Ceiling fan
A ceiling fan and fan blade technology, applied in the field of electric ceiling fans and their efficiency, can solve problems such as air flow distribution and fan reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
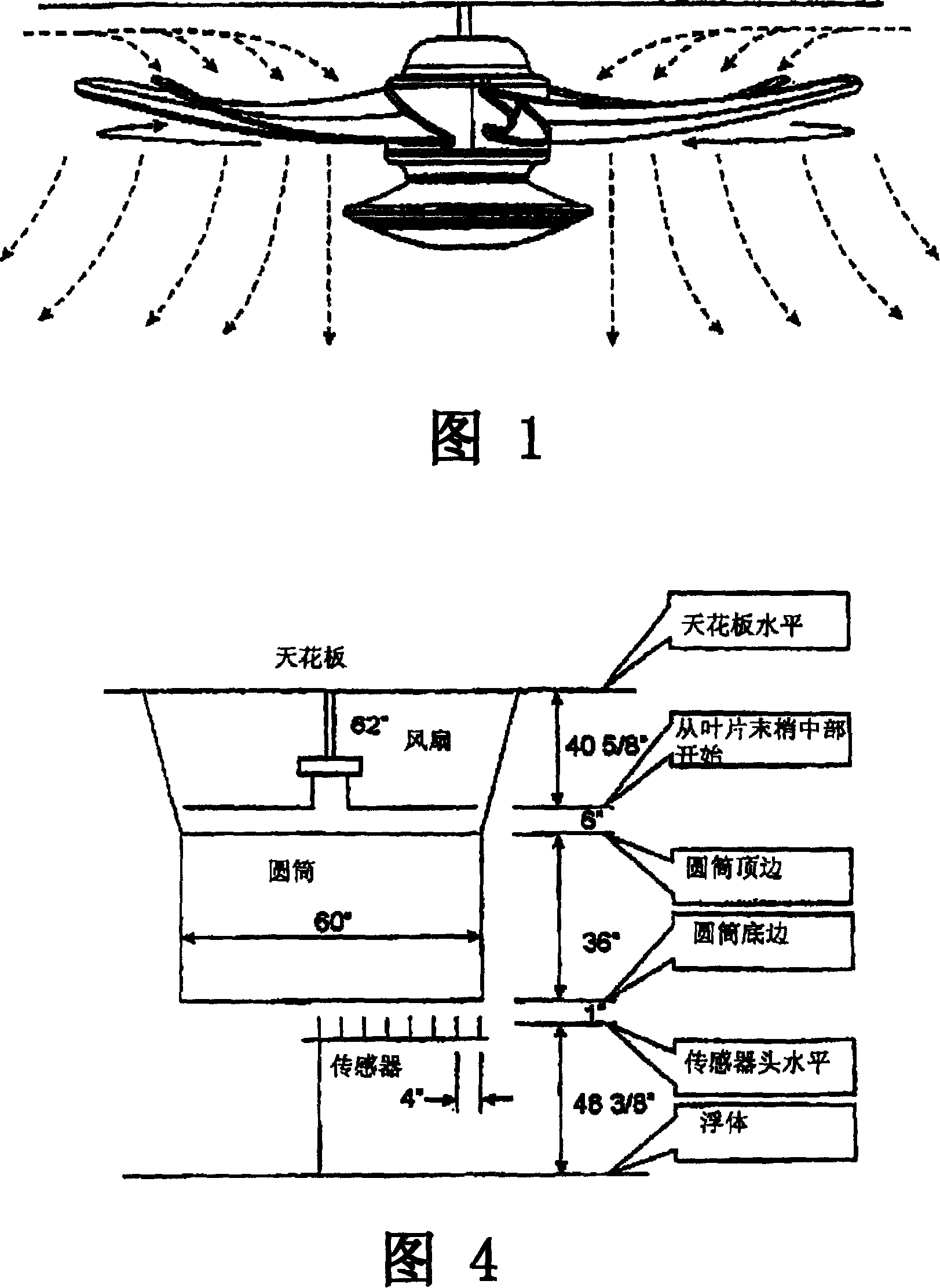
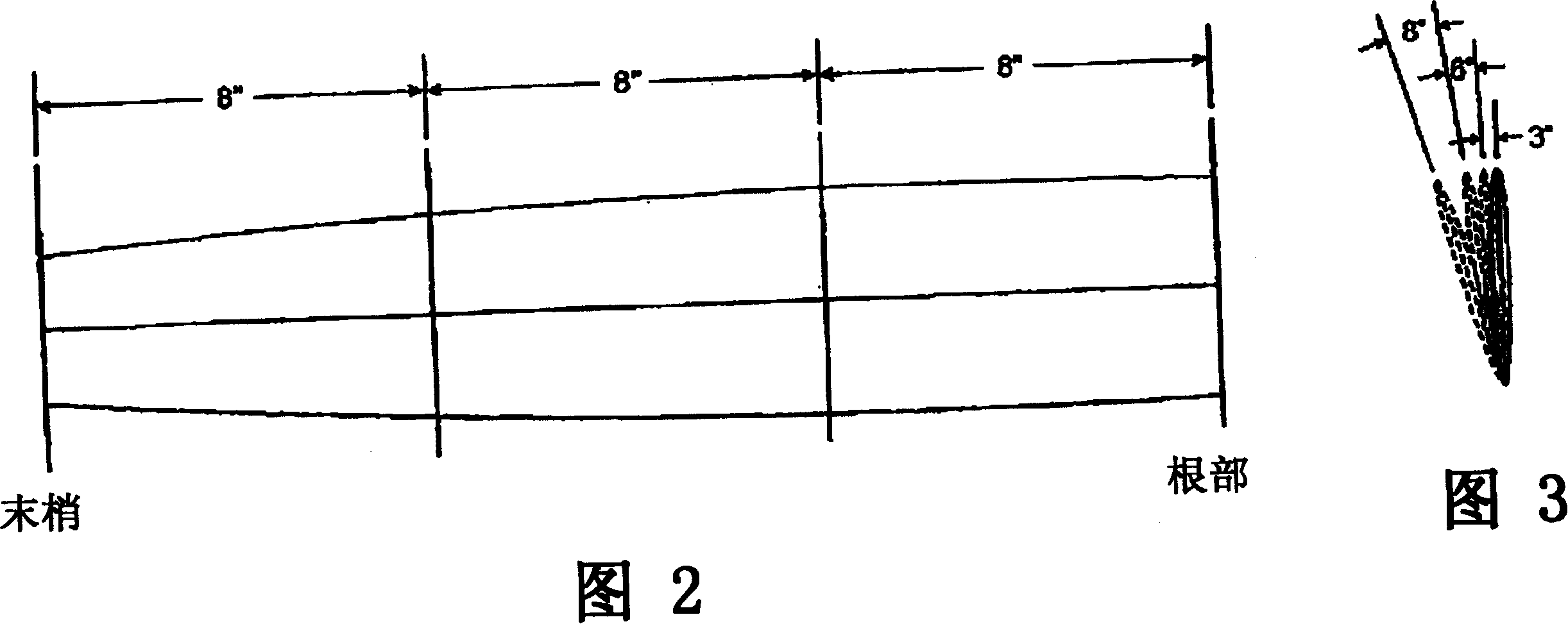
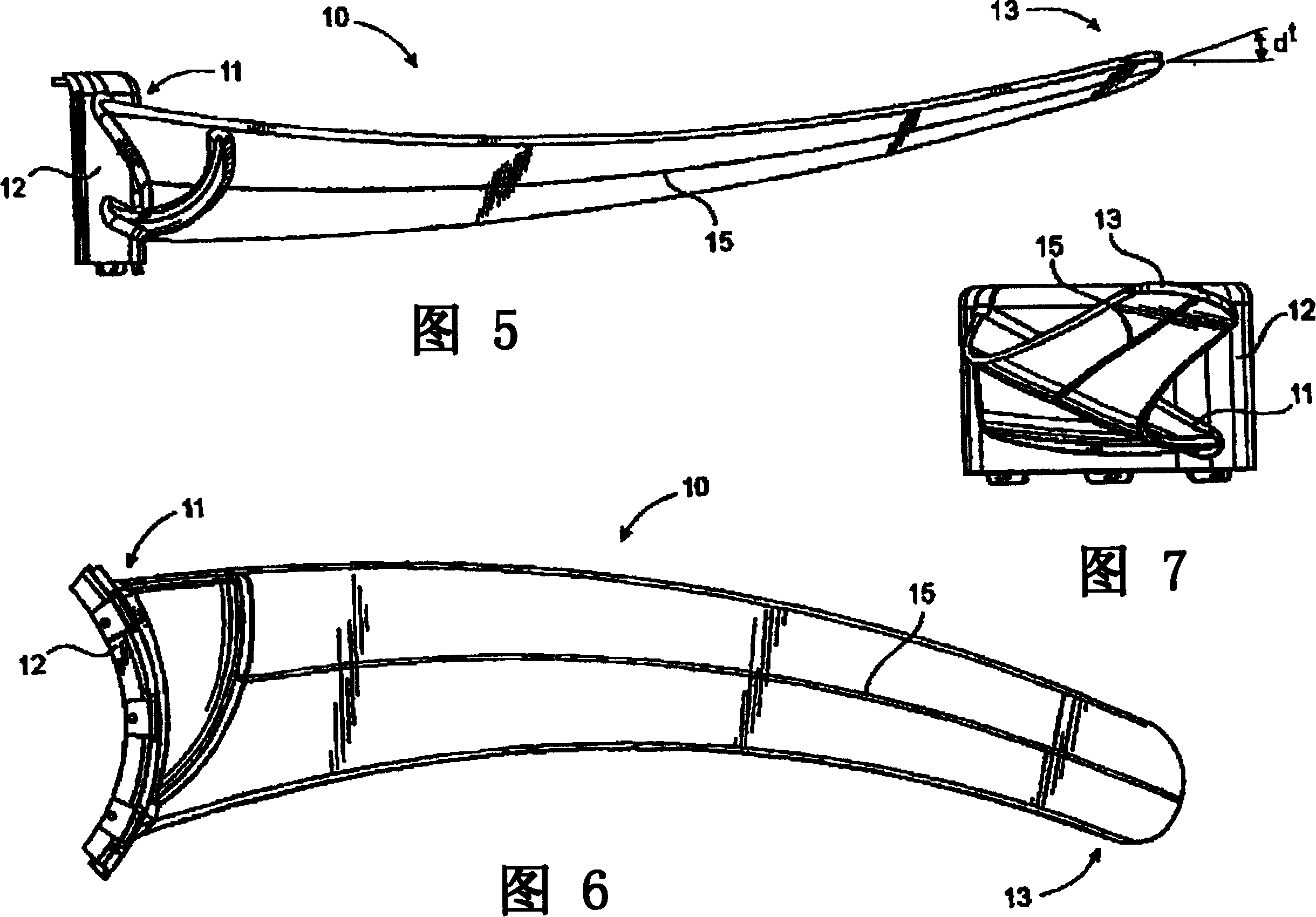
[0019] The fan blade technology disclosed in US Patent Application No. 6,039,541 follows the assumption that all airflow entering the fan blades is from a direction perpendicular to the plane of rotation of the blades. Furthermore, as is used in aircraft propeller theory, it is also assumed that the airflow flows at a constant velocity from the root of the blade to the tip of the blade. Utilizing this assumption, the twist angle from the root end to the tip is assumed to be a certain value when designing the blade.
[0020] The purpose of twisting the blades is an attempt to optimize the relative angle of attack of the airflow direction with respect to the blade surface. This is done to ensure that the blade operates at an optimal angle of attack from its root to its tip. This change in angle is to accommodate the fact that the tip of the blade is moving faster than the diameter of the root of the blade, and this increase in speed changes the relative airflow direction over t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com