Continuous extrusion process for producing grafted polymers
A technology of grafted polymers and polymers, applied in the field of functionalized polymers, can solve the problems of being unsuitable for high functionalization, reducing molecular weight, and not being able to obtain high functionality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: Comparison
[0090] The effect of molecular weight reduction by shear modification prior to grafting polymers was tested in a continuous extrusion reactor comprising two extruders connected in series. The purpose of the trials was to investigate the feasibility of carrying out molecular weight reduction and grafting together in a single continuous extrusion reactor. Table 4 shows the processing sections and corresponding operating conditions for each extruder.
[0091] Table 4: Processing section and operating conditions of Example 2
[0092] Extruder #1
[0093] The graft polymer produced with the above operating conditions has the following characteristics:
[0094] Table 5: Properties of the graft polymer produced in Example 2
[0095] Bound maleic anhydride (wt%)
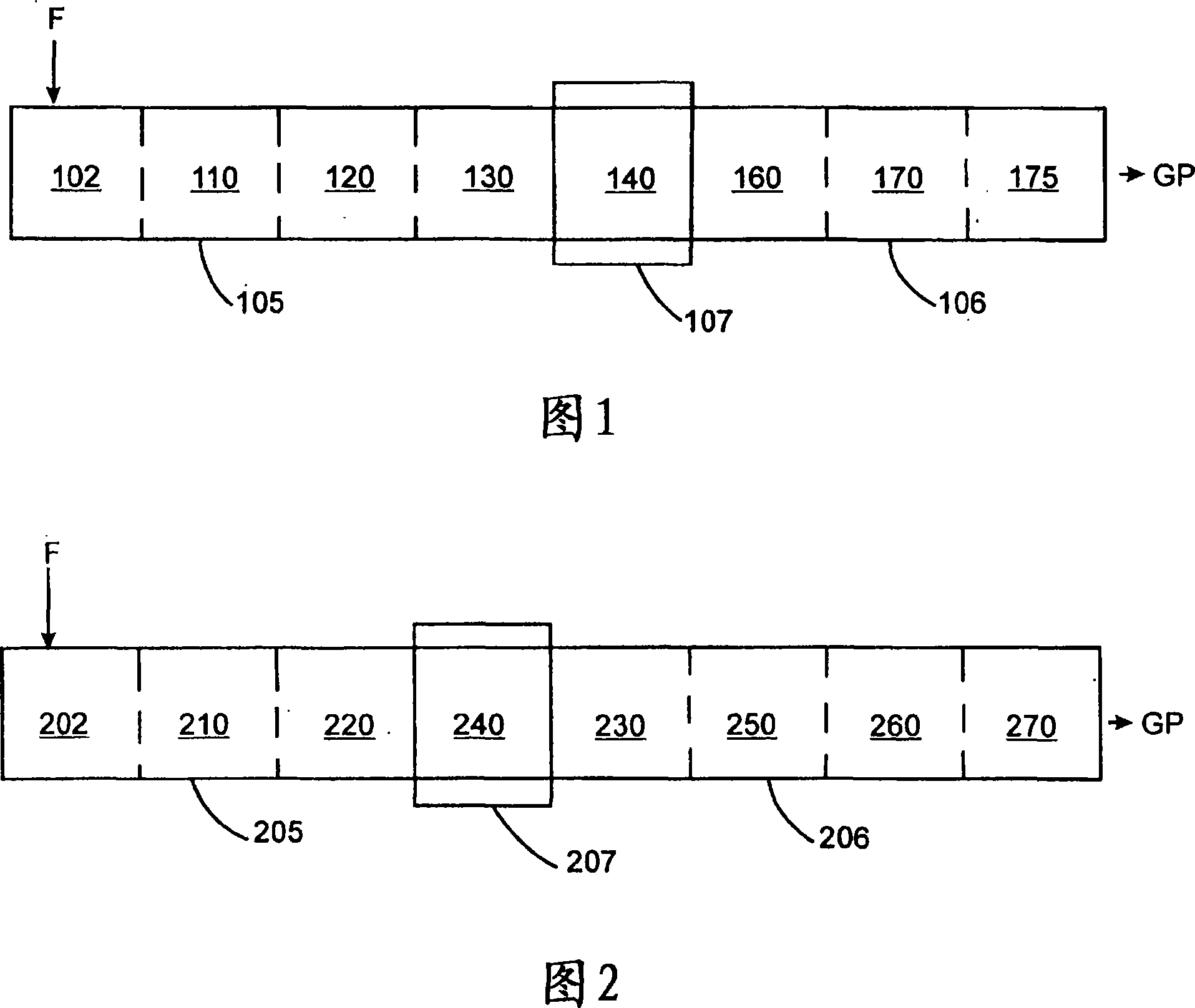
[0096] Example 2 shows that no grafting was measured when the polymer was first sheared to reduce its molecular weight and then functionalized. One explanation for thi...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Example 3: Invention
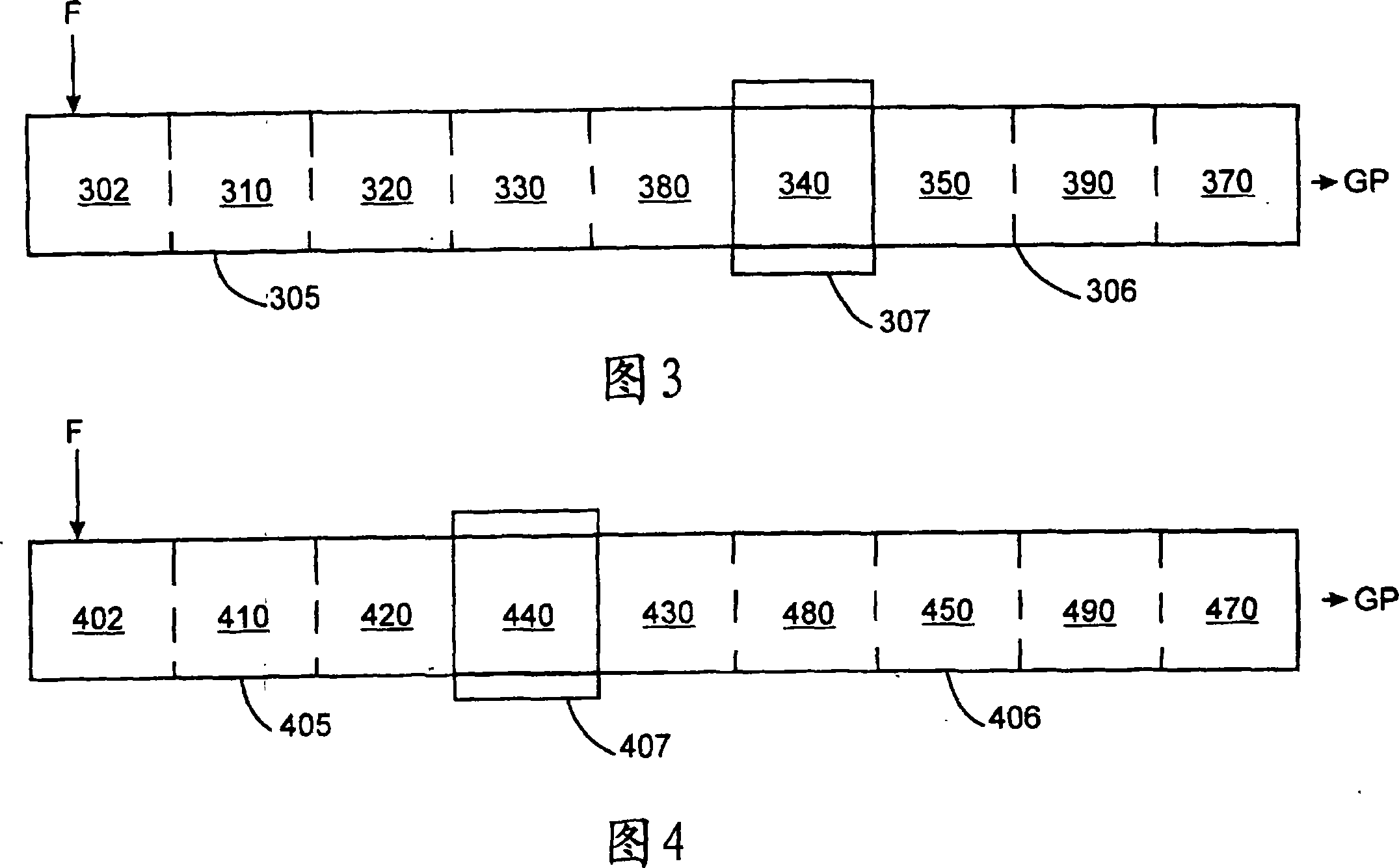
[0098] The method of the fourth embodiment (as shown in Figure 4) is operated. Table 6 shows the processing sections and corresponding operating conditions for each extruder.
