Optical disk recording method employing a plurality of recording areas and apparatus therefor
a technology of optical disk and recording area, which is applied in the direction of digital signal error detection/correction, instruments, recording signal processing, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of power consumption, difficult to reduce the size of the apparatus, and excessive access time, so as to minimize the rotational speed change and reduce the rate of motor spindle rotation. , the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
(Embodiment 1)
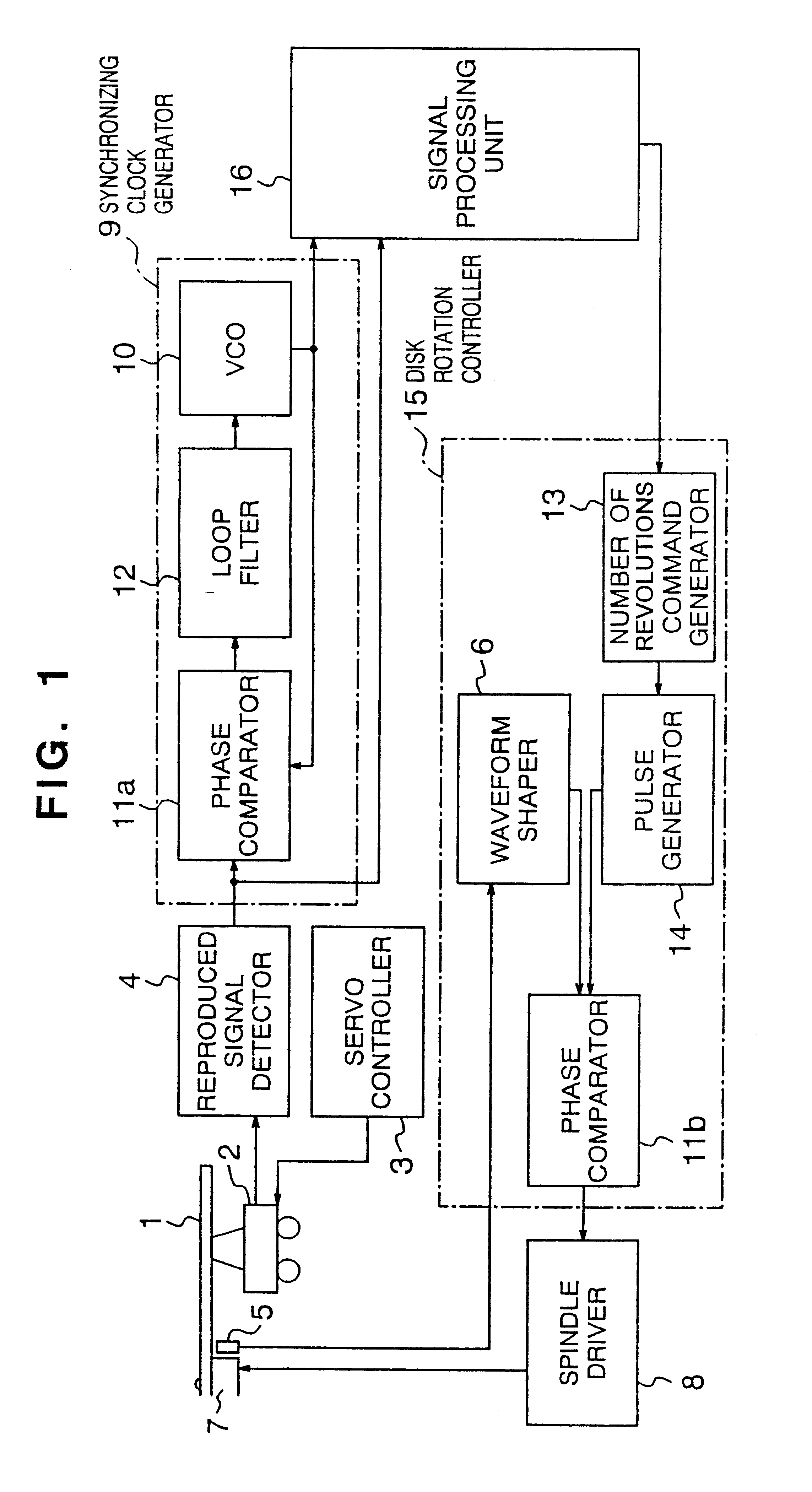
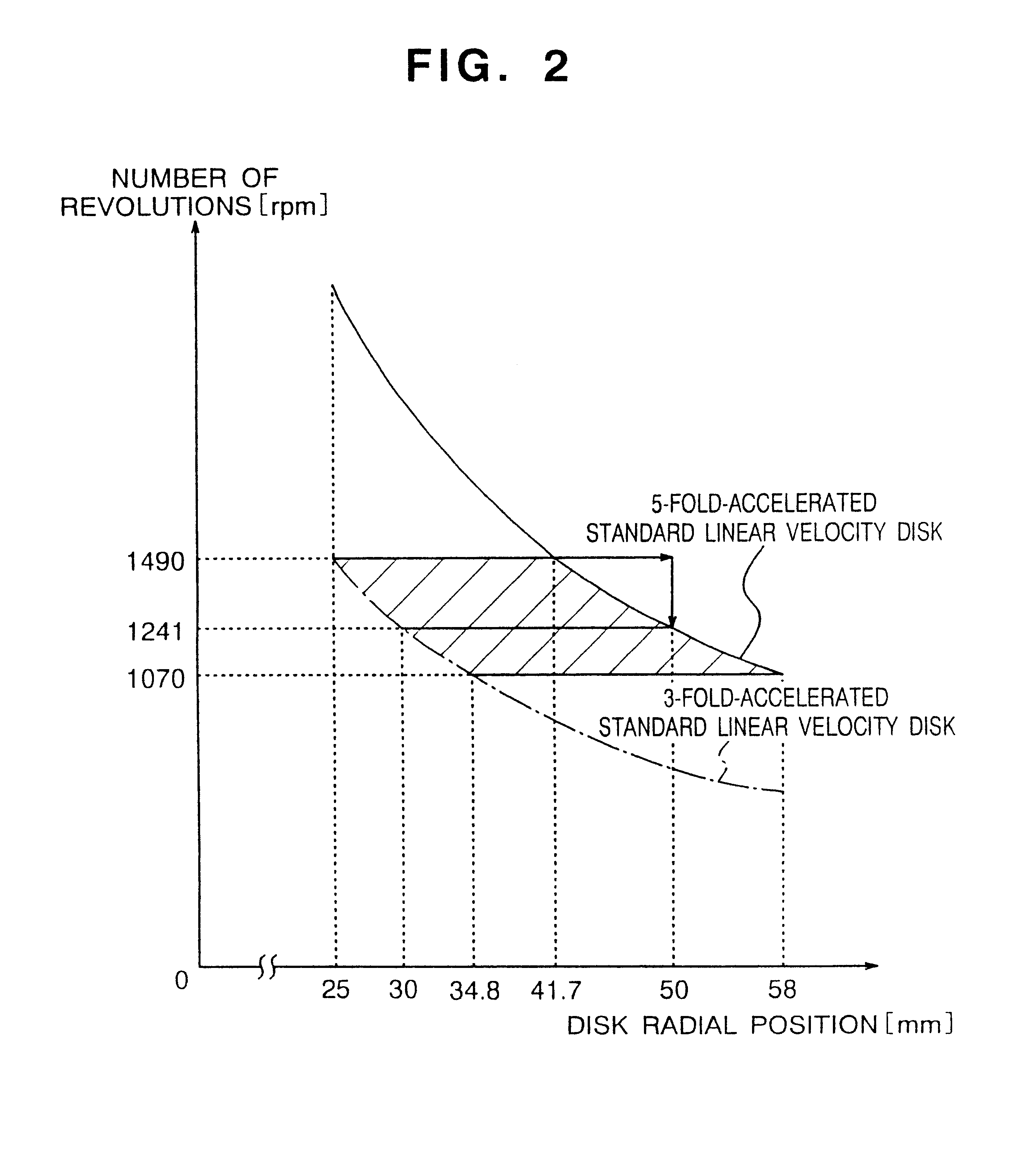
Referring to the accompanying drawings, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 is a block diagram of the optical disk apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention. Reference numeral 1 denotes an optical disk on which data has been recorded at constant linear velocity (CLV), 2 denotes a servo controller for causing the optical pickup 2 to follow the runout and eccentricity of the optical disk 1, 4 denotes a reproduced signal detector for digitizing the signal reproduced from the pickup 2, 7 denotes a spindle motor which rotates with an optical disk mounted thereon, 5 denotes an encoder for generating an analog rotation signal in accordance with the motor spindle rotation, 6 denotes a waveform shaper for digitizing the analog rotation signal, 13 denotes a number of revolutions command generator (corresponding to a processor such as a CPU) for calculating a number of revolutions according to the reproducing position on ...
embodiment 2
(Embodiment 2)
A second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the optical disk apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 3, reference numeral 1 denotes an optical disk, 2 denotes an optical pickup, 3 denotes a servo controller, 4 denotes a reproduced signal detector, 7 denotes a spindle motor, 5 denotes an encoder, 6 denotes a waveform shaper, 13 denotes a number of revolutions command generator, 14 denotes a pulse generator, 11a and 11b denotes phase comparators, 8 denotes a spindle driver, 10 denotes VCO, 12 denotes a loop filter, 16 denotes a signal processor, 9 denotes a synchronizing clock generator, and 15 denotes a disk rotation controller. Those components, being the same as in the first embodiment, are designated by the same reference numerals and their descriptions are omitted. Reference numeral 17 denotes an access controller for controlling an acces...
