Method and apparatus for enhanced nano-spectroscopic scanning
A nano-lens technology, applied in the field of nano-spectroscopy scanning, can solve the problems of not revealing, enhancing spectral resolution, and interpreting multiple samples without giving suggestions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
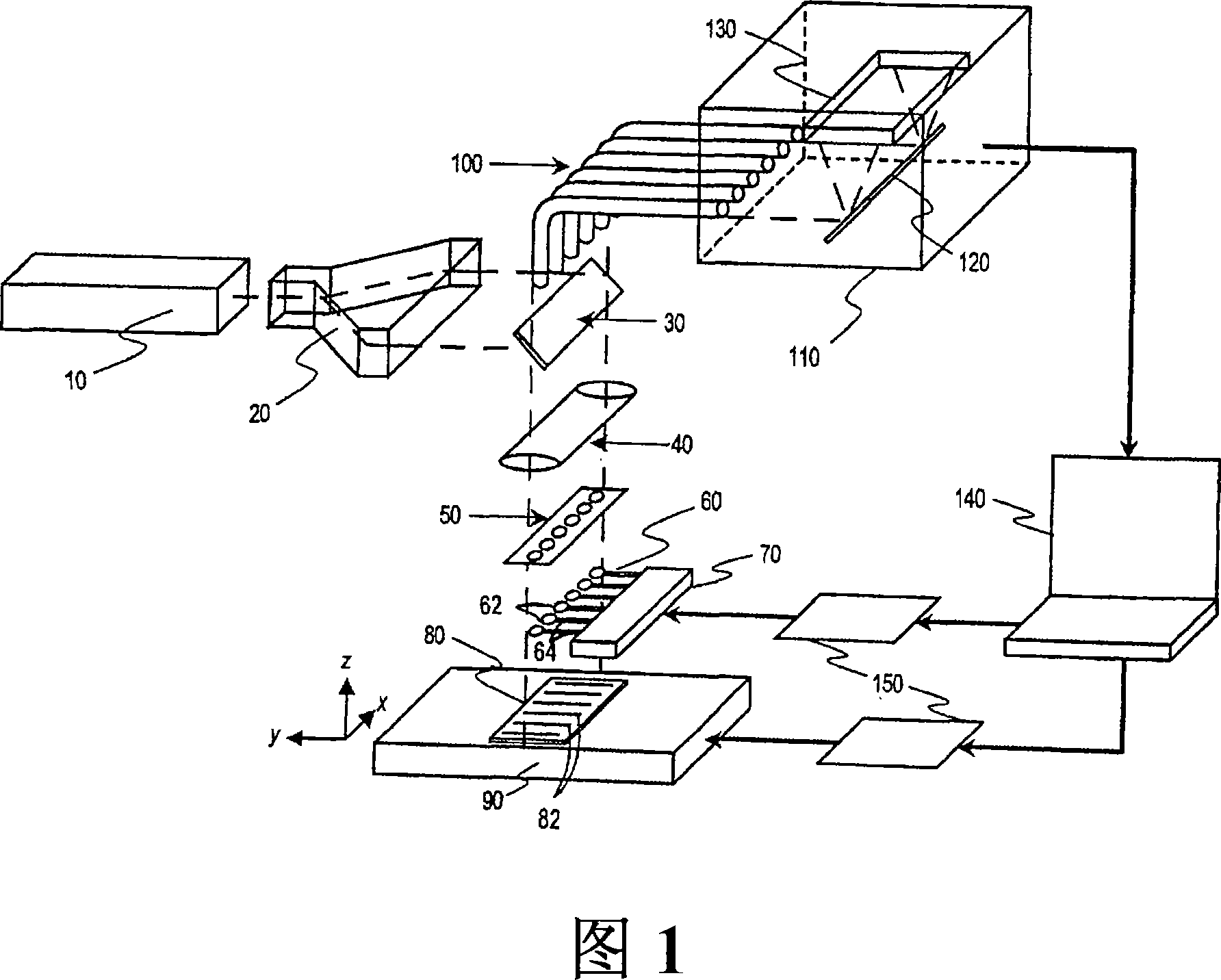
[0044] A. Definition
[0045] Unless otherwise specified, the following terms have the following meaning, "plasmon resonant metal" includes any metal, such as gold, silver or aluminum, which can support a surface electromagnetic mode - surface plasmon polarization (SPP), ie photon and plasmon coupled modes.
[0046] "Chemical groups" in a sample can include subunits in polymers, or parts of subunits, such as nucleic acid bases, or chemically substituted molecular groups, such as hydroxyl, amine, alkyl, acid or aldehyde groups. These chemical group identities are manifested by unique enhanced Raman spectroscopy signals or signatures.
