and function technology, applied in relational databases, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable data quality improvement, and inability to provide exact analysis, so as to reduce the number of system calls, reduce time, and reduce the strain on the computer system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
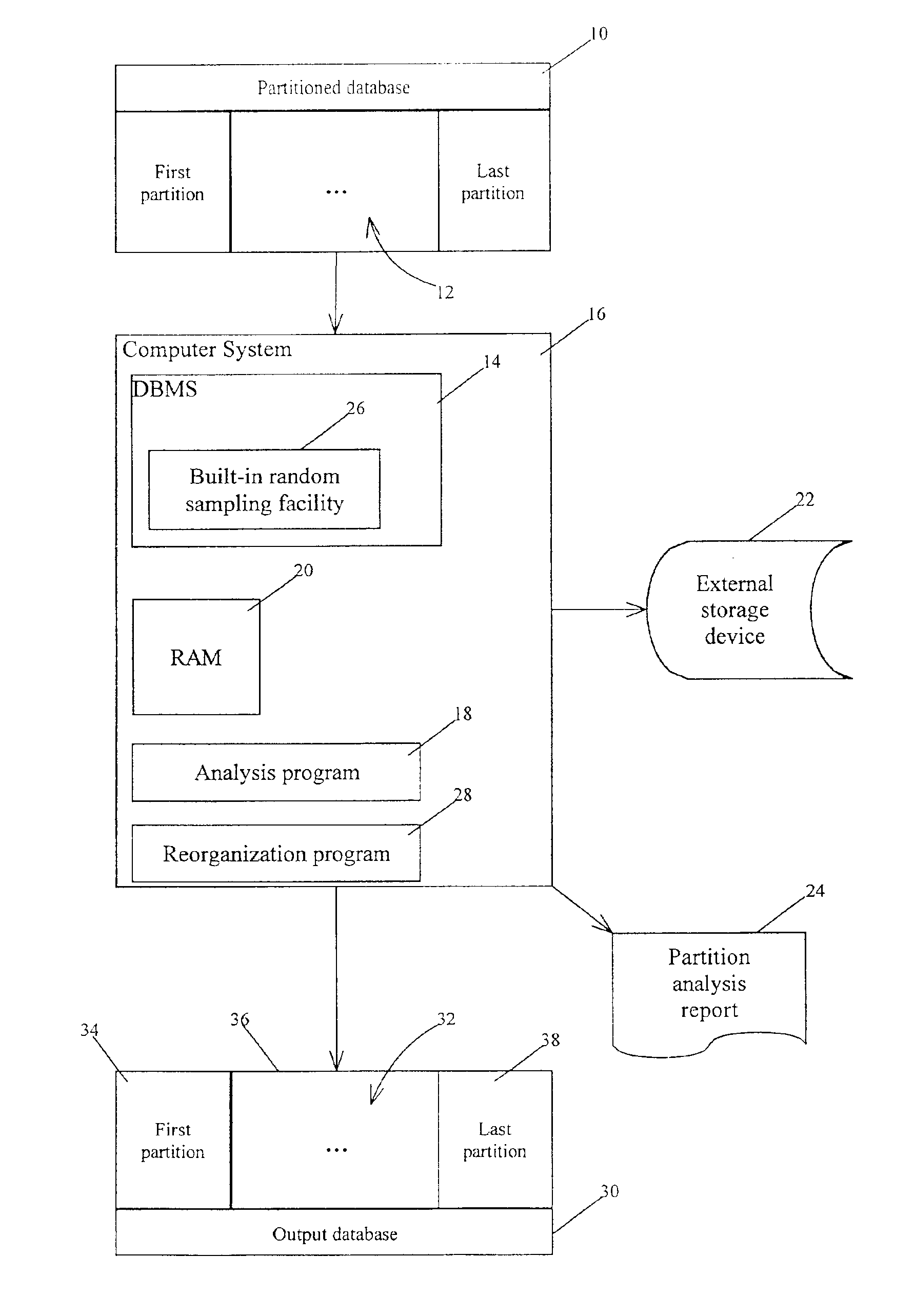
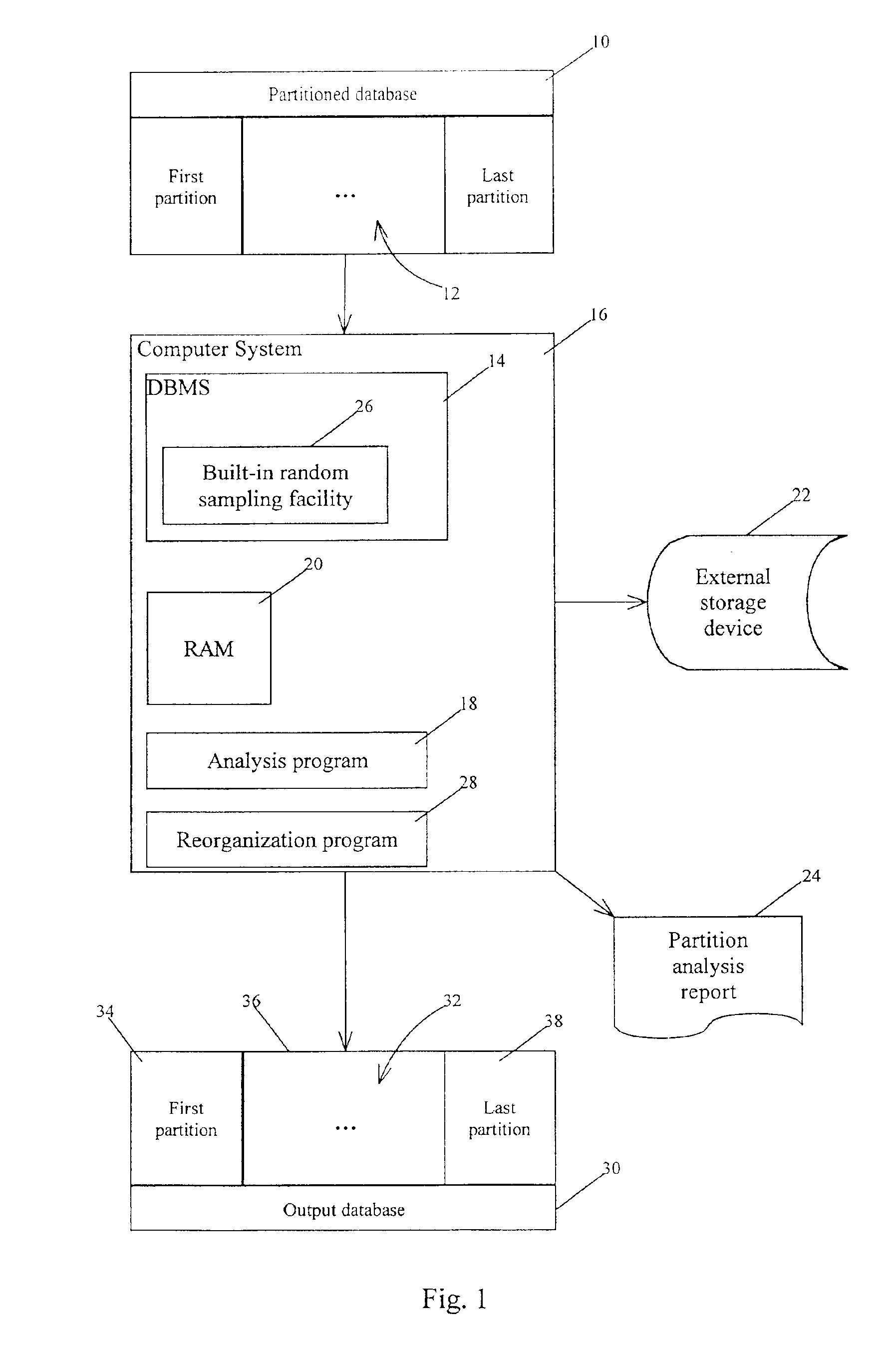
[0038]The capacity of DL / I databases is limited by the maximum size of a data set that can be addressed by a four-byte relative byte address (RBA). Many other databases in use presently suffer from similar size limitations. In current full function databases managed by database management systems such as IMS, multiple data sets are supported. This helps to increase the capacity of the database. One requirement, however, is that all segments of the same type must be in the same data set. As a result, when one data set is full, the database is deemed to be essentially full even if empty space exists in the remaining data sets. As a consequence, methods have been developed to extend the capacity of such databases.
