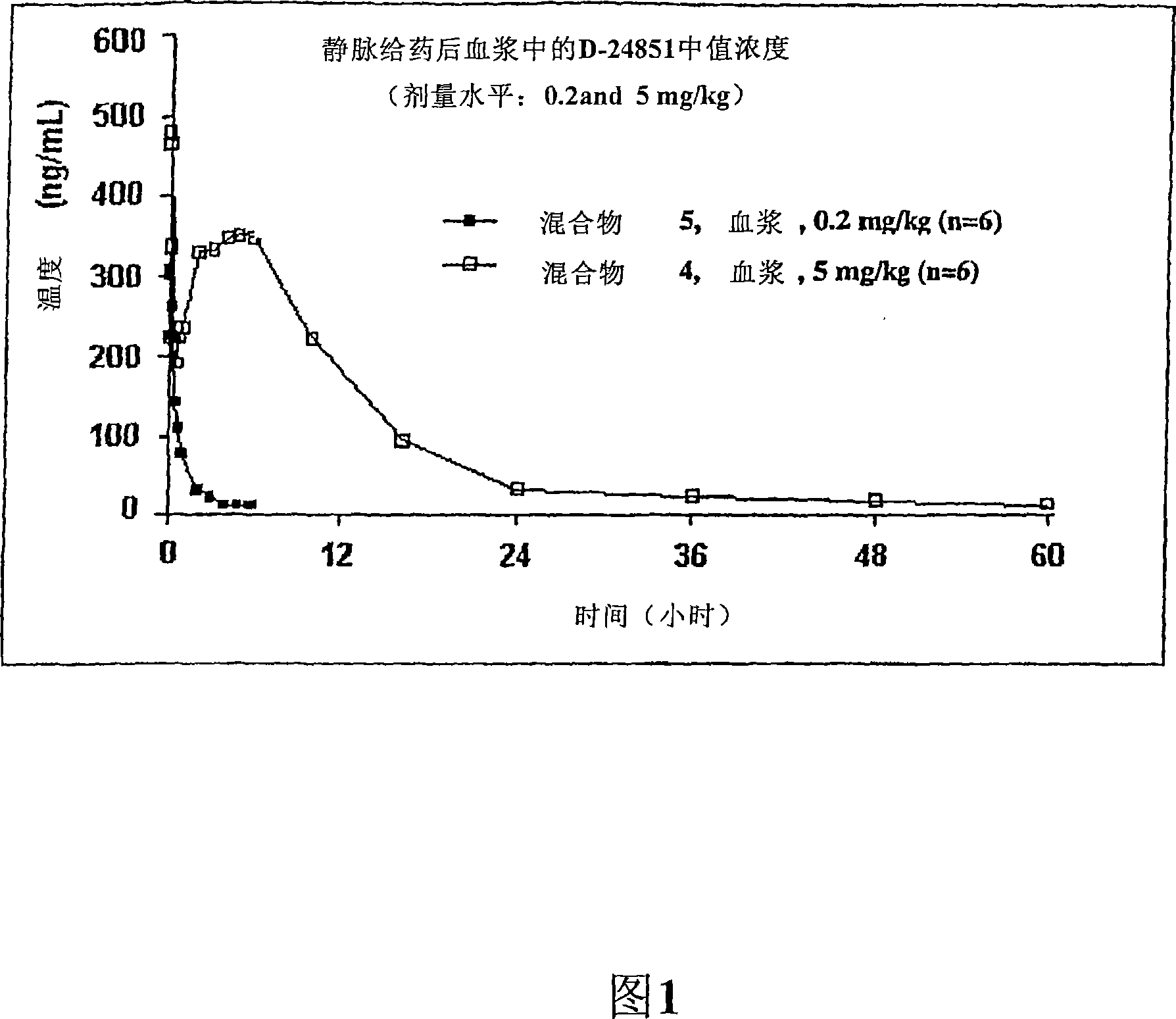
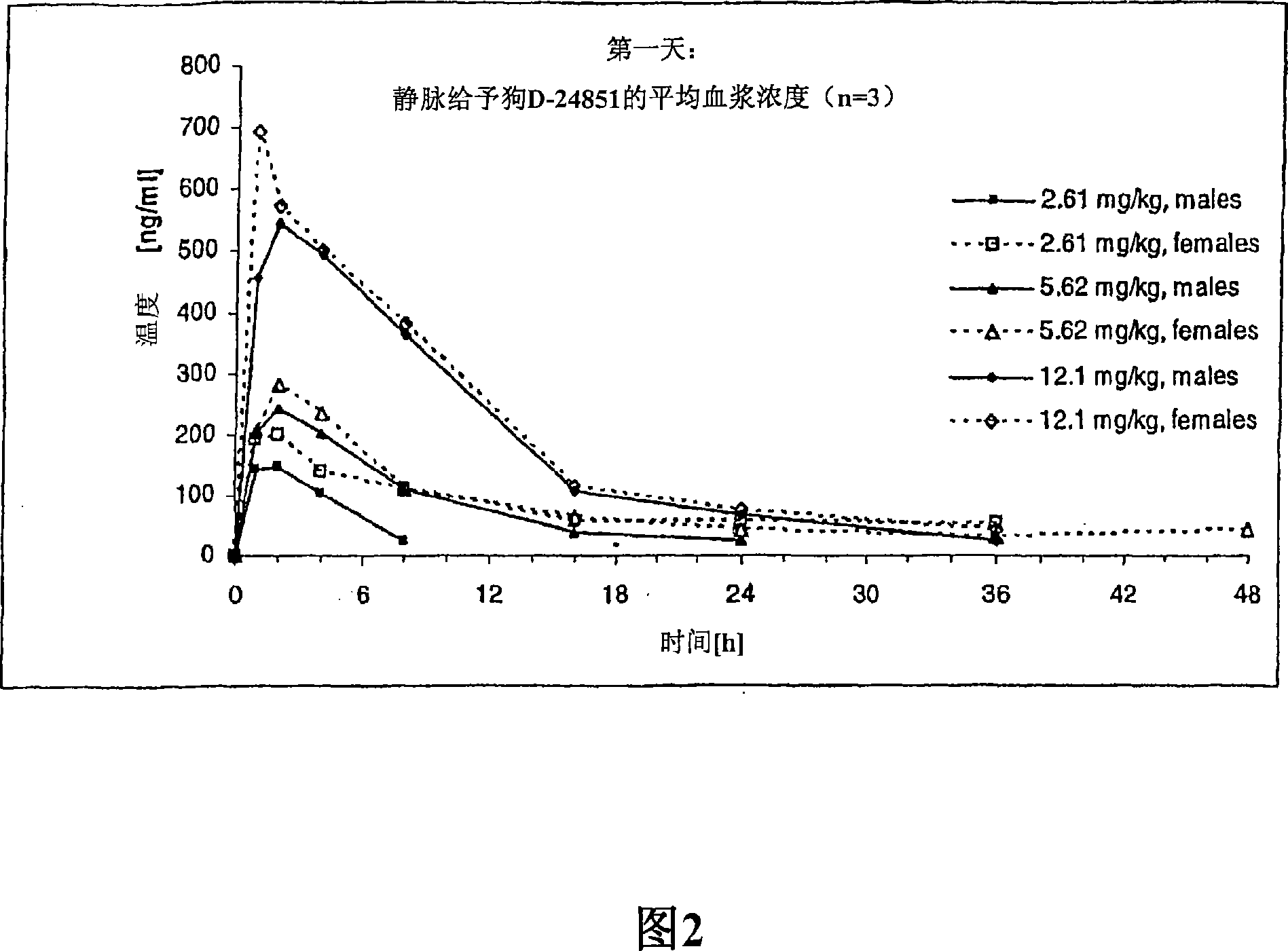
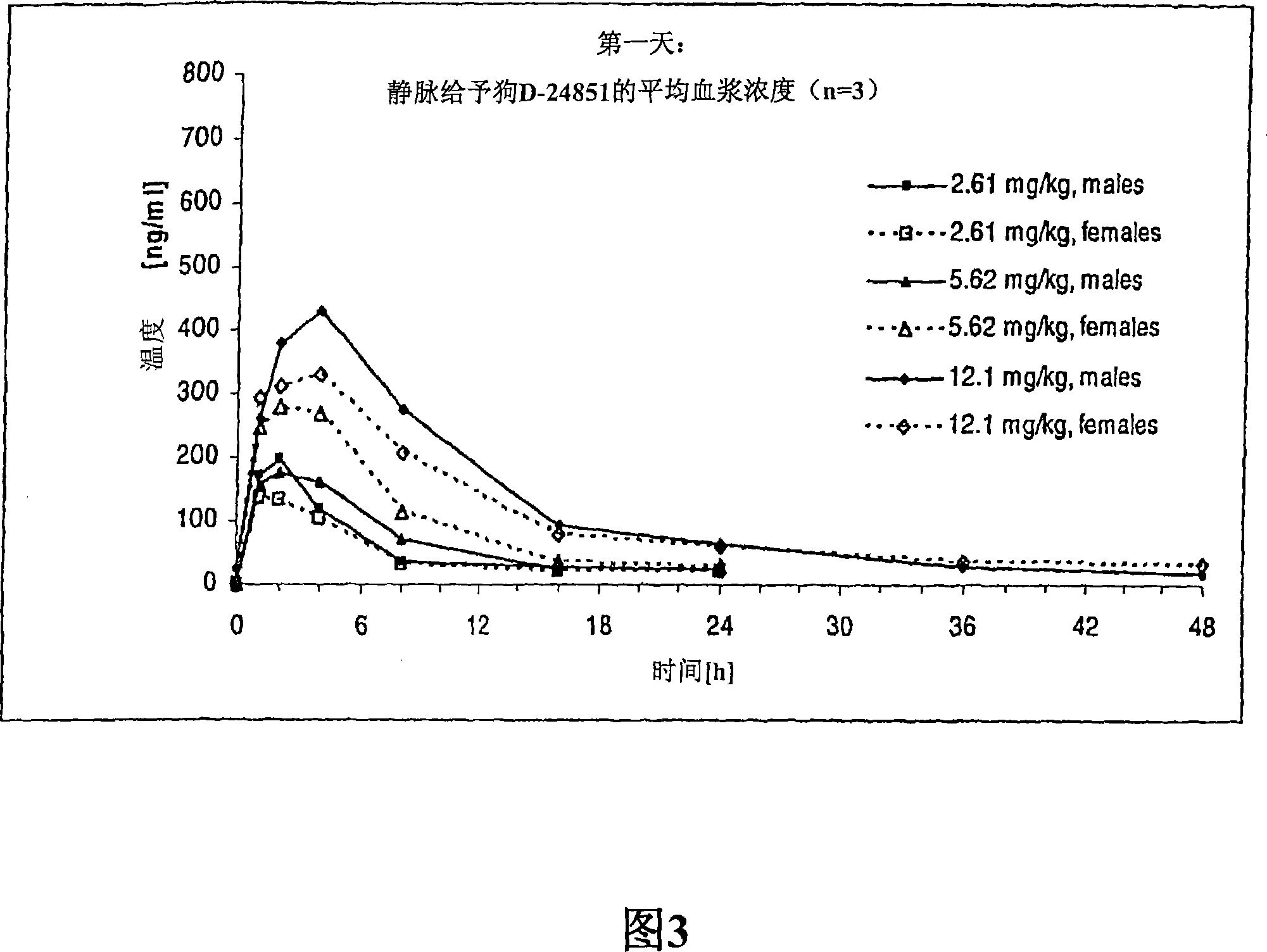
Nanoparticulate compositions of tubulin inhibitor compounds
A technology of tubulin inhibition and nanoparticle, which can be used in drug combination, drug delivery, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as microtubule instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0192] Example 1: Small scale preparation (300 g) of a suspension of D-24851 (composition 1)
[0193] An aqueous surfactant solution containing 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 2.2% glycerol (tension agent), and 0.142% disodium phosphate (buffer) was cooled to low temperature (<10°C). The lactic acid solution of D-24851 and Poloxamer 188 was added to the above surfactant solution. The two solutions are mixed to form a suspension. The total suspension weight is 300 g, and the drug concentration is about 1% (w / w). Immediately after the precipitation, carry out high-pressure homogenization, the pressure is about 10,000 psi, and the temperature is <70°C. Lactic acid was