Dual-layer recordable optical recording medium
An optical recording medium, double-layer technology, applied in the direction of optical recording carrier, data recording, recording carrier material, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient rewriting characteristics of the optical disc, and the high transmittance of the first information layer, etc., and achieve a small refractive index , high sensitivity, high reflectivity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0099] (Preparation of double-layer recordable optical recording media)
[0100] First and second substrates made of polycarbonate resin, each having a diameter of 120 mm, a thickness of 0.58 mm, and grooves (depth=21 nm, track pitch=0.43 μm) on its surface, were prepared first.
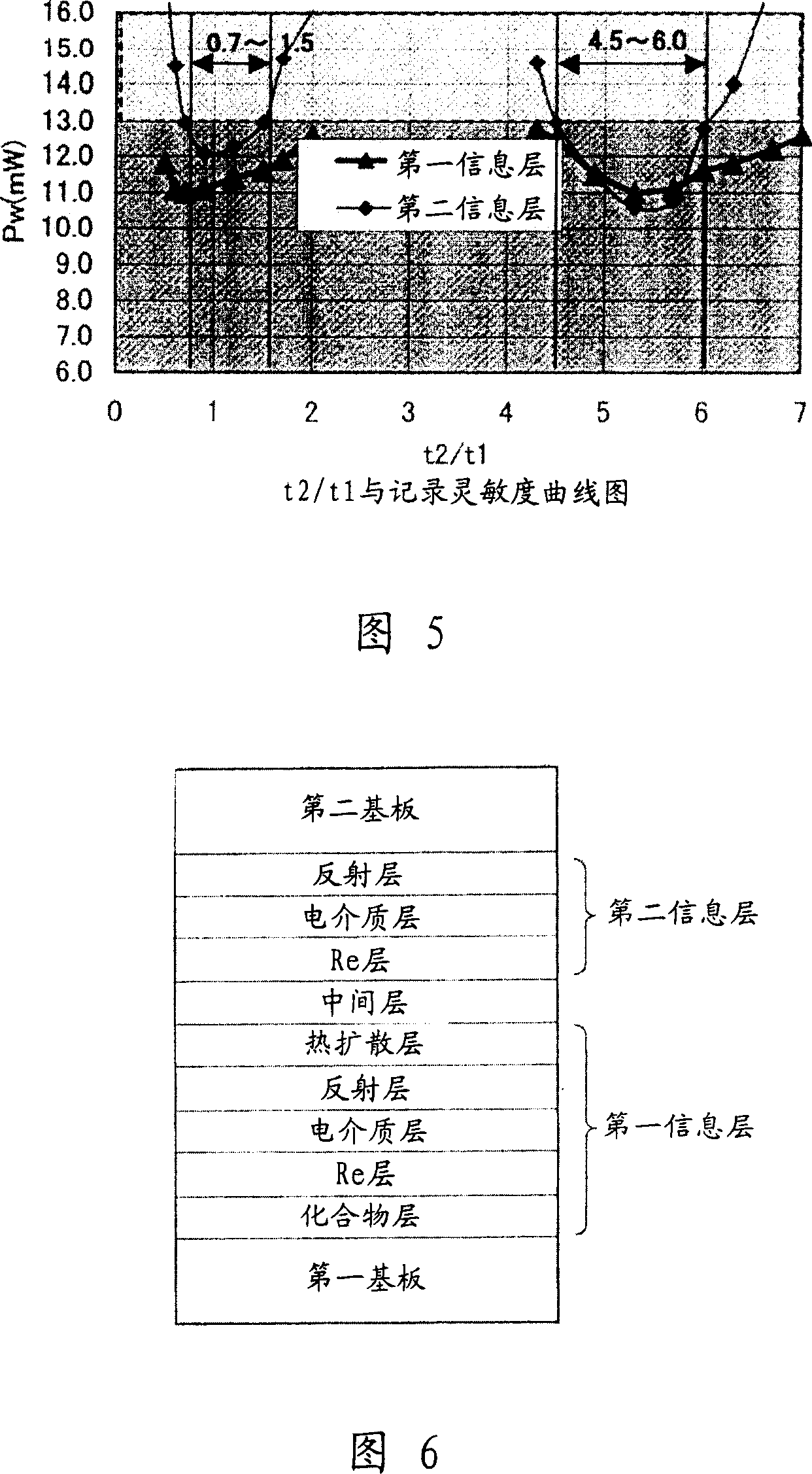
[0101] In a single-wafer sputtering apparatus (Balzers), the following layers are sequentially deposited on the first substrate to form the first information layer: 2 o 3 A compound layer containing typical elements made of Bi 2 o 3 Made of Re layer with a thickness of 20nm, made of ZnS-SiO 2 (80:20 (mol%)) and a thickness of 20 nm, a reflective layer made of Ag and a thickness of 15 nm, and a thermal diffusion layer made of IZO and a thickness of 50 nm.