[0099] Table 6: Processing section and operating conditions of Example 3
[0100] Extruder #1
[0101] The graft polymer produced with the above operating conditions has the following characteristics:
[0102] Table 7: Characteristics of the grafted polymer produced in Example 3
[0103] Bound maleic anhydride (wt%)
[0104] Example 3 shows that the method according to the fourth embodiment can be used to produce a commercially useful product. High throughput is produced by drying the polymer in the first extruder, connecting the first extruder with a flow diverter to a second extruder where the two reactants are used for injection The incorporation of maleic anhydride and sufficient extruder headroom in the second extruder to achieve a moderate re...
Embodiment 4
[0105] Example 4: Invention
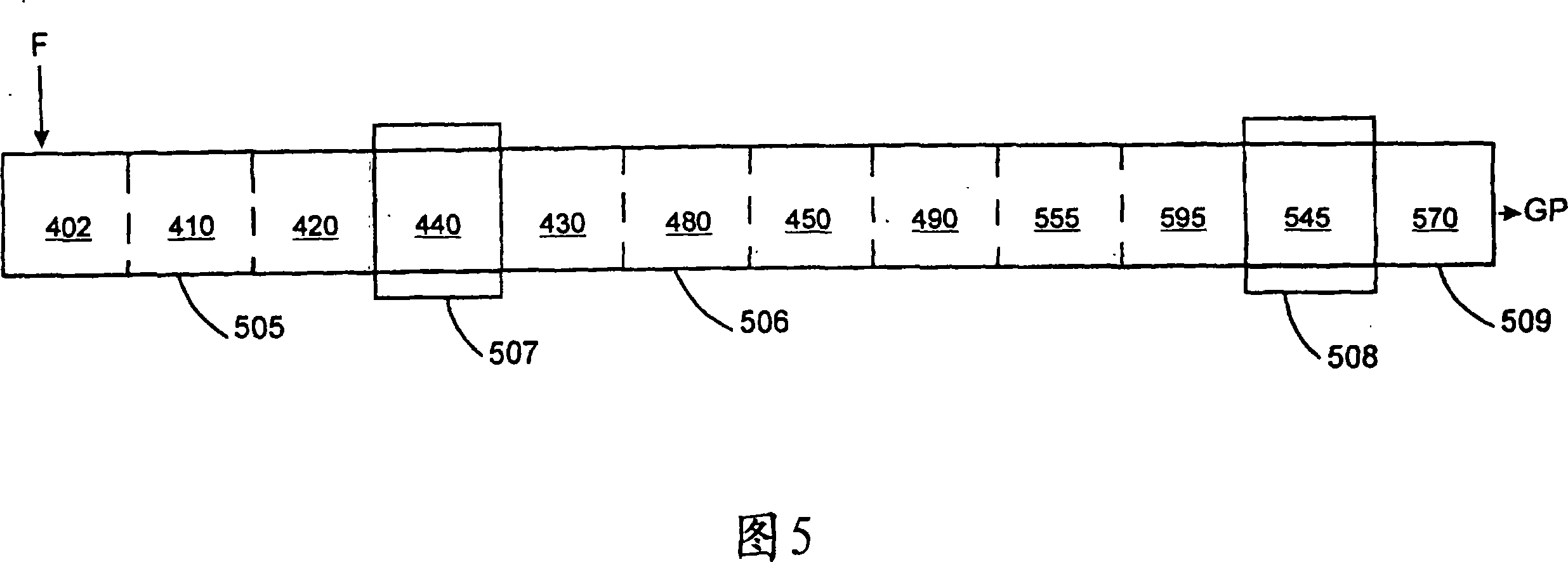
[0106] A method according to a third embodiment (shown in FIG. 3 ) is carried out. By performing the first injection in the first extruder and utilizing a transition section that provides additional reaction residence time, grafted polymers with high amounts of maleic anhydride can be produced with a higher overall efficiency of reactant utilization. Table 8 shows the processing sections and corresponding operating conditions for each extruder.
[0107] Table 8: Processing sections and operating conditions of Example 4
[0108] Extruder #1
[0109] The graft polymer produced with the above operating conditions has the following characteristics:
[0110] Table 9: Properties of the graft polymer produced in Example 4
[0111] Bound maleic anhydride (wt%)
[0112] Example 4 shows that by moving the first reactant injection to the first extruder and by using a transition section to provide additional reactor residence time, a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com