Improvement of T cell mediated immunity
A cell and cell group technology, which can be used in medical preparations containing active ingredients, endocrine system diseases, peptide/protein components, etc., and can solve problems such as memory cell deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
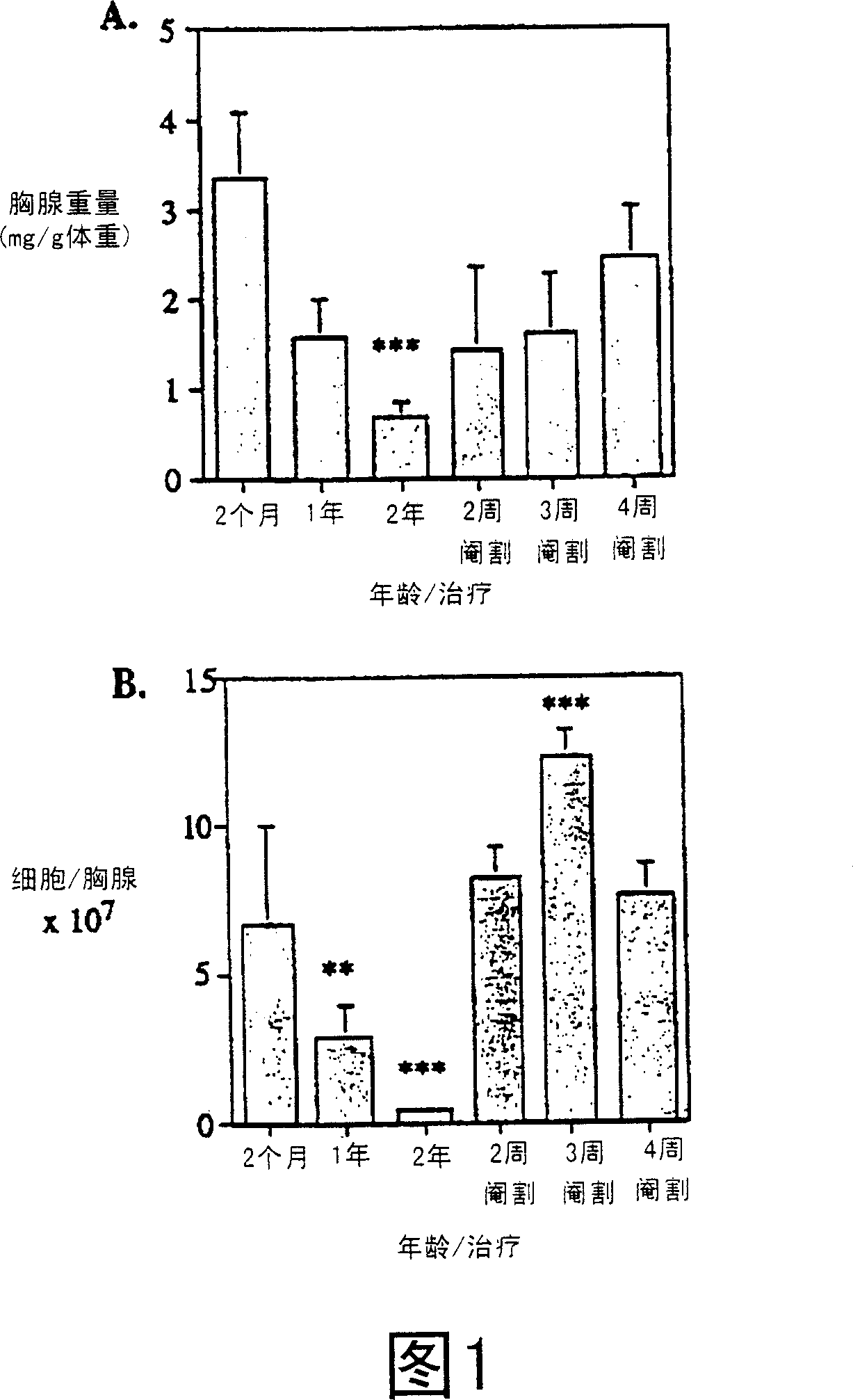
[0073] Example 1: Reversion of age-induced thymic atrophy
[0074] Materials and Methods
[0075] animal
[0076] CBA / CAH and C57B16 / J male mice were obtained from CentralAnimal Services, Monash University, and housed under conventional conditions. Ages range from 4-6 weeks to 26 months and are indicated where relevant.
[0077] castration
[0078] By intraperitoneal injection of 0.3 mL of 0.3 mg xylazine (Xylazine; BayerAustralia Ltd., Botany, New South Wales, Australia) and 1.5 mg of ketamine hydrochloride (Cordamine; Parke-Davis, Caringbah, New South Wales, Australia) Anesthetize the animal with a solution in saline. Surgical castration is performed by incision of the scrotum to expose the testes, which are ligated with sutures and then removed along with the surrounding fatty tissue.