[0102] In a similar manner, the following layers were sequentially deposited on the second substrate to form the second information layer: a reflective layer made of Ag with a thickness of 100 nm, a layer made of ZnS-SiO 2 (80:20 (mol%)) and a...
example 2
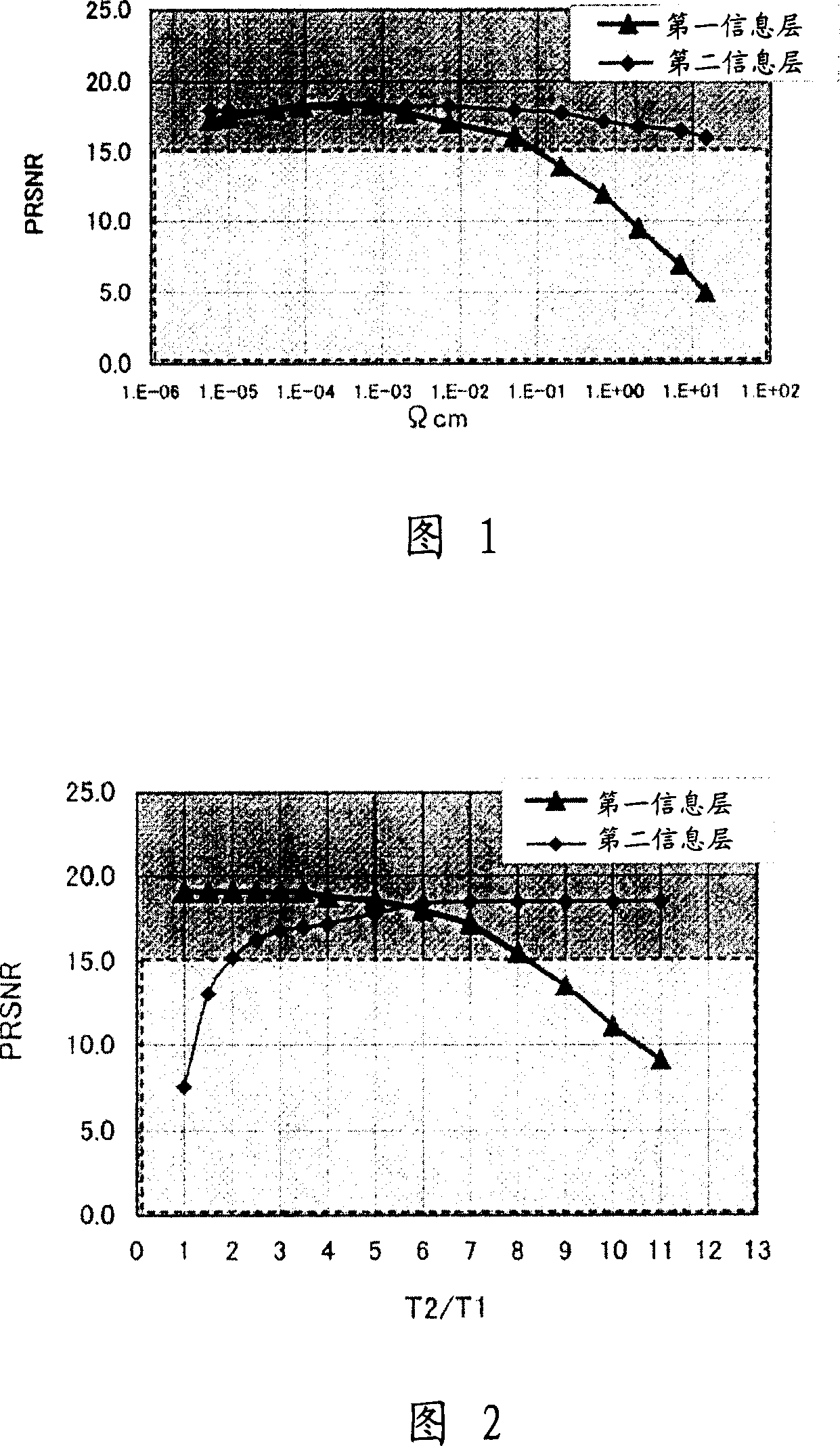
[0109] A double-layer recordable optical recording medium was fabricated in a manner similar to that described in Example 1, except that T2 was set differently by changing T1 (thickness of the Ag reflective layer of the first information layer) and T2 (thickness of the IZO thermal diffusion layer) / T1 ratio, and measure the value of PRSNR. More specifically, various T2 / T1 ratios were obtained by setting the thickness (T1) of the Ag reflective layer at 10 nm, 15 nm, and 20 nm and setting a different thickness (T2) for each thickness.