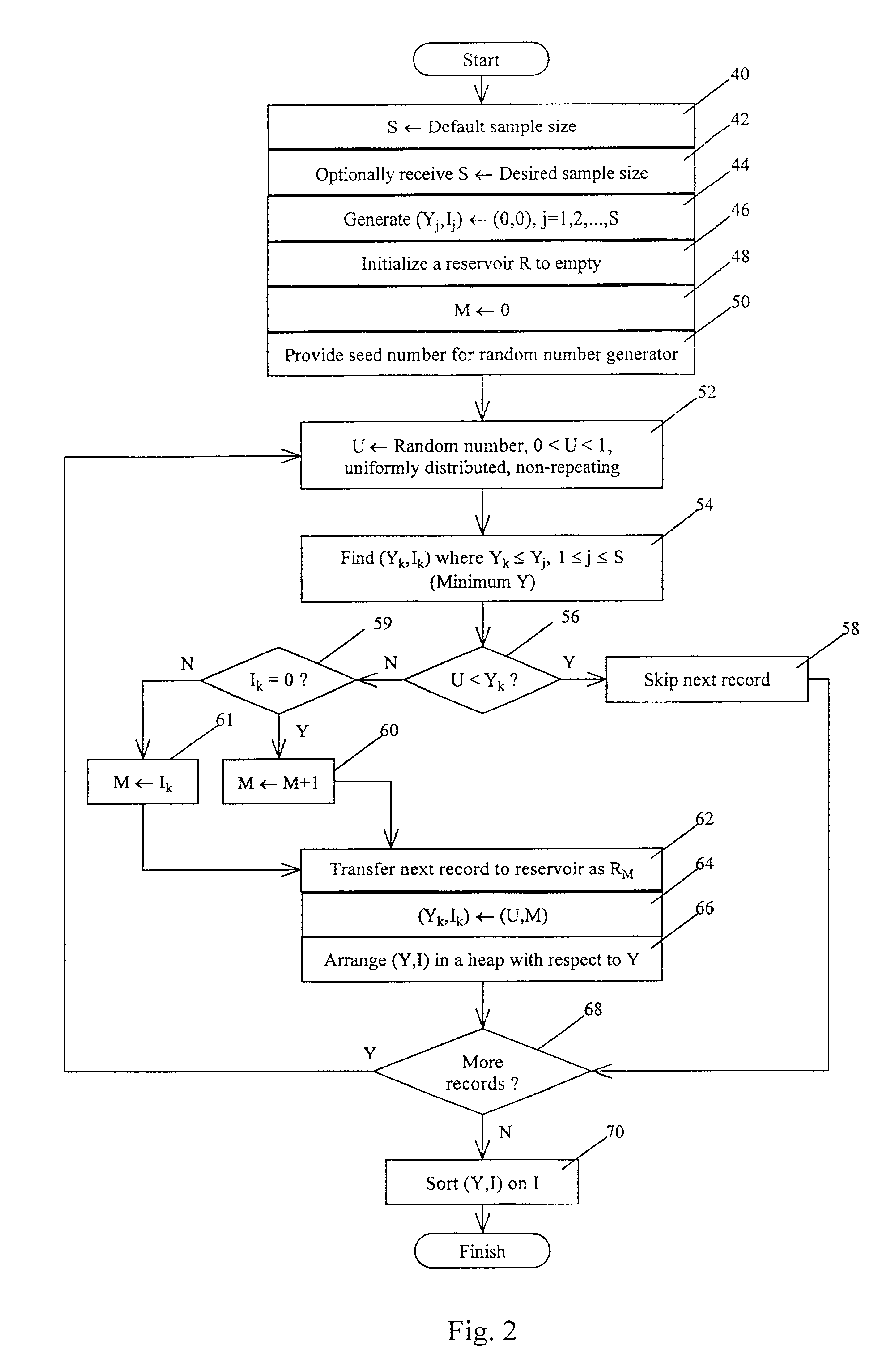
[0039]As shown in FIG. 1, partitioning removes the data set limitation by relieving the restriction that all occurrences of the same segment type must be in the same data set. Partitioning database 10 groups database records into sets of partitions 12 that are treated as a sin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com