Motor control unit
A control device and motor technology, applied in the direction of motor generator control, AC motor control, electric controller, etc., can solve problems such as difficult positioning, and achieve the effect of improving position resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Hereinafter, Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 3 .
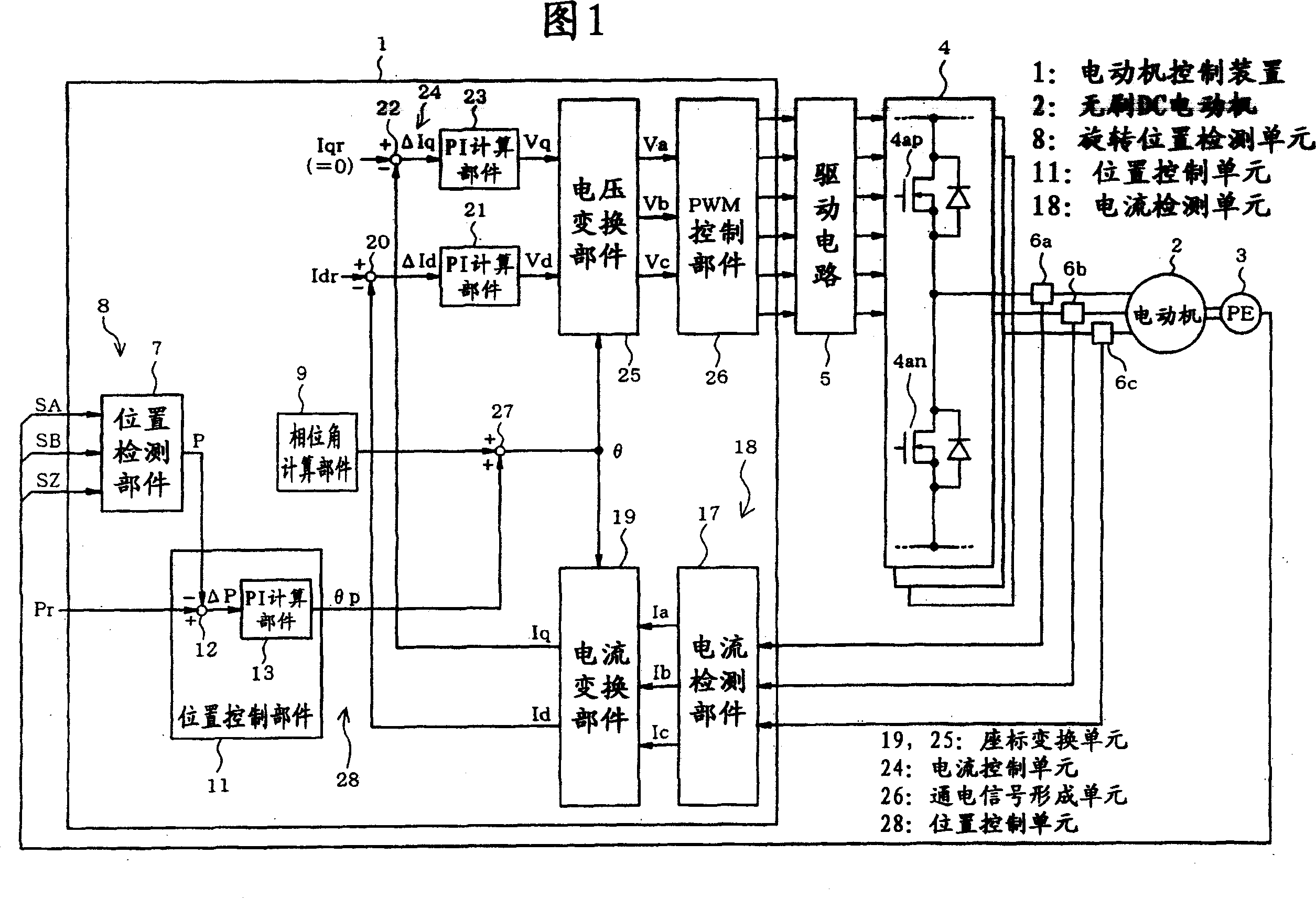
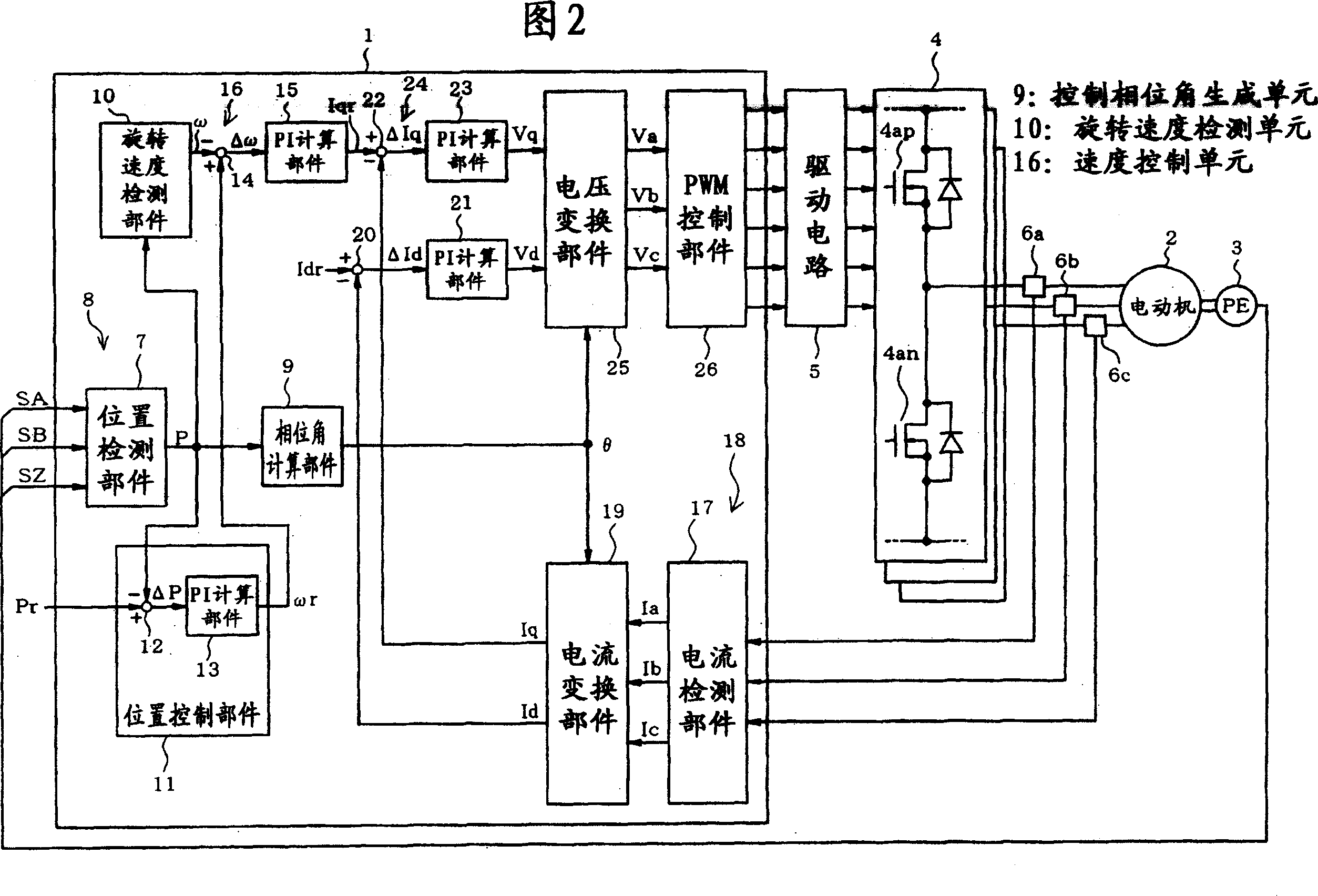
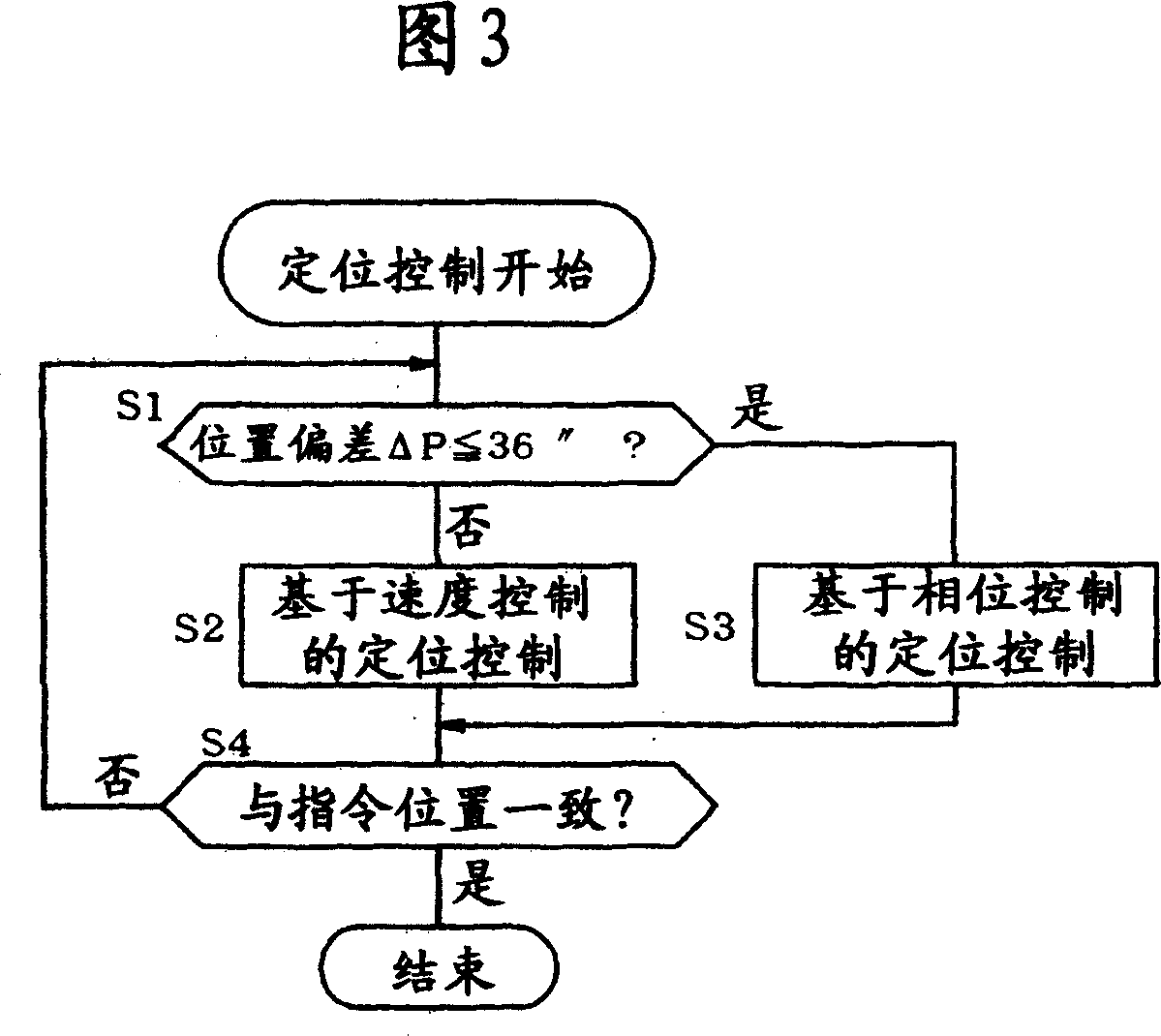
[0025] Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the structure of the motor control system. When the position deviation ΔP is large, the motor control device 1 adopts the same structure as the prior art shown in FIG. The deviation Δω correspondingly obtains the speed feedback loop of the command current as a secondary loop (hereinafter referred to as positioning control based on speed control). In this regard, if the position deviation ΔP is less than or equal to the specified value, as shown in Fig. 1, the following position feedback loop (hereinafter referred to as positioning control based on phase control) is adopted, that is, when