A device and method for low-density checksum LDPC parallel coding
A low-density check code and LDPC code technology, which is applied in the field of low-density check code LDPC parallel encoding devices, can solve problems such as constraints on the implementation of LDPC code encoding, no implementation plan, and difficulty in applying high-speed data transmission systems, etc., to achieve Improve coding efficiency, avoid multiplication operations, and enhance scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
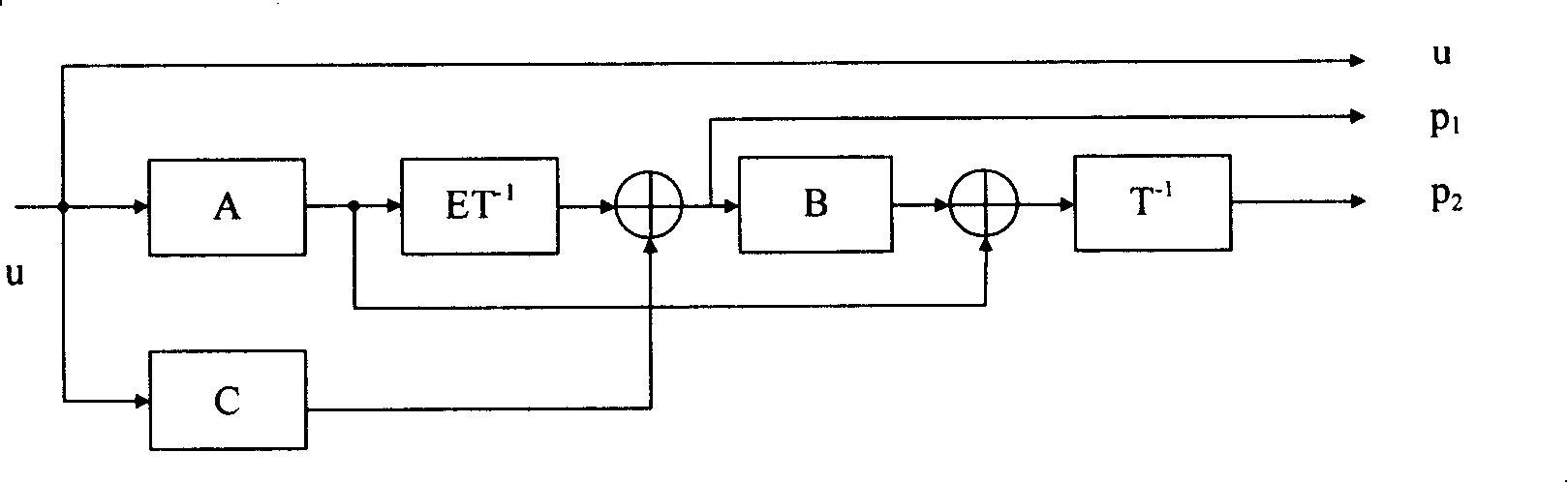
[0148] The following takes the 1 / 2 code rate LDPC code in IEEE P802.16e as an example to illustrate the specific implementation process of the encoding. Table 1 shows the base matrix H corresponding to the parity check matrix of the LDPC code bm , where n b =24, m b =12, z=96, code length n=2304, 1~12 columns of the matrix correspond to information bits, 13~24 columns correspond to parity bits, -1 corresponds to z×z zero matrix, and others correspond to z×z unit matrix to the right number of cycles.
[0149] Table 1 The base matrix of the 1 / 2 code rate LDPC parity check matrix
[0150] 1
2
3
4
-5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
1
-1
94
7
3
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
55
83
-...
