Method for autonomous dynamic voltage and frequency scaling of microprocessors and computer system
A technology of computer systems and microprocessors, applied in the field of adaptive dynamic management, to achieve the effect of improving the performance of the overall computer system, improving the overall performance, frequency and voltage saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
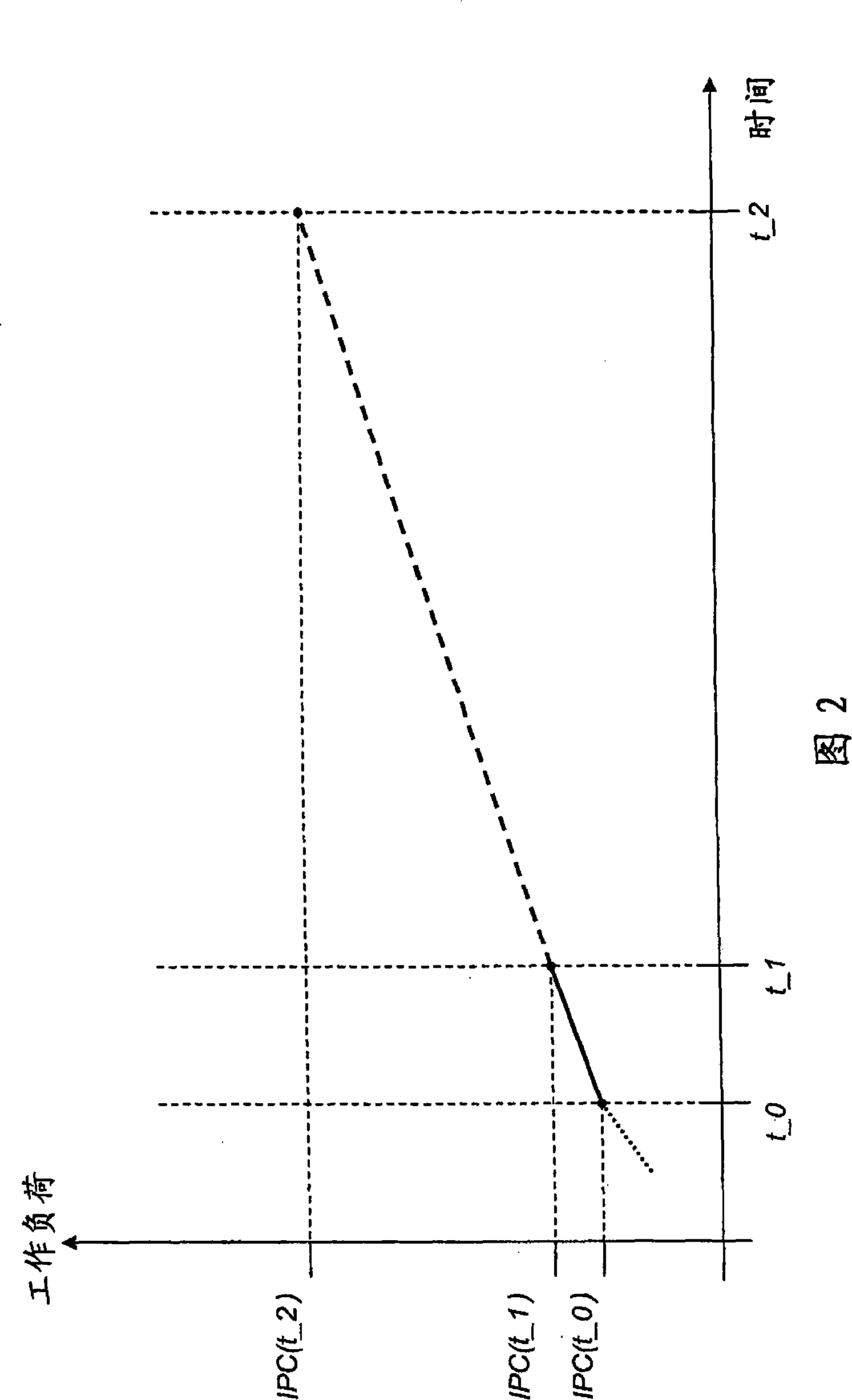
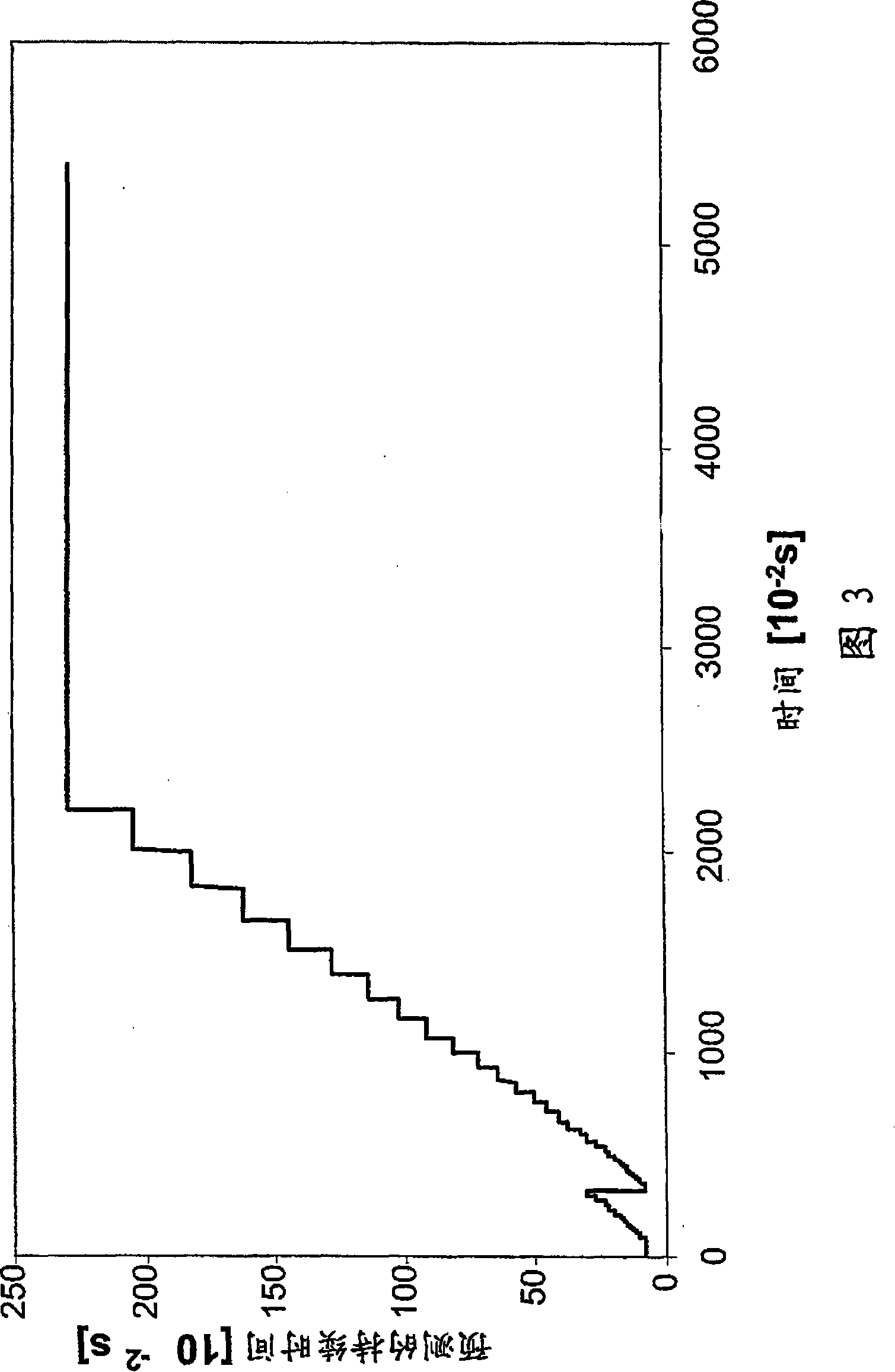
[0040] turbo mode
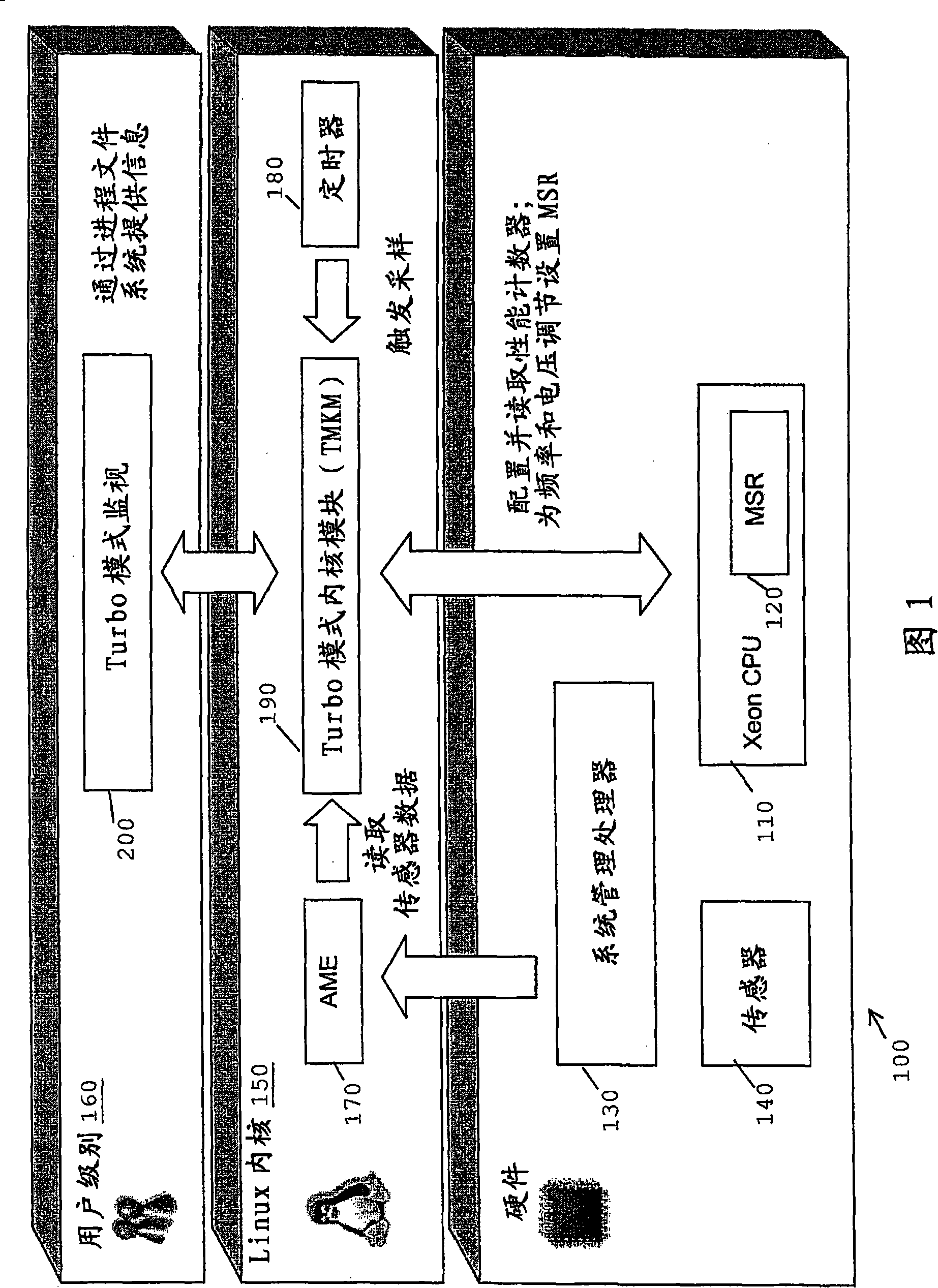
[0041] FIG. 1 shows the system architecture of an embodiment of the present invention in a computer system 100 . Said embodiment is called Turbo mode. In the computer system 100 , a Xeon microprocessor is used as a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 110 . A Xeon microprocessor can control its operation through the use of a set of MSRs (Model Specific Registers) 120 . The system management processor 130 controls the operation of the computer system 100 . It uses a set of hardware sensors 140 to monitor the hardware elements of the computer system 100 including the CPU 110 . The computer system 100 executes an instance of the Linux operating system, while an instance of the Linux kernel 150 and various processes run at the user level 160 of the Linux operating system.
[0042]The Linux kernel 150 includes various kernel modules that can, inter alia, create kernel threads that run in parallel. The present invention uses the AME (Autonomous Energy Management) 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com