Distributed differential coupling combined power system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
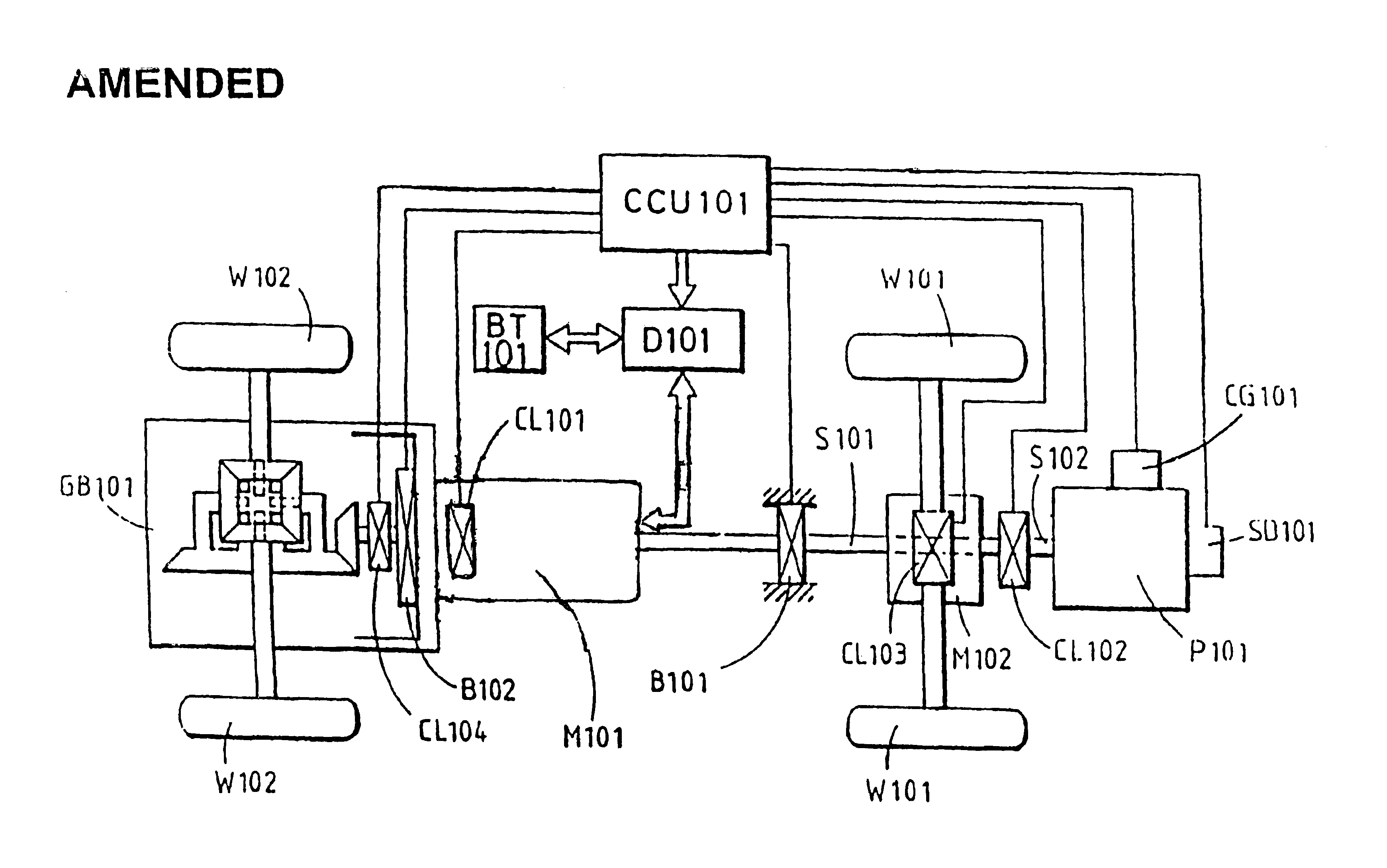
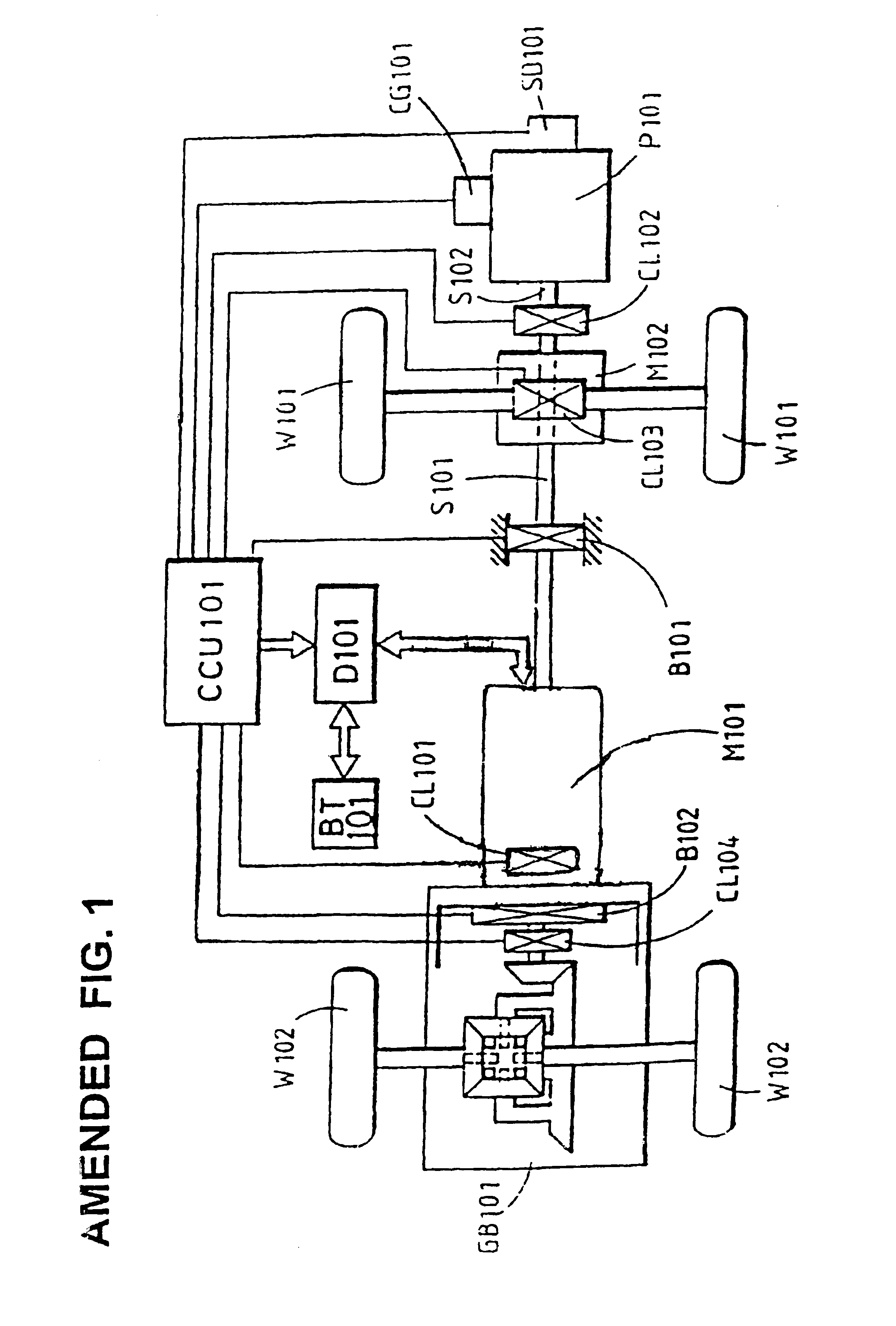
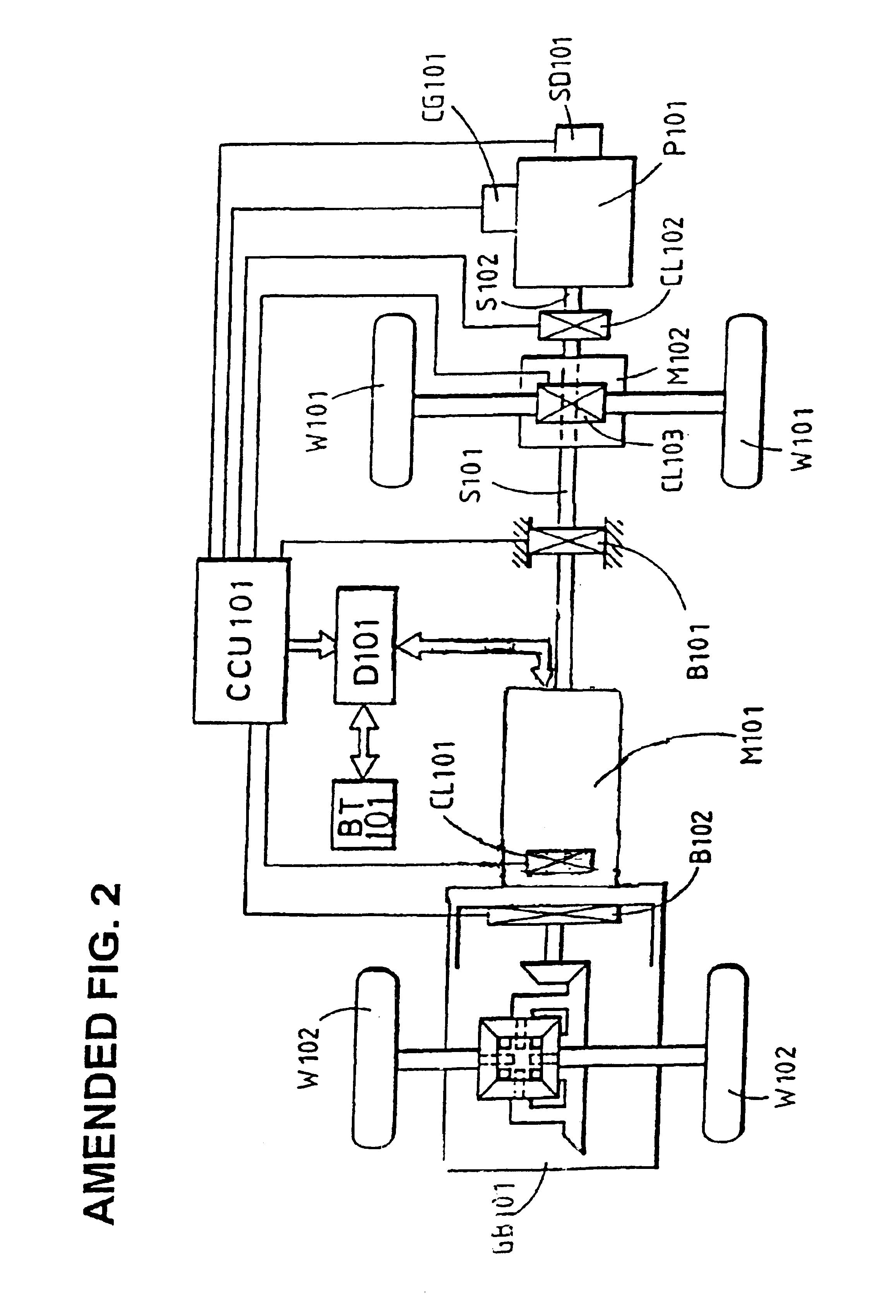
[0015]FIG. 1 shows a preferred embodiment of a distributed differential coupling combined power system, including the following principal elements:
[0016]A drive side rotational power source, having an output which is first supplied to control the front section load and then transmitted to the input end of a two-end shaft type electromagnetic coupling device to drive a rear section load.
[0017]An electromagnetic coupling device connected by a direct transmission to another load, through a transmission component to another load, or through a differential gear system to a differentially acting load such as the side rear wheels of a vehicle.
[0018]More specifically, the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 1 includes the following elements:
[0019]A drive side rotational power unit P101 in the form of an internal combustion engine or other power source, wherein the rotational output shaft S102 coupled to a middle transmission device and a control interface M102 through a clutch CL102. Engine P101...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com