FeZrNdYB nano block alloy having hard magnetism and method for preparing same
A nano-block, hard magnetic technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of amorphous limitation, achieve good hard magnetism, overcome the effect of complex processing technology and simple technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
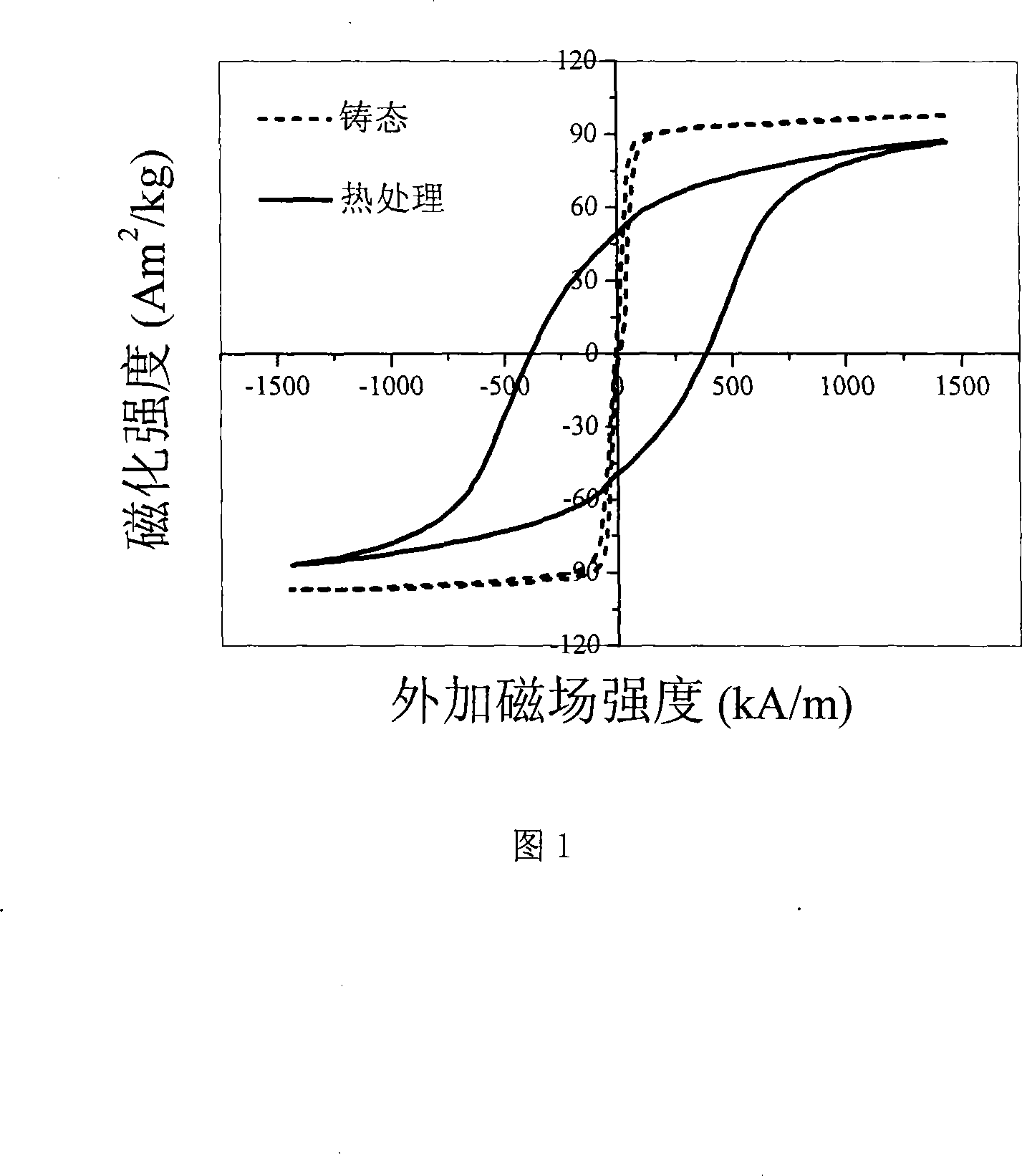
[0023] The composition (atomic percentage) of the hard magnetic FeZrNdYB nano-bulk alloy in this embodiment is: Fe 68%, Zr 2%, Nd 5%, Y 4%, B 21%. The preparation process and steps are as follows: prepare 20 grams of industrially pure metal raw materials Fe, Zr, Nd, Y and FeB alloy according to the FeZrNdYB nano-block alloy composition of this embodiment, and then use a vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace under argon protection Carry out smelting, the smelting current density is 150A / cm 2 , the alloy was smelted repeatedly for 4 times; the copper mold negative pressure suction casting method was used to cast, and a bulk amorphous alloy with a size of 1mm×10mm×80mm was obtained. Put the above bulk amorphous alloy at 690°C with a vacuum of 4×10 3 Under the condition of Pa, vacuum annealing is carried out, and the annealing time is 30 minutes, and finally the FeZrNdYB nanometer block alloy with excellent hard magnetic properties of the present invention is prepared.
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The composition (atomic percentage) of the hard magnetic FeZrNdYB nano-bulk alloy in this embodiment is: Fe 68%, Zr 2%, Nd 5%, Y 4%, B 21%. The preparation process and steps are as follows: prepare 20 grams of industrially pure metal raw materials Fe, Zr, Nd, Y and FeB alloy according to the FeZrNdYB nano-block alloy composition of this embodiment, and then use a vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace under argon protection Carry out smelting, the smelting current density is 150A / cm 2 , the alloy was smelted repeatedly for 4 times; the copper mold negative pressure suction casting method was used to cast, and a bulk amorphous alloy with a size of 1mm×10mm×80mm was obtained. The above bulk amorphous alloy was heated at 860°C with a vacuum of 4×10 -3 Under the condition of Pa, vacuum annealing is carried out, and the annealing time is 30 minutes, and finally the FeZrNdYB nanometer block alloy with excellent hard magnetic properties of the present invention is prepare...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com