Apparatus for the continuous manufacture of a spunbond web
a technology of yarn and yarn, which is applied in the direction of filament/thread forming, filament manufacturing, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, complex needle-punching devices, and increased disadvantages, and achieves low cost, functional reliability, and simple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
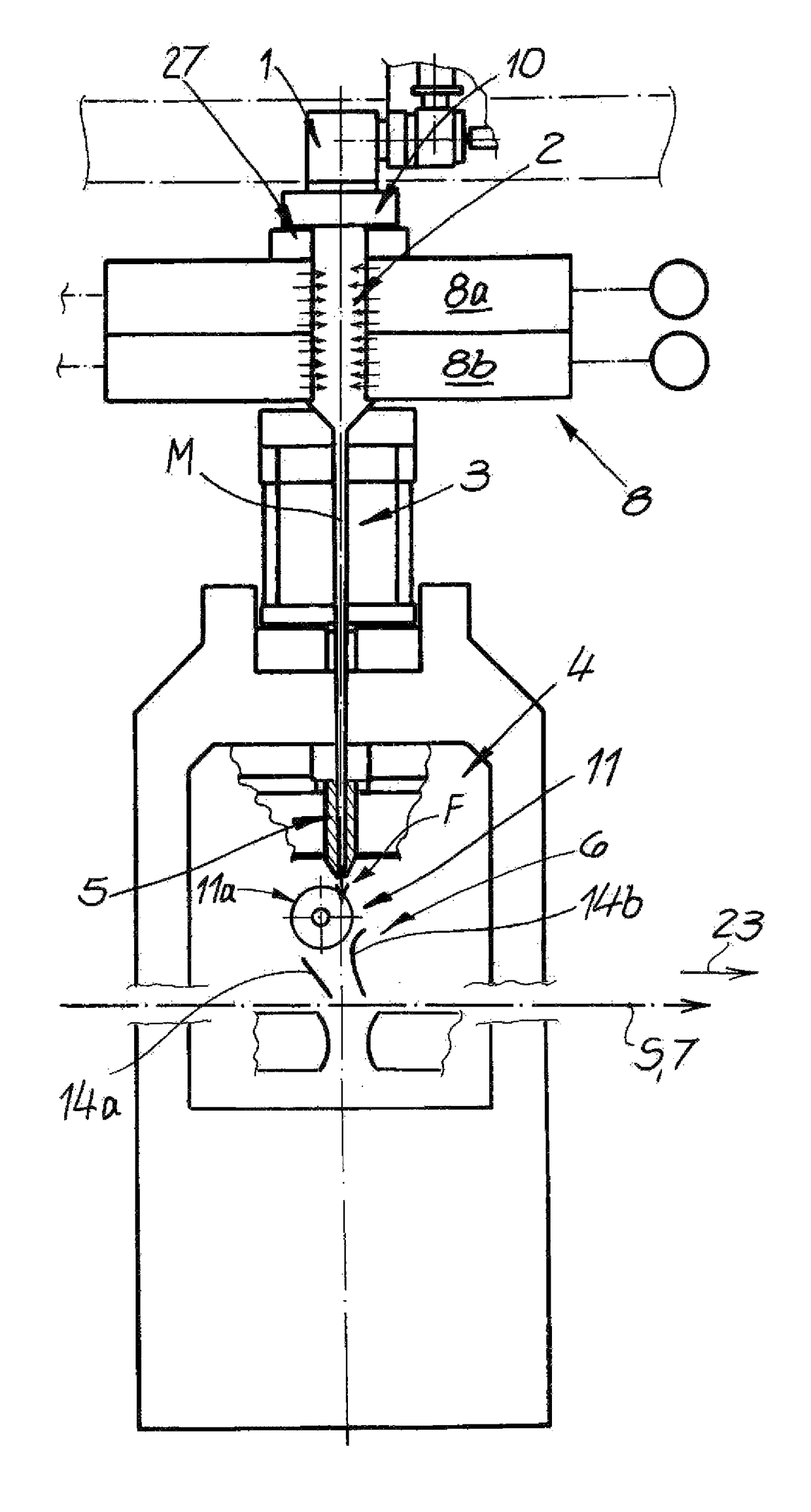
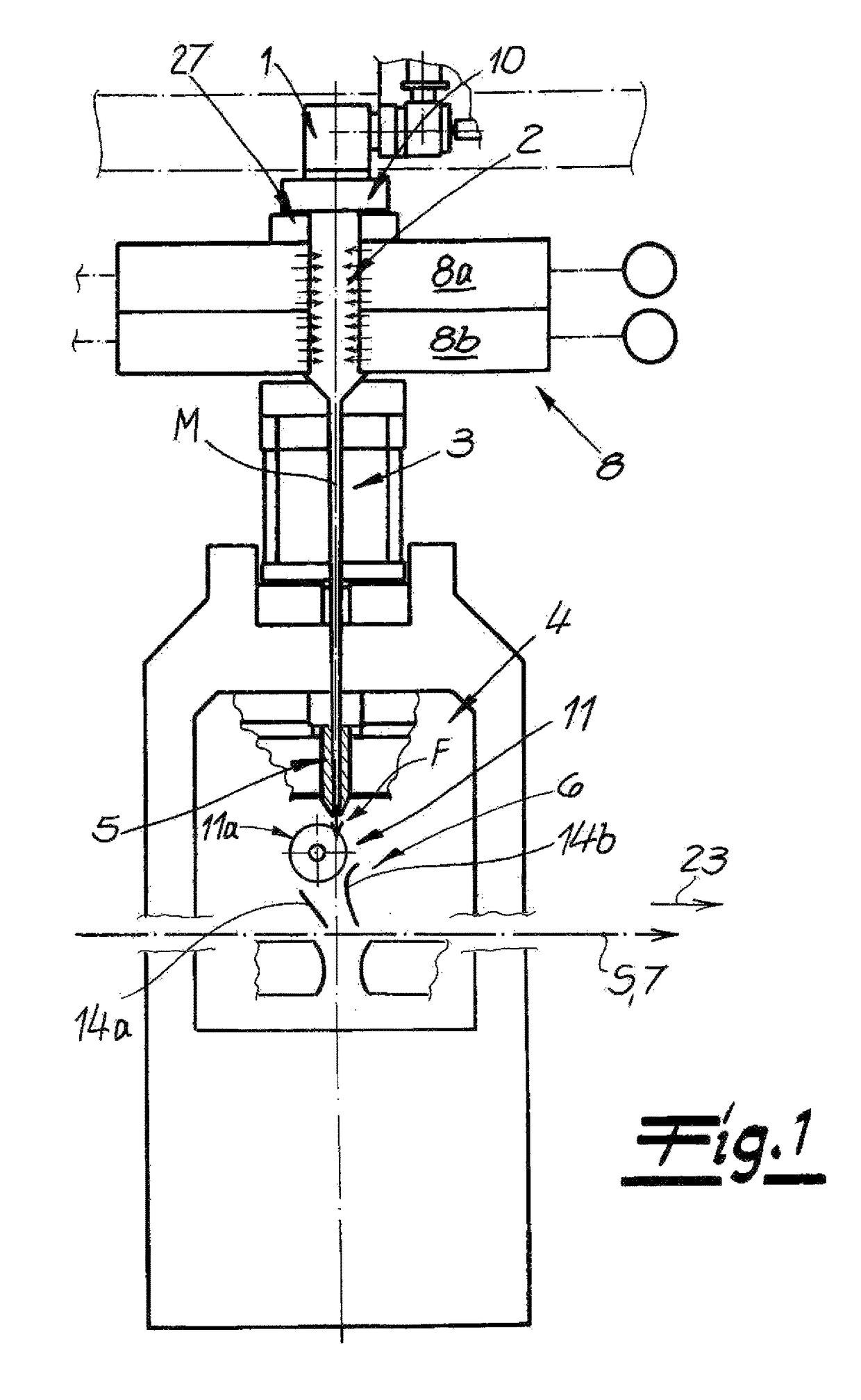
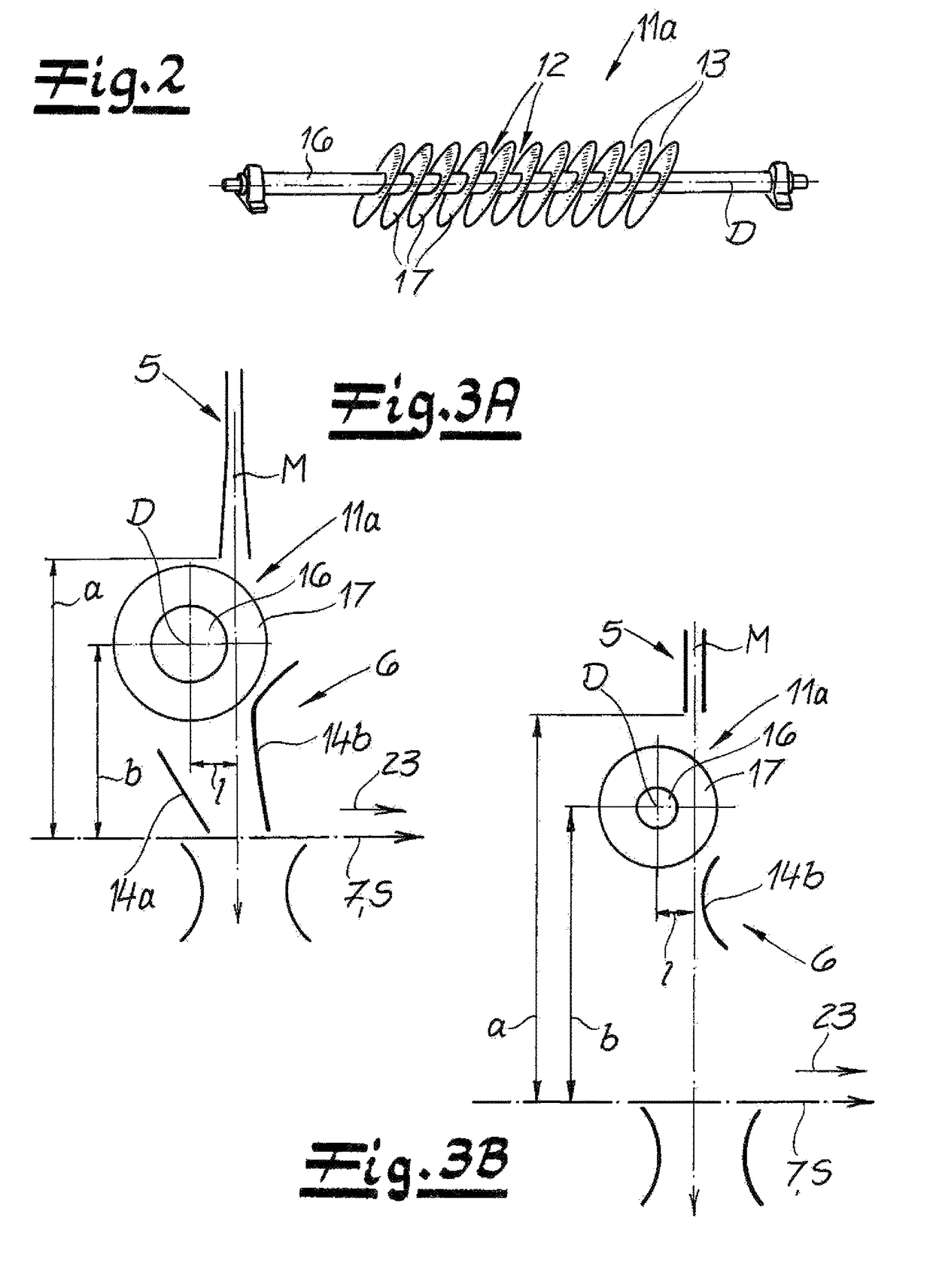
[0045]FIG. 1 shows an apparatus for the continuous manufacture of a spunbond web S from aerodynamically stretched filaments of thermoplastic plastic. The apparatus has a spinneret 1 and a cooling chamber 2 underneath the spinneret and into which process air can be introduced in order to cool the filaments. Adjoining the cooling chamber 2 is an intermediate passage 3 followed in the direction of travel of the filaments, by a stretcher 4 having a stretching passage 5. Adjoining the stretching passage 5 is a deposition unit 6. A deposition device as a continuously circulating conveyor belt 7 for the deposition of the filaments for the spunbond web S is provided underneath the deposition unit 6. Here, the assembly comprising the cooling chamber 2, the intermediate passage 3, and the stretcher 4—except for the air supply in the cooling chamber 2—is a closed system. A further air supply is therefore not provided in this assembly.
[0046]FIG. 1 also shows that an air supply chamber 8 next to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com