Use of C1 inhibitor for the prevention of ischemia-reperfusion injury
a technology of ischemia and perfusion injury, which is applied in the direction of drug composition, peptide/protein ingredients, extracellular fluid disorder, etc., can solve the problems of infarction if not reversed, ischemia of the cerebral tissues served, and further indirect damag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
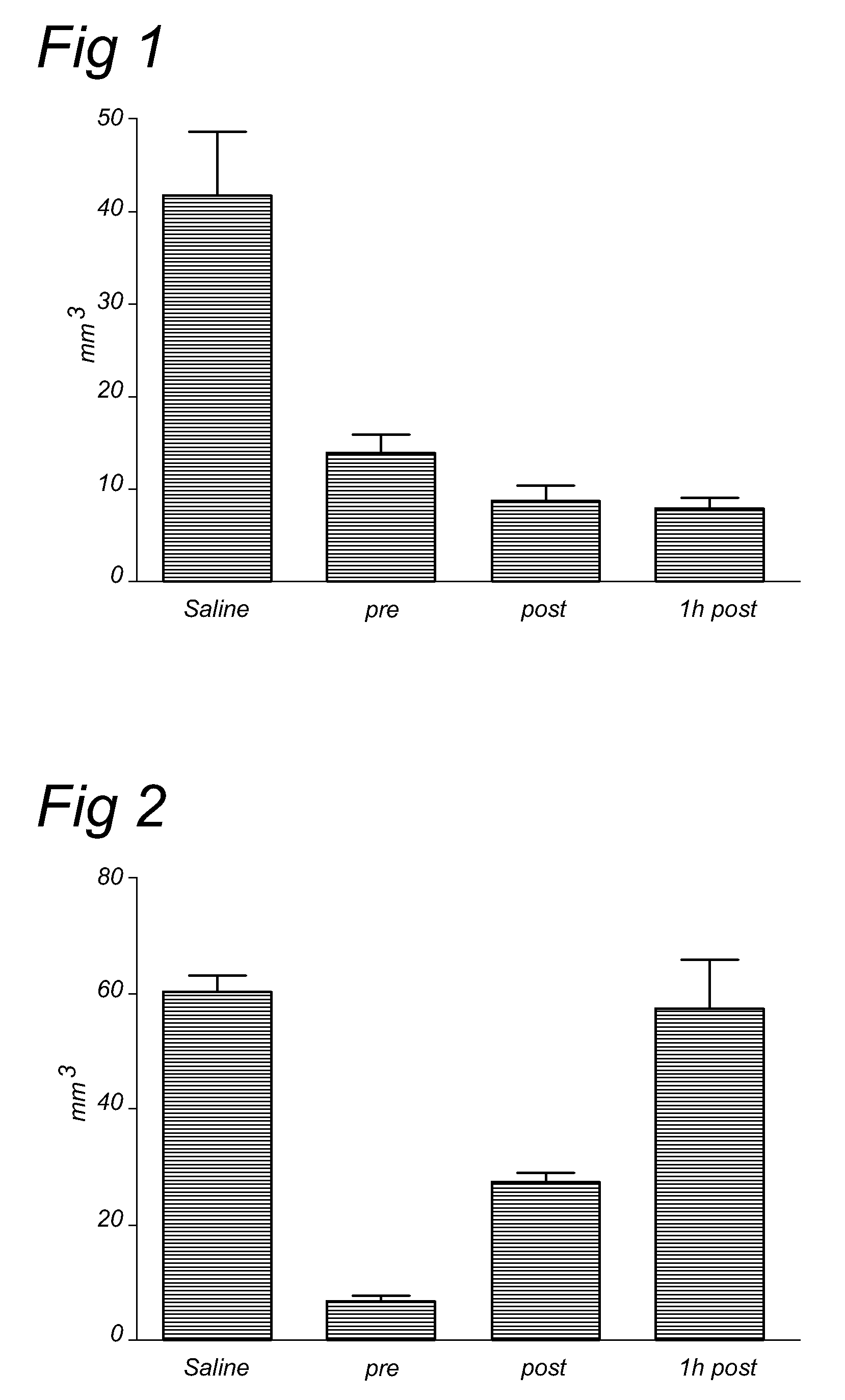
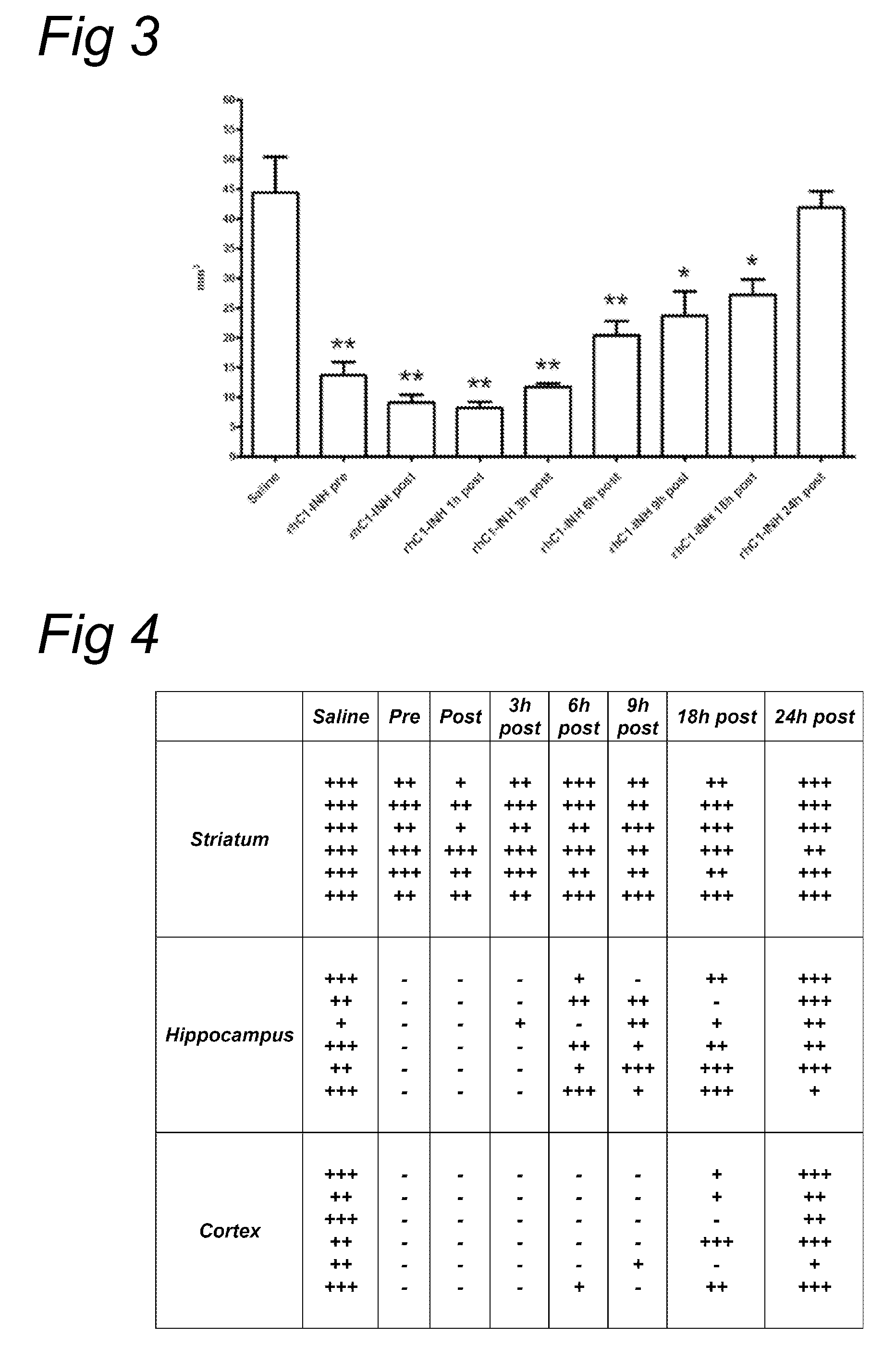
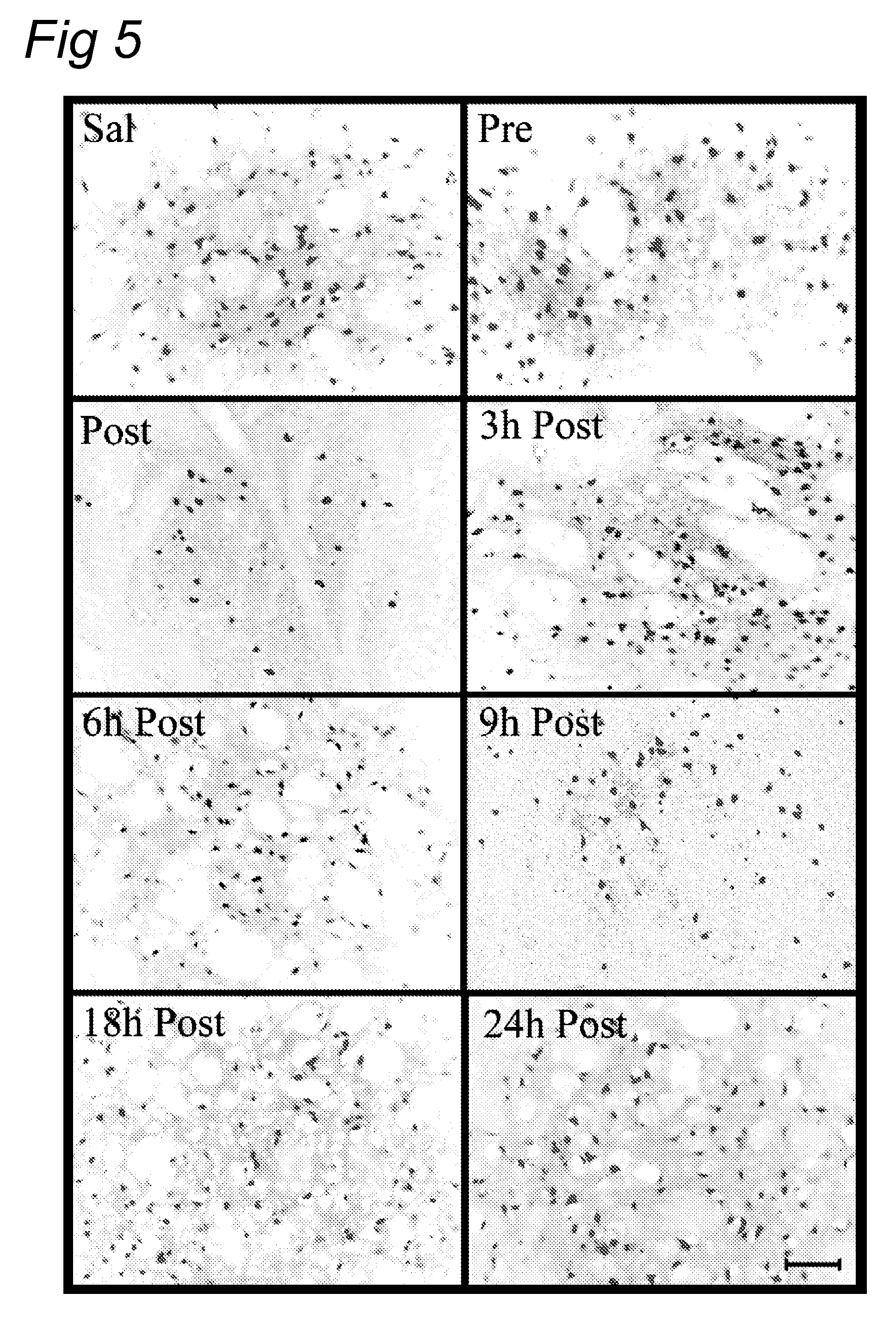
[0076]Previous experiments showed that a single dose of rhC1INH (15 U / mouse) administered at the beginning of the ischemic period, significantly reduces ischemic volume, as assessed 48 hours after ischemia in our mouse model of cerebral focal ischemia in a manner very similar to plasma derived C1INH. In this Example we have explored the time window of efficacy for rhC1INH neuro-protective activity on the ischemic volume and functional deficits. We have also studied the effect of rhC1INH on seven-days outcome by assessing the neurodegeneration and glial response.
1. Methods
1.1 Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia
