Wettability and fluid displacement in a well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
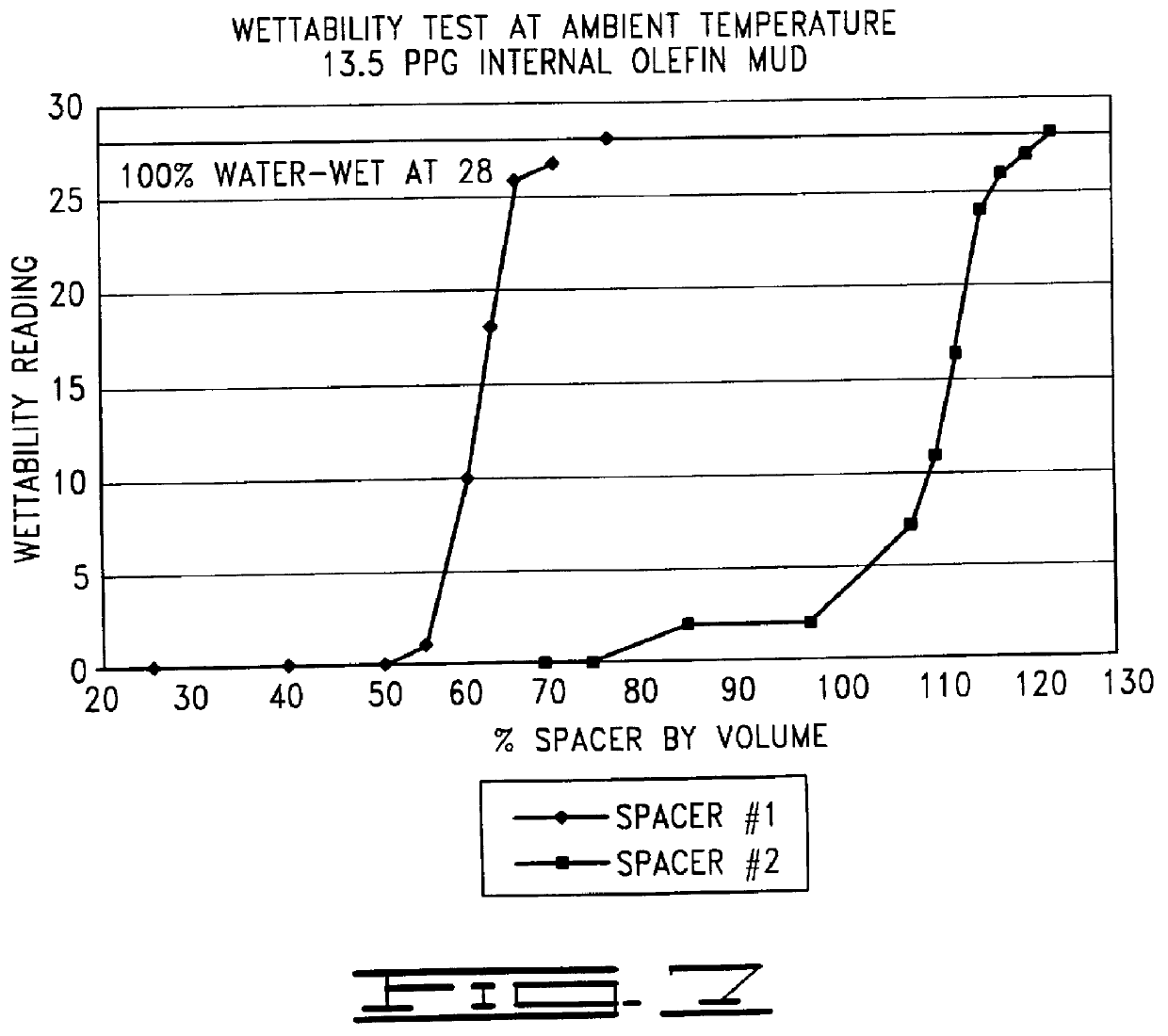
Examples
Embodiment Construction
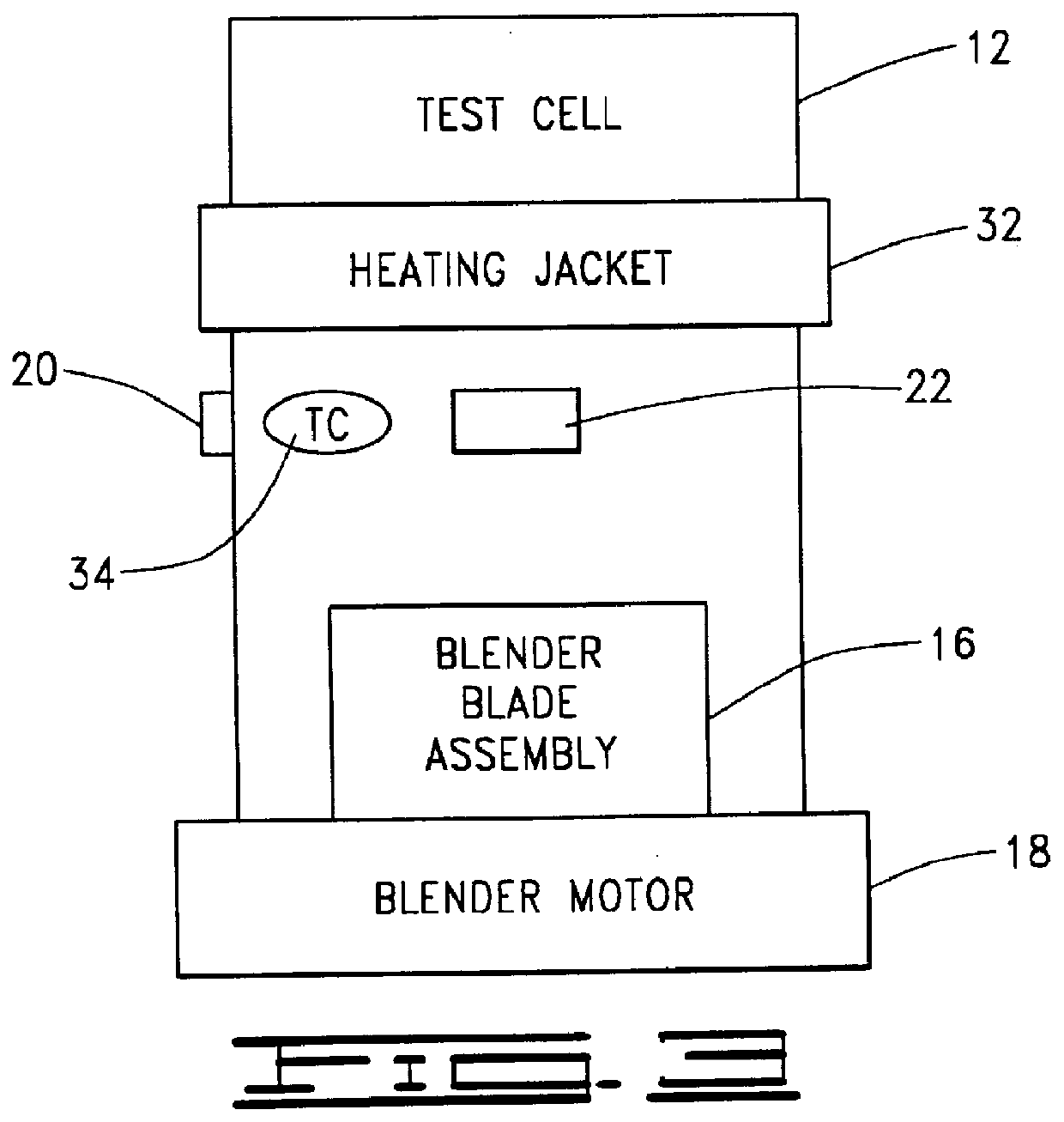
The present invention will be described with reference to cementing an oil or gas well after the well has been drilled in a conventional manner. The drilling process uses an oleaginous external / aqueous internal fluid. One