Method for quantitative analysis of metal element contained in resin material
A resin material and metal element technology, applied in the field of quantitative analysis of metal elements, can solve the problems of Pb or Cd loss, lower analysis accuracy, and inaccurate measurement values, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] European polyethylene standard substances (BCR-680, BCR681) were prepared as samples, and the measured values thereof were guaranteed values.
[0052] A 0.2 gram sample was contained in a cylindrical container having a bottom composed of glassy carbon having a center line average roughness Ra of 1 micron on the inner surface. The centerline average roughness Ra was measured using "Talysurf 5" (trade name of a surface roughness meter manufactured by Taylor Hobson Inc.). Then, 5 ml of aqueous nitric acid solution having a concentration of 30% by weight and 5 ml of aqueous sulfuric acid solution having a concentration of 30% by weight were charged into the container, and then the container was placed on a hot plate, and the container was heated at 150° C. to decompose the sample (by Standard substance made of polyethylene). In addition, a container made of glassy carbon was fixed inside a muffle furnace, and the sample was carbonized at 450 °C to remove sulfuric acid, n...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Three cylindrical containers each having a bottom and made of glassy carbon were prepared. The centerline average roughness (Ra) of the glassy carbon on the inner surface of these containers was different from each other. Specifically, the centerline average roughness (Ra) of the glassy carbon on the inner surface measured by a surface roughness meter "Talysurf5" manufactured by Taylor Hobson Inc. was 1,000 micrometers, 100 micrometers or 10 micrometers. The container has an inner diameter of 70 mm and a height of 80 mm. Then, 10 ml of an aqueous sulfuric acid solution having a concentration of 30% by weight was charged into each of these containers. In addition, these containers were each placed in a muffle furnace and gradually heated to 400°C, 450°C, 500°C, 550°C, and then to 600°C, thereby measuring the inner surface of the container at each heating temperature using the above-mentioned surface roughness meter The average surface roughness Ra on the median line. ...
Embodiment 3 and comparative example 3
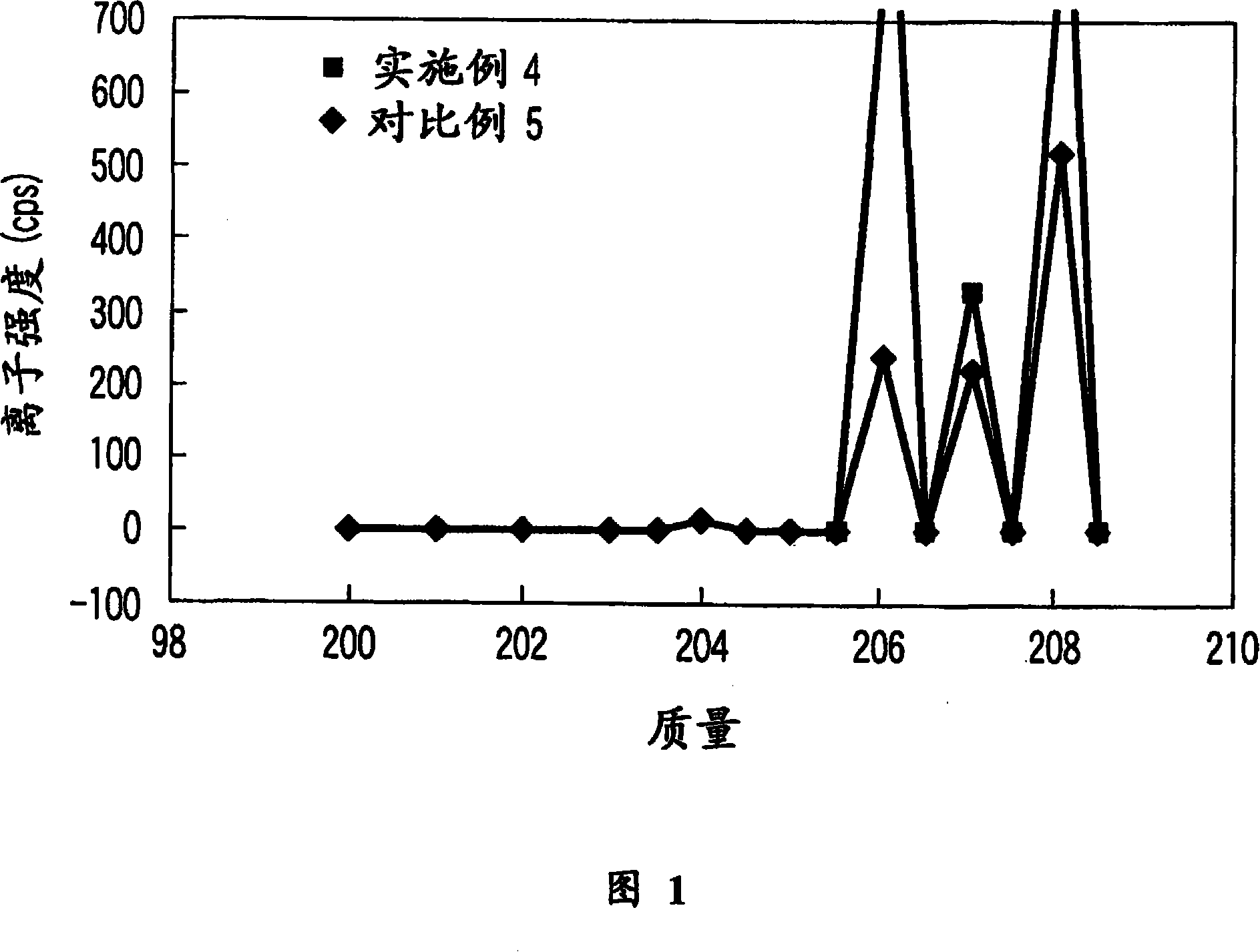
[0069] Using the same standard sample (BCR-680) as used in Example 1, a sample solution was prepared by a method similar to Example 1 and Comparative Example 2, and the isotope of lead was quantitatively analyzed. Figure 1 shows the results.
[0070] As is clear from FIG. 1 , in Comparative Example 3 using a platinum crucible, the detection of 206Pb and 208Pd was greatly hindered by platinum compared to Example 3 using a container made of glassy carbon.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com