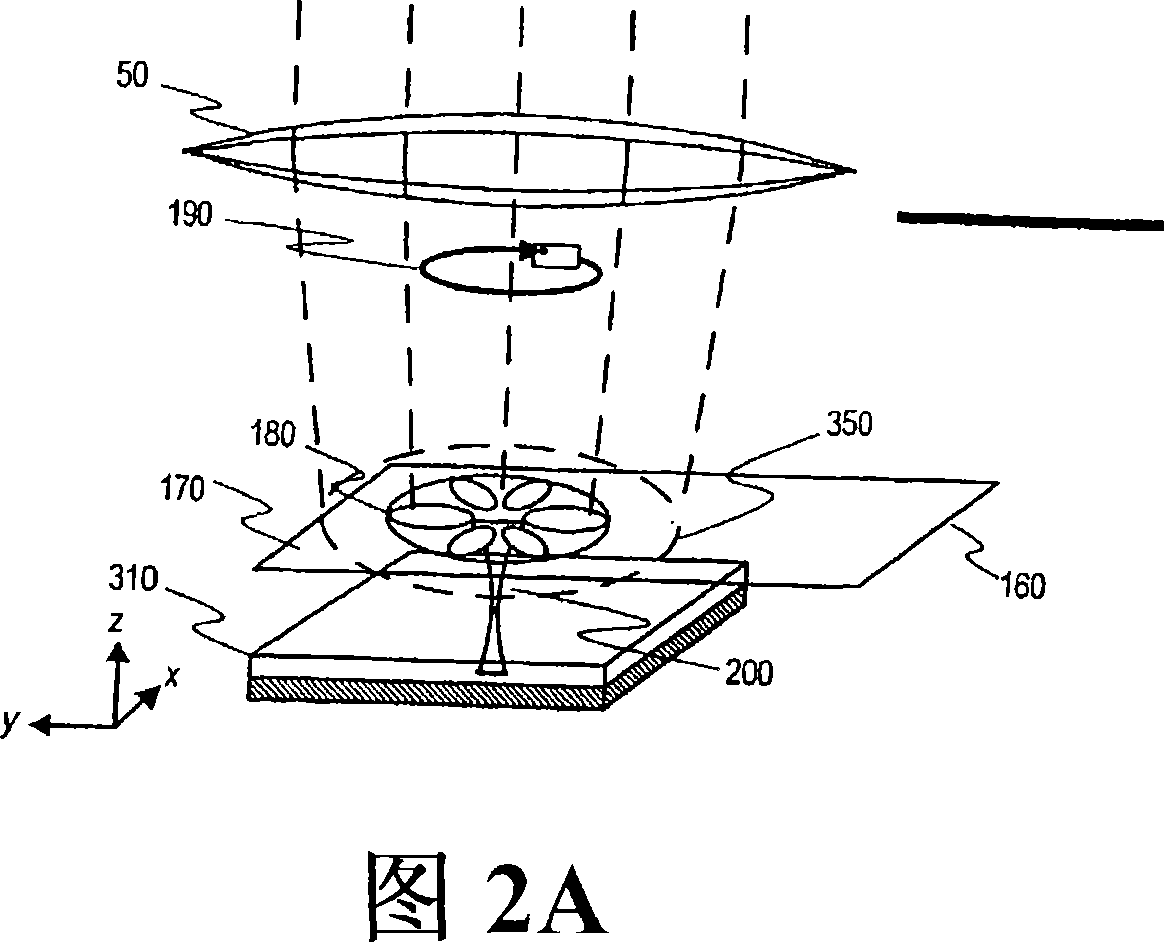
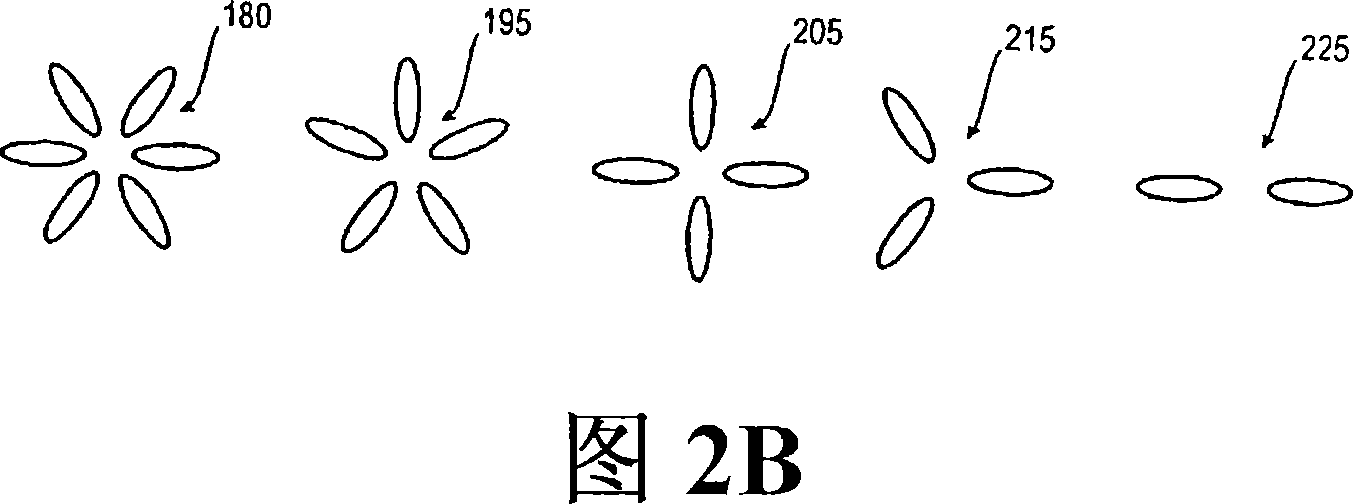
[0047] "Gap mode" refers to the electromagnetic orthogonality between two or more plasmon particles excited by an external electromagnetic field at a distance between two or more plasmon particles when they are placed near (less than 40 nm) a metal surface, preferably a plasmon resonant metal surface. mode or electromagnetic eigenvalues. Exampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com