embodiment 3
(Embodiment 3)
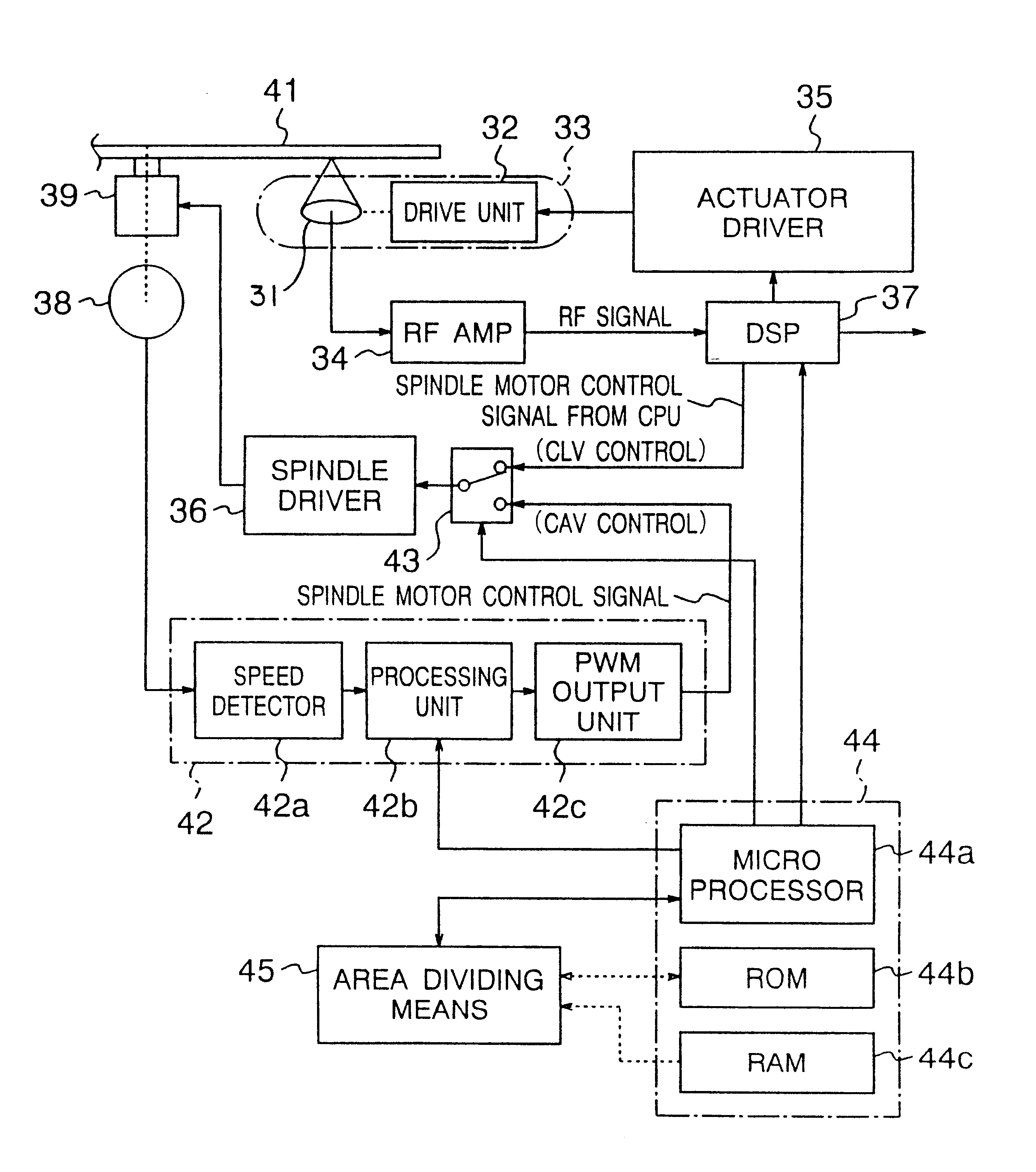
A third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. FIG. 5 is a block diagram of the optical disk apparatus in the third embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 5, reference numeral 1 denotes an optical disk, 2 denotes an optical pickup, 3 denotes a servo controller, 4 denotes a reproduced signal detector, 7 denotes a spindle motor, 5 denotes an encoder, 6 denotes a waveform shaper, 13 denotes a number of revolutions command generator, 14 denotes a pulse generator, 11a and 11b denote phase comparators, 8 denotes a spindle driver, 10 denotes VCO, 12 denotes a loop filter, 16 denotes a signal processor, 9 denotes a synchronizing clock generator, and 15 denotes a disk rotation controller. Those components, being the same as in the first embodiment, are designated by the same reference numerals and their descriptions are omitted. Reference numeral 18 denotes a linear velocity detector for detecting the linear velo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| linear velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| linear velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| rotating velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com