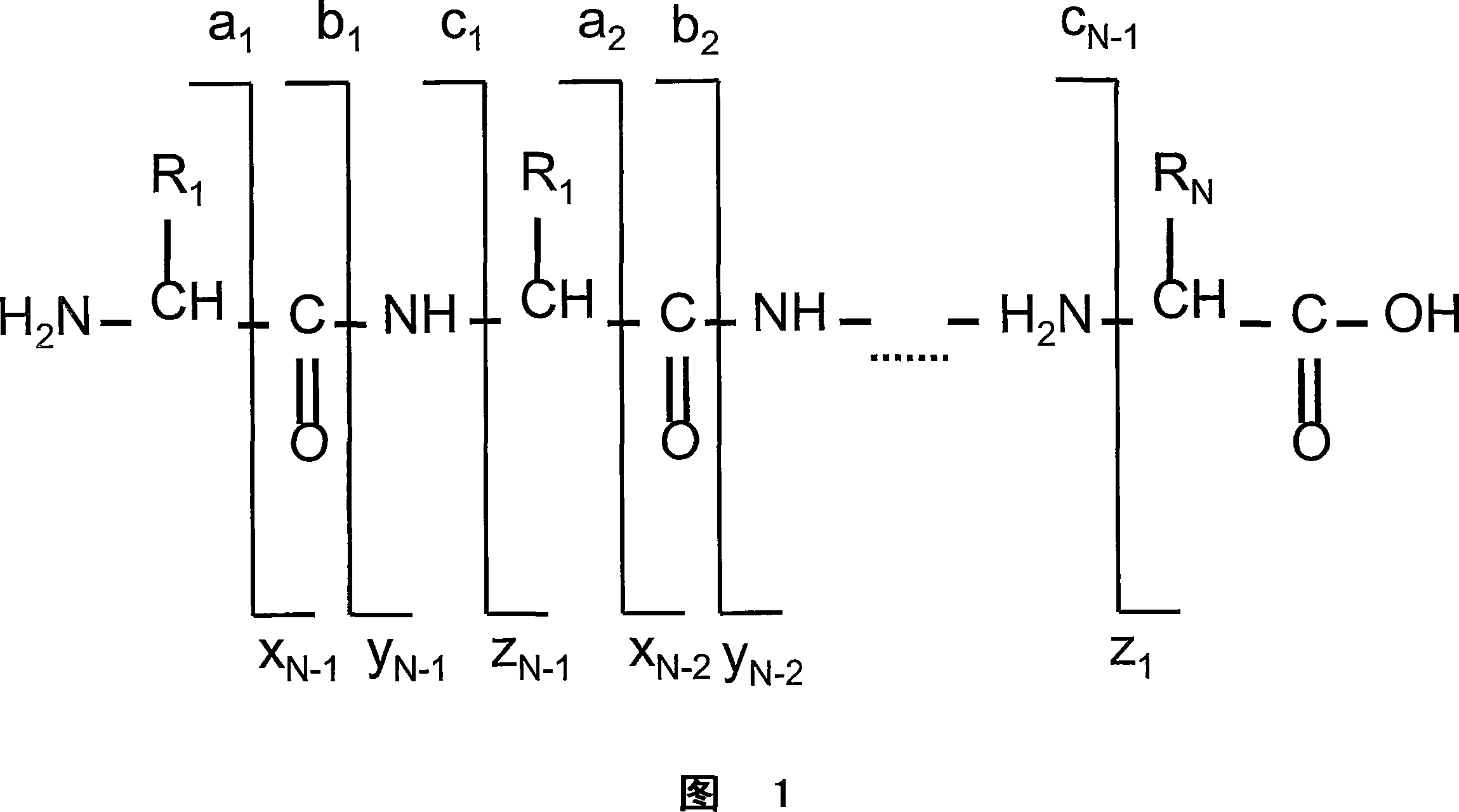
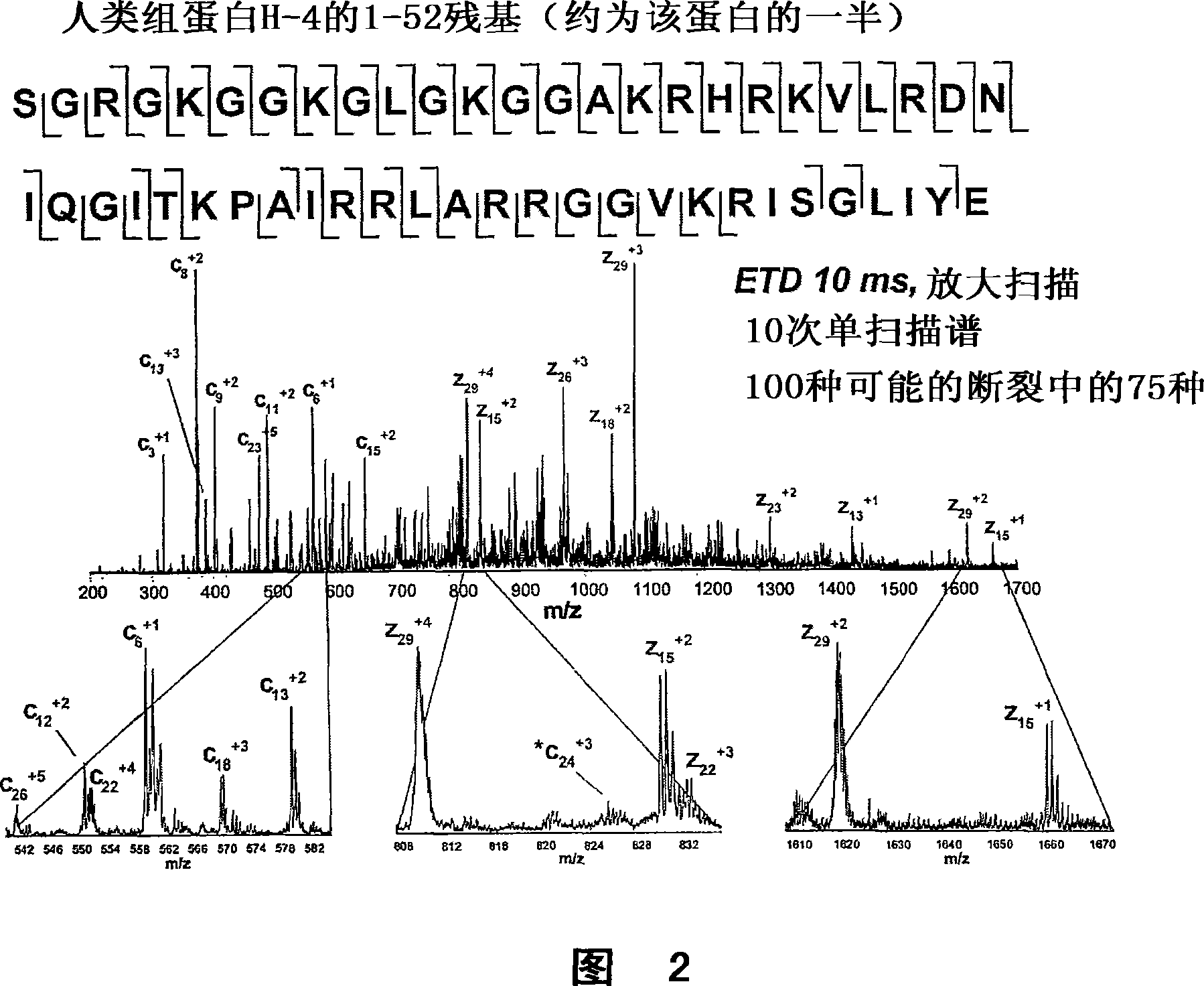
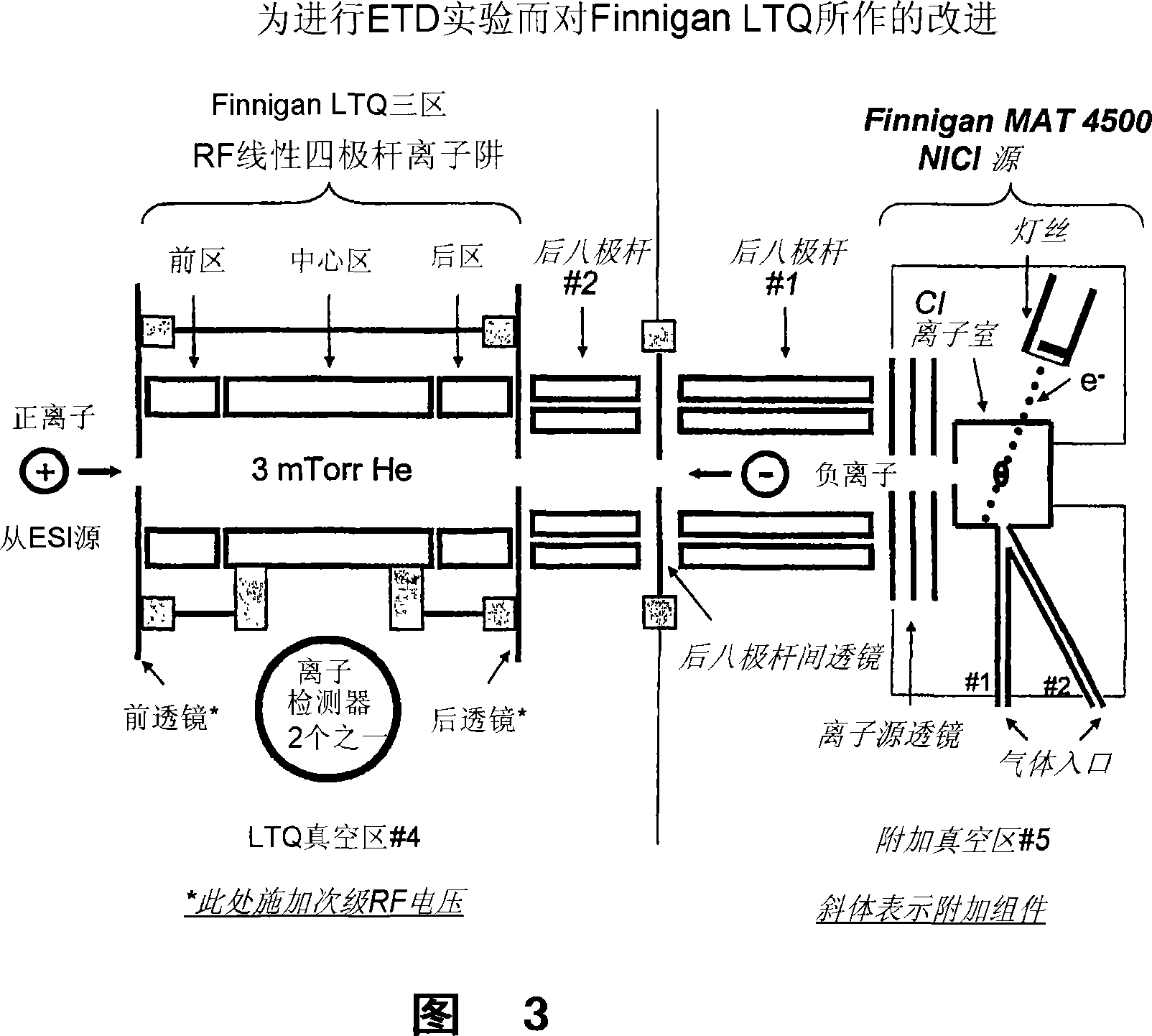
Simultaneous sequence analysis of amino- and carboxy-termini
A carboxyl-terminal, amino-terminal technique, applied in the field of simultaneous sequence analysis of amino and carboxyl-terminal ends
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0041] According to the present disclosure, there is provided a method for rapid sequence analysis of the amino and carboxyl termini of intact proteins or large protein degradation products using mass spectrometry and multiple ion / ion reactions. In one embodiment, the method provides a rapid means of identifying or confirming the presence of a polypeptide 30, 40, 50 or more amino acids in length from a sample. A sample may contain the polypeptide of interest in pure form (eg, greater than 99% pure), or may contain other polypeptides or compounds. Samples can also be derived from complex mixtures of other proteins / peptides, such as whole cell lysates. More particularly, in one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of performing a first ion-ion reaction (electron transfer