Statistical trace-based methods for real-time traffic classification
a traffic classification and statistical trace technology, applied in the field of content delivery, can solve the problems of high processing overhead, insufficient traffic characteristics of resource utilization alone, and no longer valid known approaches to traffic classification, and achieve the effects of low overhead, simple and inexpensive on-line real-time classification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
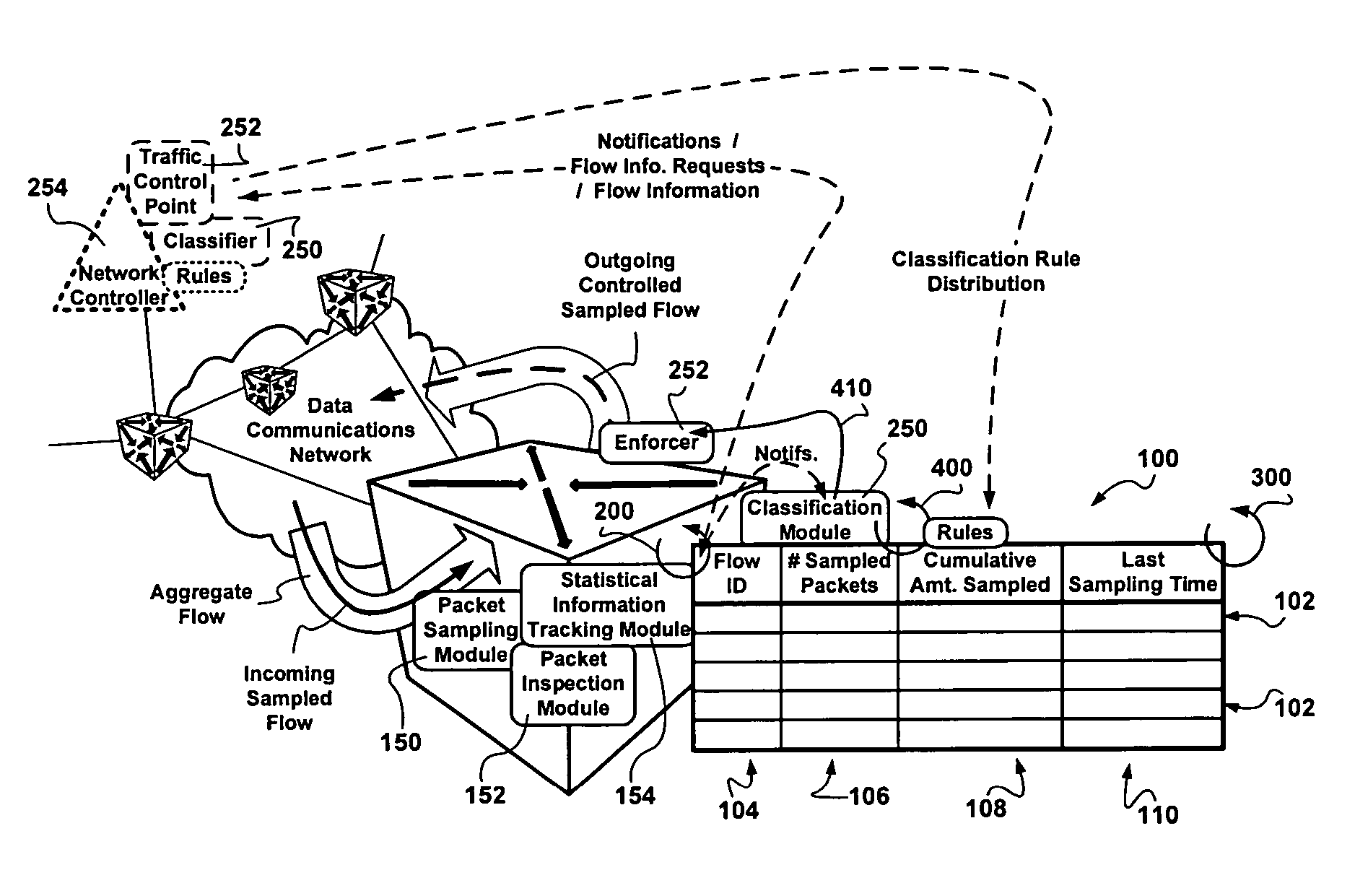
