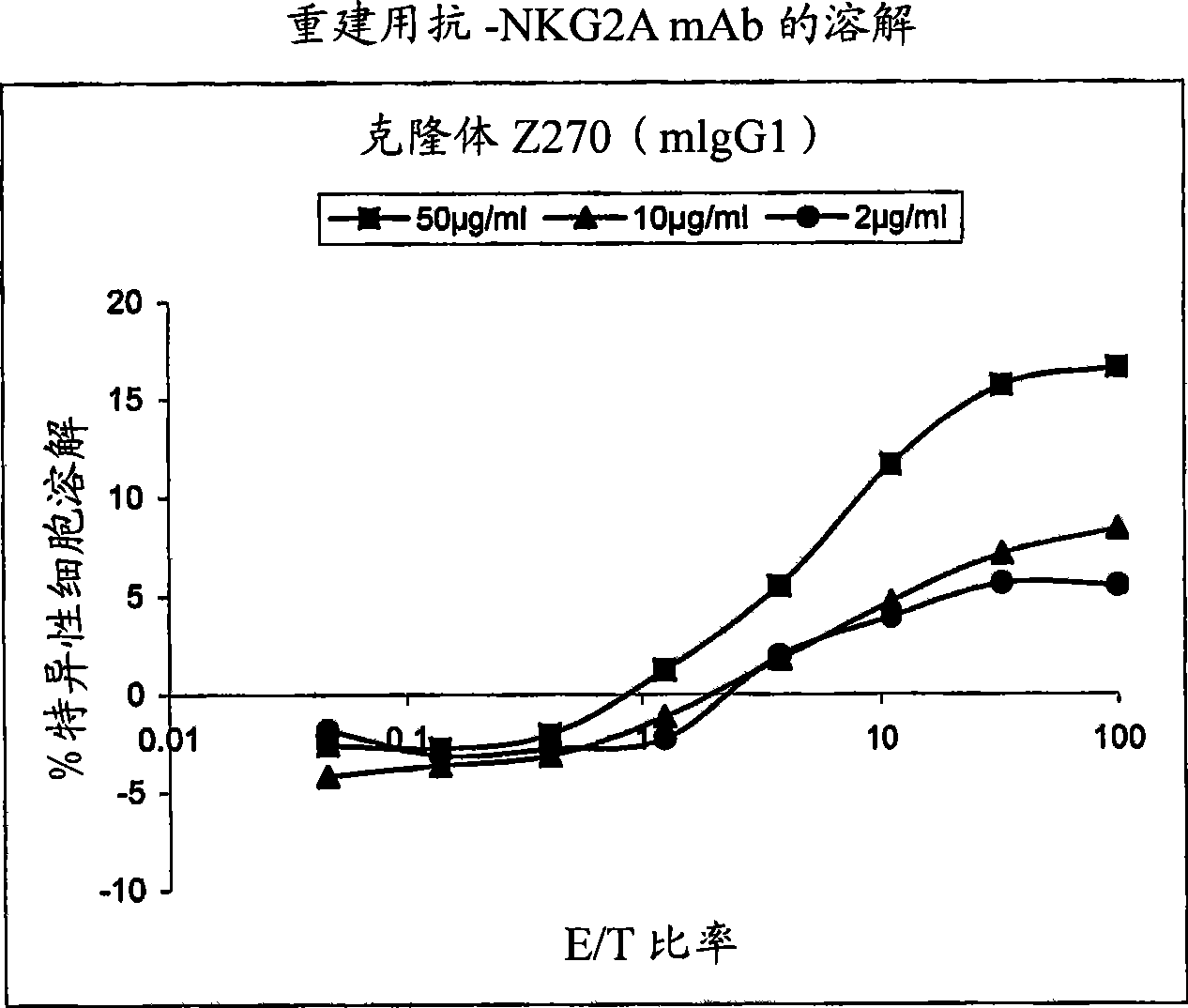
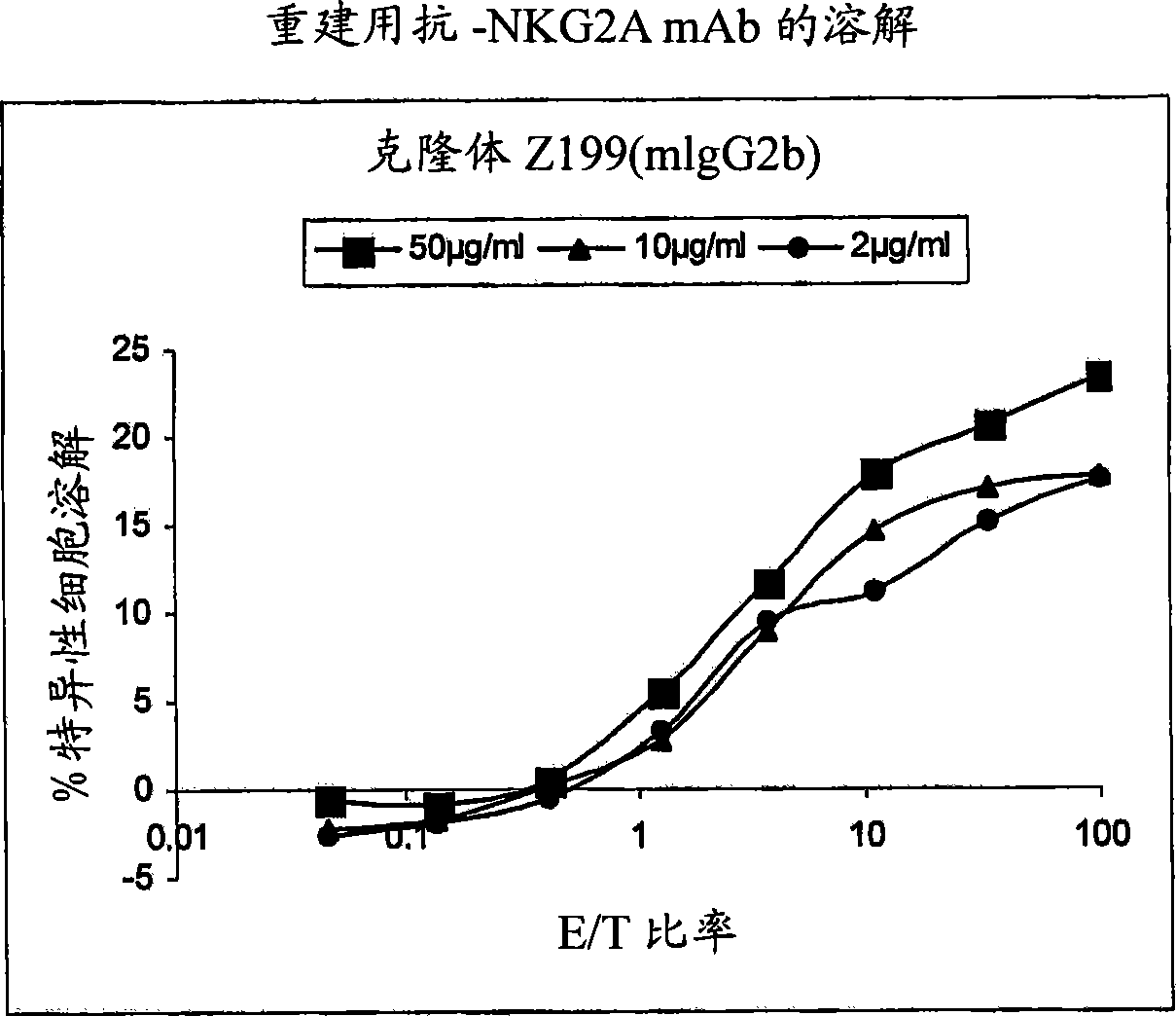
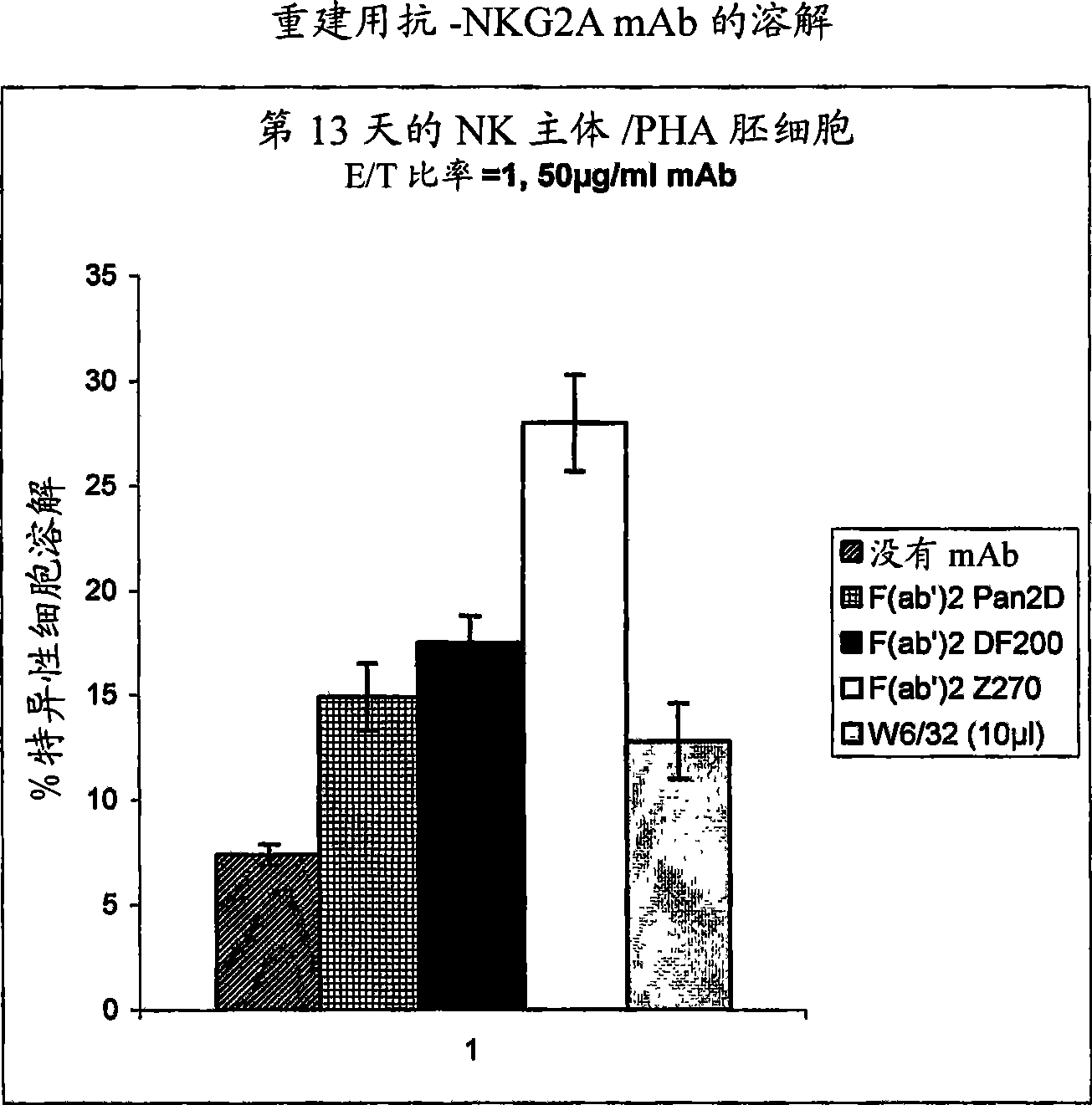
Monoclonal antibodies against NKG2A
A monoclonal antibody, single-chain antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulin, etc. difficult to predict, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0122] The production of monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies is well known in the art, and any of a number of available techniques may be used (see, e.g., Kohler & Milstein, Nature 256:495-497 (1975); Kozbor et al., Immunology Today 4:72 (1983); Cole et al., pp. 77-96 in Monoclonal Antibodies and Cancer Therapy (1985)). Techniques for the production of single chain antibodies (US Patent No. 4,946,778) can be adapted to produce antibodies directed against a desired polypeptide (eg, NKG2A). Furthermore, transgenic mice or other organisms, such as other mammals, can be used to express humanized, chimeric or similarly modified antibodies. Alternatively, phage display technology can be used to identify antibodies and heterologous Fab fragments that specifically bind an antigen of choice (see, e.g., McCafferty et al., Nature 348:552-554 (1990); Marks et al., Biotechnology 10:779-783 (1992)). In a specific embodiment, the method comprises selecting from a library or repertoire a mo...
Embodiment 1
[0253] Example 1: Autologous mediated by a subset of CD94 / NKG2A+KIR-NK cells iDC kill
[0254] Polyclonal NK cells cultured in the presence of exogenous IL-2 initially exhibited strong lytic activity against iDCs. Thus, in this study, polyclonal NK cell populations isolated from AM, AC, and DB donors effectively killed autologous or allogeneic iDCs. However, in the presence of appropriate anti-HLA class I mAbs, the lytic activity against autologous iDC was enhanced.
[0255] These data may be the result of disrupted inhibitory interactions that occur between self class I HLA on DCs and inhibitory receptors on NK cells. On the basis of these results, we hypothesize that only a fraction of the entire NK cell pool exhibits spontaneous cytotoxicity against iDCs, and that due to potent inhibitory interactions between their receptors and HLA class I molecules, effect, other NK cells do not have this cytotoxicity. To analyze this possibility, NK cell clones isolated from donor...
Embodiment 2
[0263] Example 2 - Sensitivity of iDCs to NK-mediated cytotoxicity mirrors HLA-E class I molecular downregulation
[0264] Previous studies have demonstrated that iDCs and mDCs display significant differences in HLA class I surface expression. Thus, by using mAbs specific for monomorphic titan determinants of HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-E molecules, it has been demonstrated that maturing DCs greatly upregulate the expression of HLA class I at the cell surface. Express. Furthermore, upregulation of HLA class I represents a key mechanism by which mDCs become resistant to NK cell-mediated lysis.
[0265] To directly evaluate the expression of various HLA class I molecules on cells representing different DC maturation stages, we comparatively analyzed the expression of HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-E in monocytes (derived from the same individual expression on iDC and mDC). All HLA class I molecules were highly upregulated in mDCs compared to iDCs. Remarkably, they were si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com