[0110] From the measurement results shown in Figure 2, it can be seen that the line corresponding to the PRSNR of the second information layer shows a rapid decline when T2 / T18. decline.
example 3
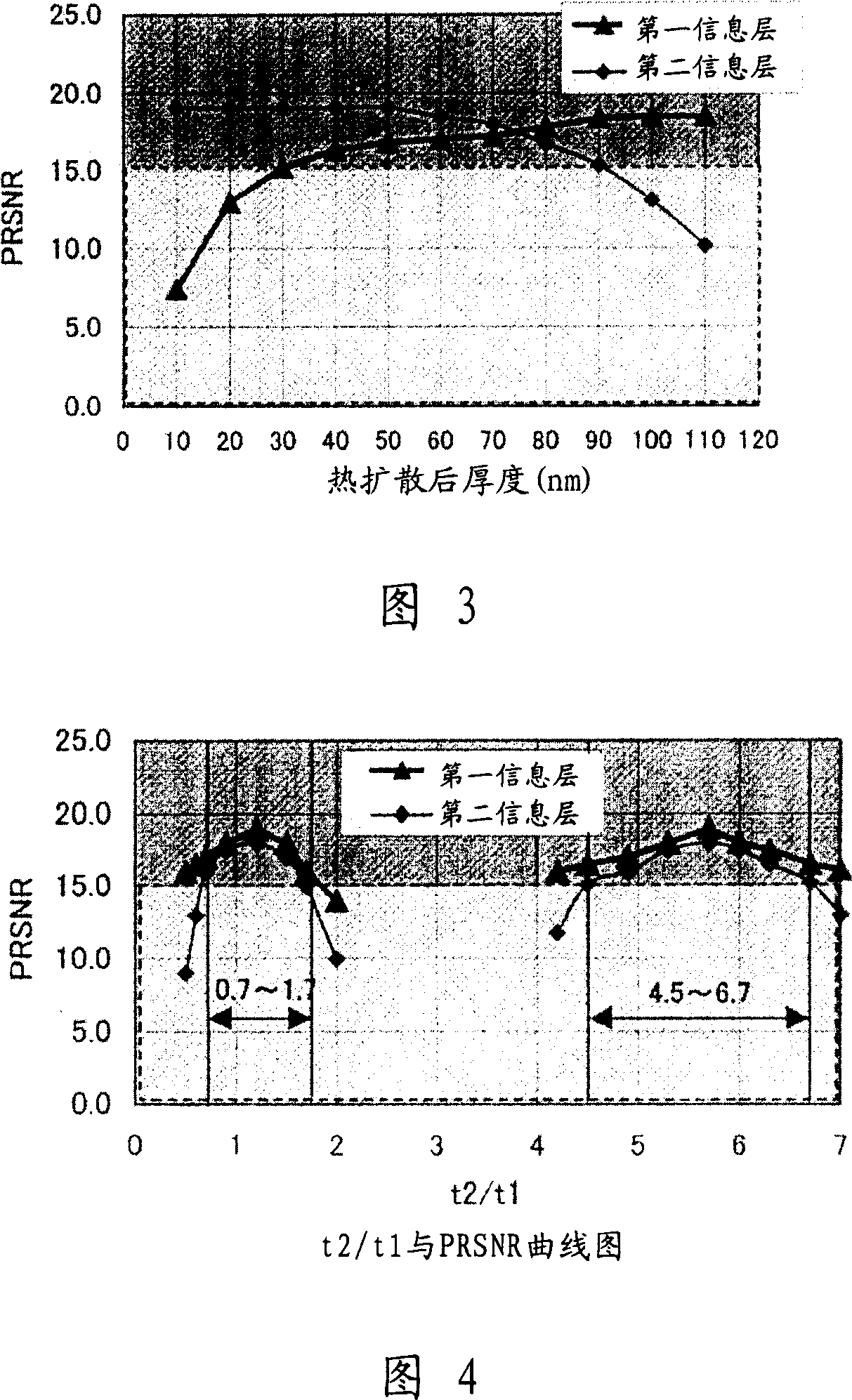
[0112] Dual-layer recordable optical recording media were fabricated in a manner similar to that described in Example 1, except that thermal diffusion layers having various thicknesses were used. PRSNR values were then measured.
[0113] From the measurement results shown in Figure 3, it can be seen that the line corresponding to the PRSNR of the first information layer shows a rapid decline when the thickness of the thermal diffusion layer is less than 30nm, and the line corresponding to the PRSNR of the second information layer decreases when the thickness of the thermal diffusion layer >90nm showed a rapid decline.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com