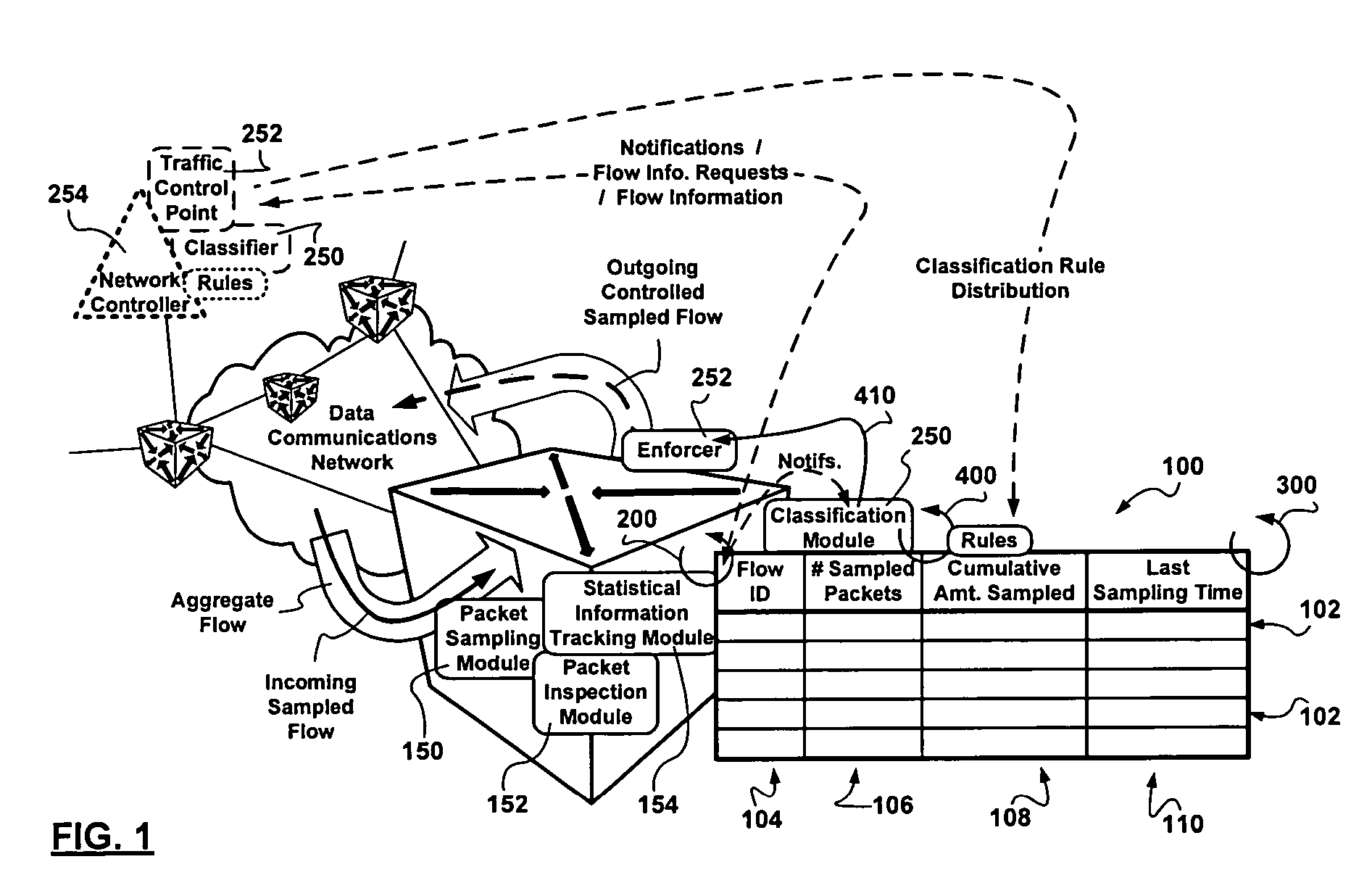
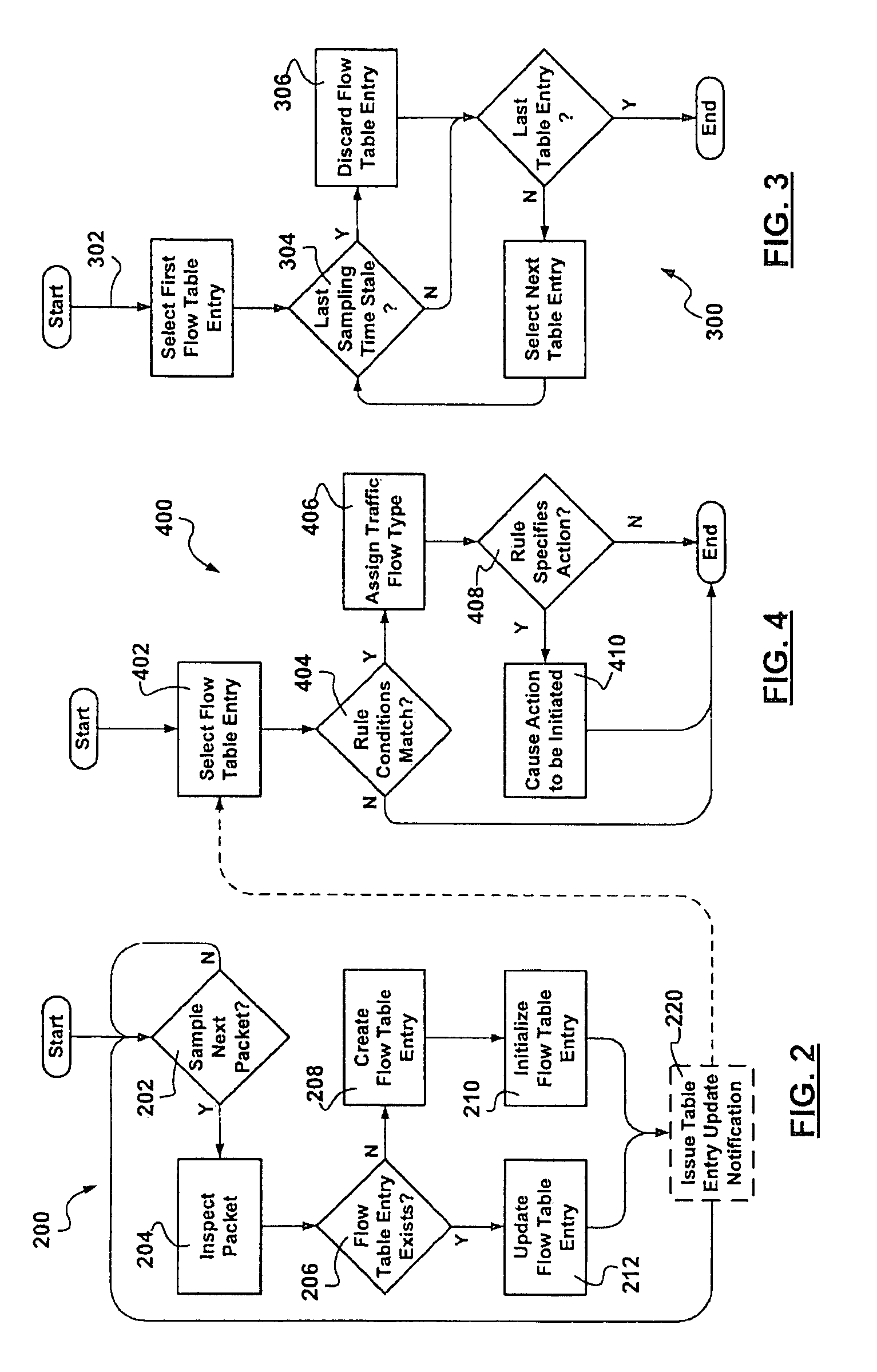
[0022]The realities of Internet service provisioning to customers are such that service level agreements are described in terms of expected aggregate traffic characteristics with the assumption that most of the user traffic is highly bursty and relatively low bandwidth such as the occasional email, intermittent web page download followed by a reading period, and the infrequent electronic bank transaction. Although the equipment is prevalent, video conferencing is relatively rare. Service level agreements include enough long-term transport bandwidth for comparatively higher bandwidth netradio audio streaming. Customers are assumed to be nice and occasional transgressions rarely translate into higher bills at the end of the month. It is assumed that nice customers do not listen to netradio, nor download MP3's from traceable and reputable sources, 24 / 7. At the same time, in view of the intense competition in communications, the available transport bandwidth in the core of the managed c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com