Embodiment 1
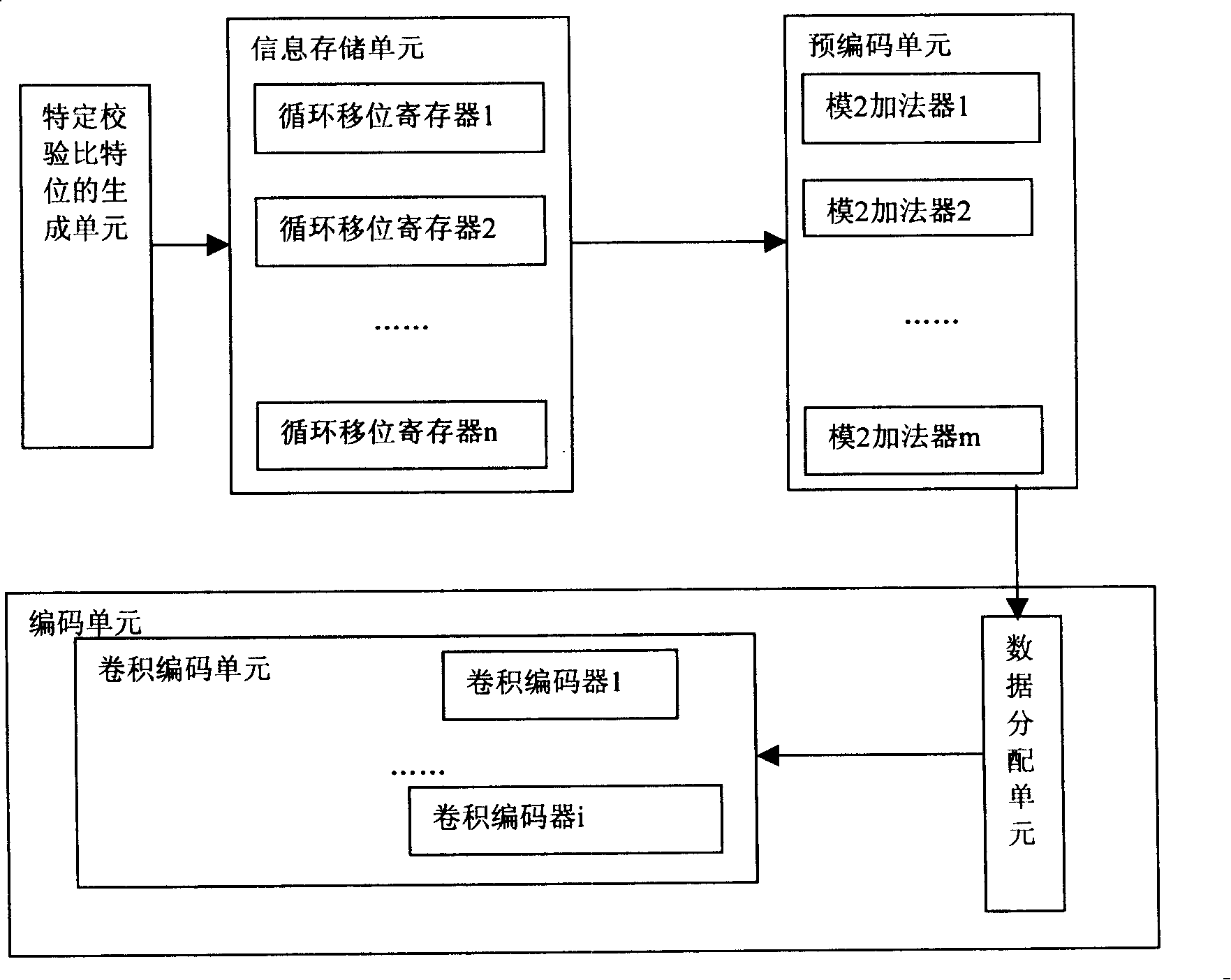
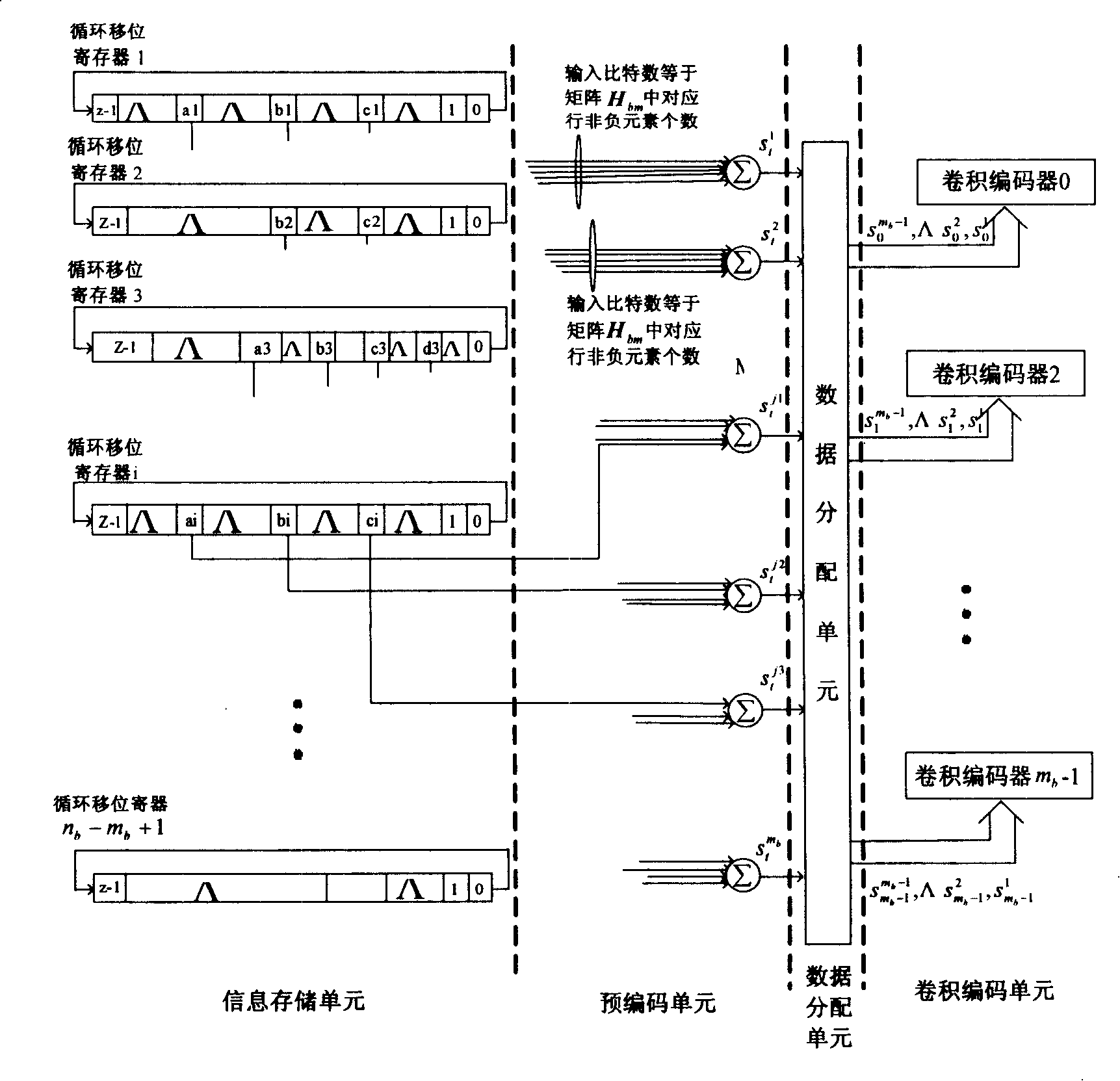
[0154] Embodiment 1: According to the technical solution, for the first precoder design process, H bm Remove the last line, and then remove the following m b -1 column, that is, remove the twelfth row in Table 1 and then remove the following 11 columns to form H″ b1 is 11×13, namely H′ given in formula (11b) bm1 Remove the last line, H bm Remove the last 11 columns to form H″ b2 is 11×11, which is H′ given in formula (11b) bm2 Remove the last line, corresponding to the encoder such as Figure 9 As shown, there are four main devices including information storage unit, precoding unit, data allocation unit and convolutional coding unit, where the information storage unit contains 13 cyclic shift registers, and the precoding unit contains m b -1=11 modulo 2 adders, the convolutional coding unit contains m b -1 = 11 recursive convolutional encoders. For the design process of the second precoder, H bm Delete the first line in Table 1, and then delete the following m b -1 co...
Embodiment 2
[0175] Embodiment 2: For the second precoder design process, after the base matrix of the parity check matrix removes the first row in Table 1, then removes the following 11 columns to form H "' b1 is 11×13, that is, remove the first 13 columns of the base matrix of the LDPC code parity check matrix shown in Table 1 in the first row of Table 1 to form the sub-matrix H given in formula (11b) bm1 Remove the first row, and the remaining 11 columns constitute the sub-matrix H given in formula (11b) bm2 Remove the first line, corresponding to the encoder such as Figure 9 As shown, there are four main devices including information storage unit, precoding unit, data allocation unit and convolutional coding unit, where the information storage unit contains 13 cyclic shift registers, and the precoding unit contains m b -1=11 modulo 2 adders, the convolutional coding unit contains m b -1 = 11 recursive convolutional encoders. For the design process of the second precoder, the base m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com