[0077]Ischemia was achieved by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) as previously described (De Simoni et al., 2003 and 2004, supra). Anesthesia was induced by 5% isoflurane in N2O / O2 (70 / 30%) mixture and maintained by 1.5-2% isoflurane in the same mixture. To confirm the adequacy of the vascular occlusion in each animal, blood flow was measured by laser doppler flowmetry (Tra...
example 2
Study on the Neuroprotective Action of rhC1-INH in Mouse Models of Focal Cerebral Ischemia
[0102]We have previously demonstrated that 15 U of rhC1-INH have a marked neuroprotective action in a model of murine cerebral ischemia / reperfusion also when administrated 1 hour after the onset of ischemia / reperfusion, at variance with pdC1-INH that, at this time of post-treatment, is no longer effective. This neuroprotection is long-lasting, in fact seven days after ischemia and treatment, ischemic brains of mice treated with rhC1-INH still show a decreased infarct size. In the following experiments we have determined the time window of efficacy (beyond 1 hour post) and the dose-response of rhC1-INH neuroprotective activity on the ischemic volume. In addition we have performed a direct comparison among pdC1-INH, rabbit and cow rhC1-INH (at the most effective dose and time-points for rabbit rhC1-INH) using the same protocol.
Methods
Animals
[0103]Procedures involving animals and their care was co...
example 3
Comparison of the Ability of RHC1INH and Plasma Derived C1INH to Inhibit Activation of the Classical and MBL Pathways
Materials and Methods
[0118]The effect of rhC1NH and pdC1INH (Cetor, Sanquin, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) on the function of the classical and lectin pathway was examined in the Wieslab TM complement system Screen (Euro-Diagnostica, Malmo, Sweeden) using two different sources of serum. One serum source is included in the kit, where it is used as a positive control (hereafter referred to as serum sample 1). The other serum sample was obtained from a commercially available pool of human serum (pool of 25 different donors; Kordia, Leiden, The Netherlands), hereafter referred to as serum sample 2. Both serum samples were incubated in independent triplo's with 0, 15, 30 and 75 μmol rhC1INH or pdC1INH for 30 min at room temperature. Therefore, stock solutions of pdC1INH and rhC1INH were diluted in water to appropriate concentrations. Volumes corresponding with 15, 30 and 75 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| half life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| half life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| plasma half life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com