[0079] Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) introduction
[0080] Mice received two intraperitoneal injections (100 mg / kg body weight in 100 microliters of PBS) of BrdU (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Lo...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Example 2: Reversal of Chemotherapy or Radiation Induced Thymic Atrophy
[0126] Following radiation or cyclophosphamide treatment, the rate of thymus regeneration was significantly increased in castrated mice (one week before or on the day of treatment).
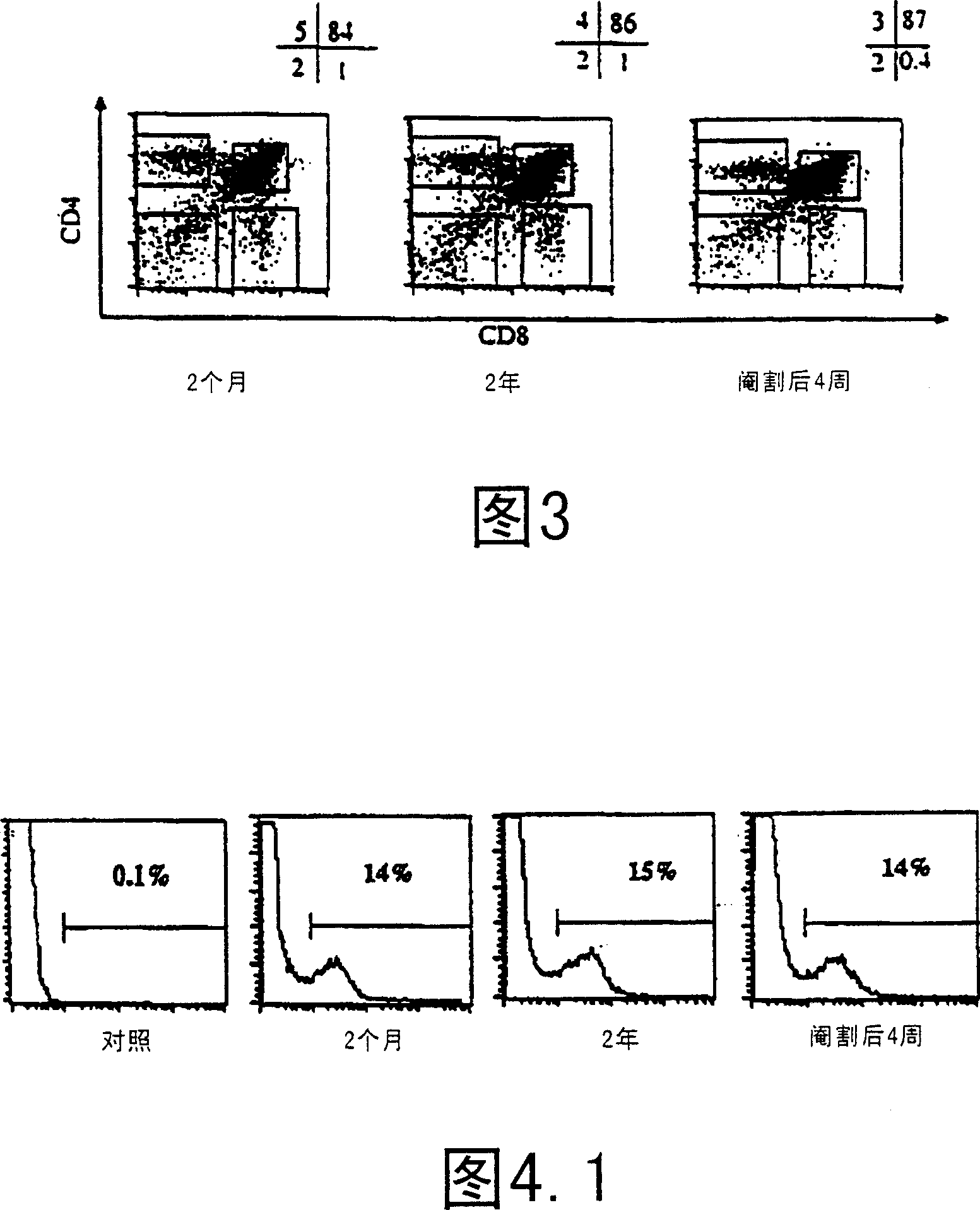
[0127] In the thymus, the structure of the irradiated mouse thymus was severely disrupted, accompanied by a decrease in rapidly dividing cells. Cortical collapse, reminiscent of aged / hydrocortisone treated thymus showing loss of DN and DP thymocytes. αβ-TCR expression on CD4+ and CD8+ SP thymocytes with evidence of downregulation-apoptotic cells. In comparison, cyclophosphamide-treated animals showed less severe disruption of thymus architecture and faster regeneration rates of DN and DP thymocytes.
[0128] By 1 week post-treatment, even at this earlier stage, castrated mice exhibited significant thymus regeneration (Figures 6, 7 and 8). In comparison, non-castrated mice exhibit a severe loss of DN and DP thymocy...