the speed feedback loop is disabled and the command current becomes Based on a constant value, the phase angle θ (hereinafter referred to as phase angle θ) is controlled in accordance with the positional deviation ΔP.
[0026] First, the control str...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Next, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 .
[0057] Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 show the structure of the motor control system, and the same reference numerals are assigned to the same parts as Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 . The motor control device 29 is different from the first embodiment in that it directly controls the voltage without having a current control loop.
[0058] When the position deviation ΔP is large, the motor control device 29 adopts a position feedback loop to obtain the command rotational speed ωr corresponding to the position deviation ΔP as shown in FIG. Velocity feedback loop for Vq (positioning control based on velocity control). The PI calculation section 30 performs PI calculation on the speed deviation Δω to generate the command q-axis voltage Vq, and thus constitutes the speed control unit 31 together with the subtractor 14 . In addition, the d-axis voltage Vd is a constant value.
[0059] If the positi...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 to 9 .
[0063] FIG. 6 shows the configuration of the motor control system, and the same parts as those in FIG. 1 are assigned the same reference numerals. When the position deviation ΔP is large, the motor control device 33 executes the positioning control based on the speed control through the same structure as in FIG. Hereinafter referred to as positioning control by phase voltage correction), that is, the phase voltages Va, Vb, and Vc are corrected and controlled in accordance with the positional deviation ΔP.
[0064] If switching to the positioning control based on phase voltage correction, the rotation speed detection part 10 and the speed control unit 16 stop processing. In addition, the phase angle calculation unit 9 stops the above-mentioned multiplication process of the number of pole pairs, and maintains and outputs the phase angle θ at the time of switching. The PI cal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com