dissociation: ETD) to dissociate polypeptide ions in a mass spectrometry system, and then performing a second A secondary ion-ion reaction (proton transfer reaction: PTR) to reduce the charge of the ion f...
Embodiment 1
[0168] Use of negative ions for electron transfer dissociation of polypeptides
[0169] According to one embodiment, FC-43 (perfluorotributylamine, PFTBA), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ), perfluoro-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane (PDCH), benzene hexafluoride (C 6 f 6 ) and anthracene were introduced into a NICI (Negative Ion Chemical Ionization) source to generate negative ions for the experiment. In all cases, the negative ions generated in the aforementioned sources produced at least some ETD products when reacted with standard peptide precursor ions. When the standard m / z calibrant FC-43 for electron impact ionization source mass spectrometers was introduced into the source, only small amounts of c and z ions were generated with very low conversion efficiency of precursors to ETD products. In later experiments, the above molecules were introduced individually into the ion source and both produced extensive c- and z-type fragmentation of our standard precursor ion, a triple-charged ...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Continuous Ion / Ion Reaction
[0175] As mentioned above, a certain negative ion mainly acts as ETD or PTR reactant. The individual reactions described above can be performed separately and sequentially by exposing positive ions to negative ions of either species. For example, highly charged peptide precursor ions (eg, z>4) can be dissociated with an ETD-inducing anion, followed by removal of those reactants and introduction of a second PTR-inducing anion. The duration of the second reaction can be adjusted so that the charge state of the product species is reduced in a controlled manner. That is, a +10 precursor peptide can be dissociated by ETD to produce fragments charged from +1 to +9. Of course, m / z resolution of the isotopic peaks of such highly charged products can be problematic; so the duration of the secondary PTR reaction can be adjusted so that the ETD product converts to a predominantly +1 charged state. The net effect of the above reactions is to convert...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com