Embodiment 3
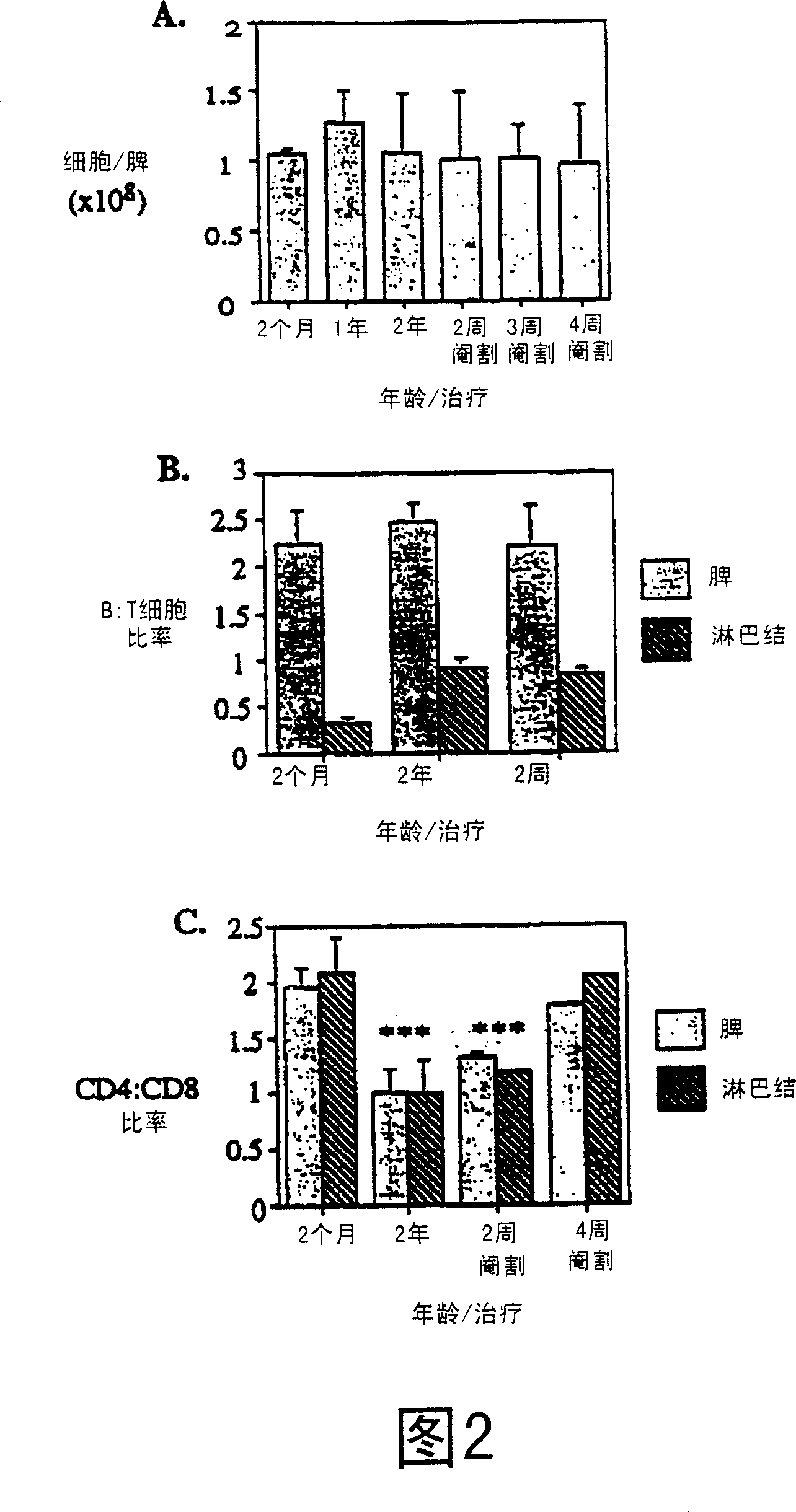
[0131] Example 3: Thymus regeneration following sex steroid suppression leads to restoration of deficient peripheral T cell function
[0132] To determine whether castration can enhance the immune response, herpes simplex virus (HSV) immunity was tested, as it allows the study of disease progression and the role of CTL (cytotoxic) T cells. Castrated mice had qualitatively and quantitatively improved reactivity to the virus. Mouse footpads were immunized and popliteal (draining) lymph nodes were analyzed on day 5 post immunization. Additionally, footpads were taken and homogenized to determine virus titers at specific times throughout the assay.
[0133] On day 5 after immunization, castrated mice had significantly larger lymph node cellularity than aged mice (Figure 10). In addition, the number of activated cells in lymph nodes was significantly increased compared to aged controls (Figures 10 and 11). Further, the number of activated cells correlated with that found in juve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com