example of such a fluid is an oil external / water internal drilling mud emulsion designed and made as known in the art. An example of a specific drilling fluid includes:
Weight of Composition Composition in Grams oleaginous fluid 148 Ca(OH).sub.2 (lime) 3.5 organophilile clay 4 emulsifier 8 wetting agent 4 25% CaCl.sub.2 brine 106 barite 247
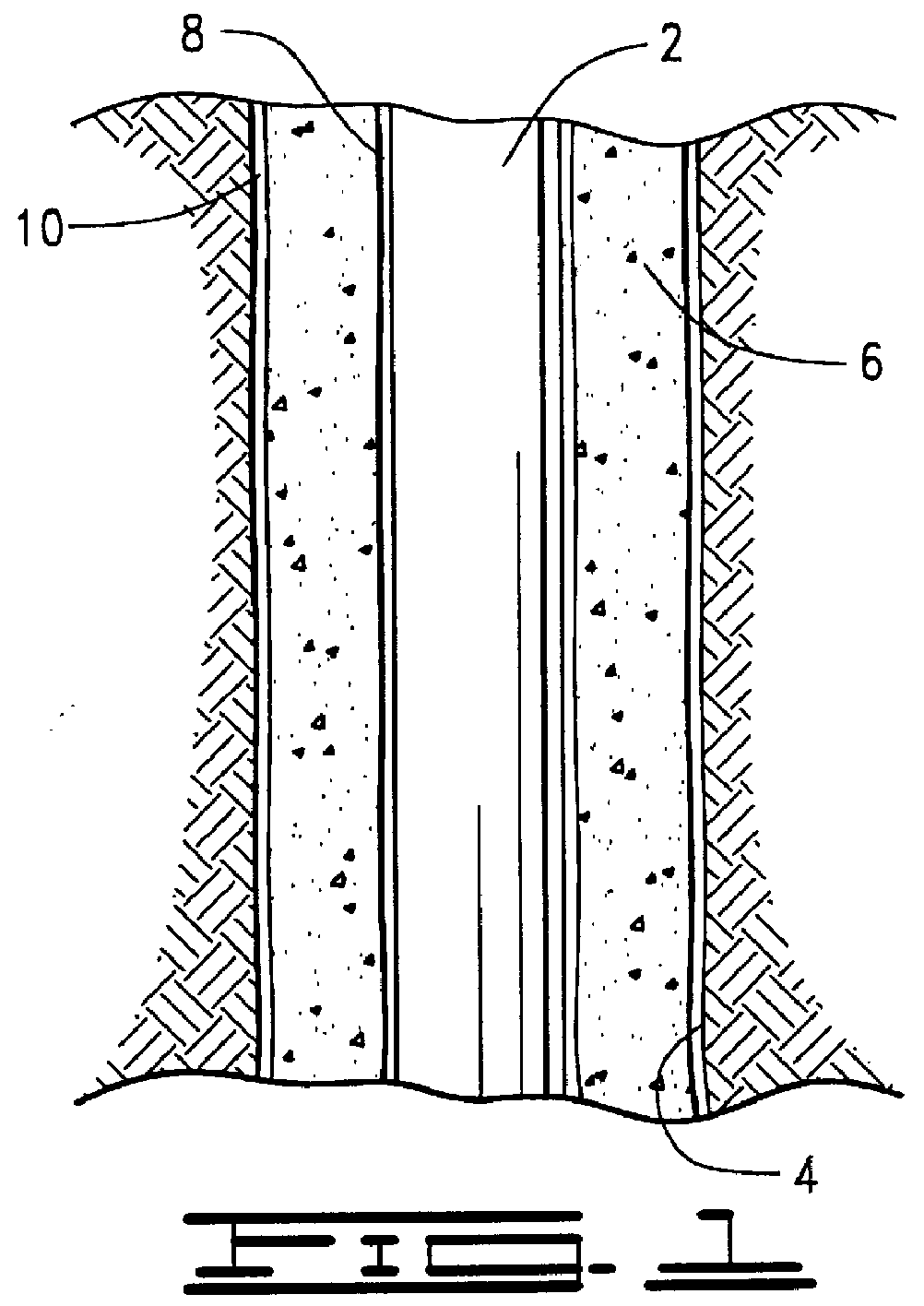
Referring to FIG. 1, a tubular string 2 (e.g., a drill string, production tubing string, casing or liner) is shown after it has been cemented into a suitably drilled wellbore 4. Cement 6 is placed in known manner (e.g., by pumping) in the annulus defined between the outer surface of the tubular string 2 and the surface of the cut wellbore 4.
Also represented in FIG. 1 is a thin layer 8 between the tubular string 2 and the inner sur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com