removed by centrifugation, and the suspension was homogenized again at about 10,000 psi at a temperature <70°C. After homogenization, the particle size of the suspension was measured using light scattering. The average particle size is about 190nm.
Embodiment 2
[0194] Example 2: Preparation of 2,000 g of a suspension of D-24851 (Composition 2)
[0195] An aqueous surfactant solution containing 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 2.2% glycerol (tension agent), and 0.142% disodium phosphate (buffer) was cooled to low temperature (<10°C). The lactic acid solution of D-24851 and Poloxamer 188 was added to the above surfactant solution. The two solutions are mixed to form a suspension. The total suspension weight was 2,000 g, and the drug concentration was about 1% (w / w). Immediately after the precipitation, carry out high-pressure homogenization, the pressure is about 10,000 psi, and the temperature is <70°C. Lactic acid was removed by centrifugation, and the suspension was homogenized again at about 10,000 psi at a temperature <70°C. After homogenization, the particle size of the suspension was measured using light scattering. The average particle size is about 325nm.
Embodiment 3
[0196] Example 3: Large scale preparation (6,000 g) of a suspension of D-24851 (Composition 3)
[0197] An aqueous surfactant solution containing 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 2.2% glycerol (tension agent), and 0.142% disodium phosphate (buffer) was cooled to low temperature (<10°C). The lactic acid solution of D-24851 and Poloxamer 188 was added to the above surfactant solution. The two solutions are mixed to form a suspension. The total suspension weight was 6,000 g, and the drug concentration was about 1% (w / w). Immediately after the precipitation, carry out high-pressure homogenization, the pressure is about 10,000 psi, and the temperature is <70°C. Lactic acid was removed by centrifugation, and the suspension was homogenized again at about 10,000 psi at a temperature <70°C. After homogenization, the particle size of the suspension was measured using light scattering. The average particle size is about 370nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com