Low noise divider
A technology of clock frequency divider and frequency division clock, which is applied in the direction of automatic power control, pulse technology, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as increasing power supply, phase noise, and edge positioning uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
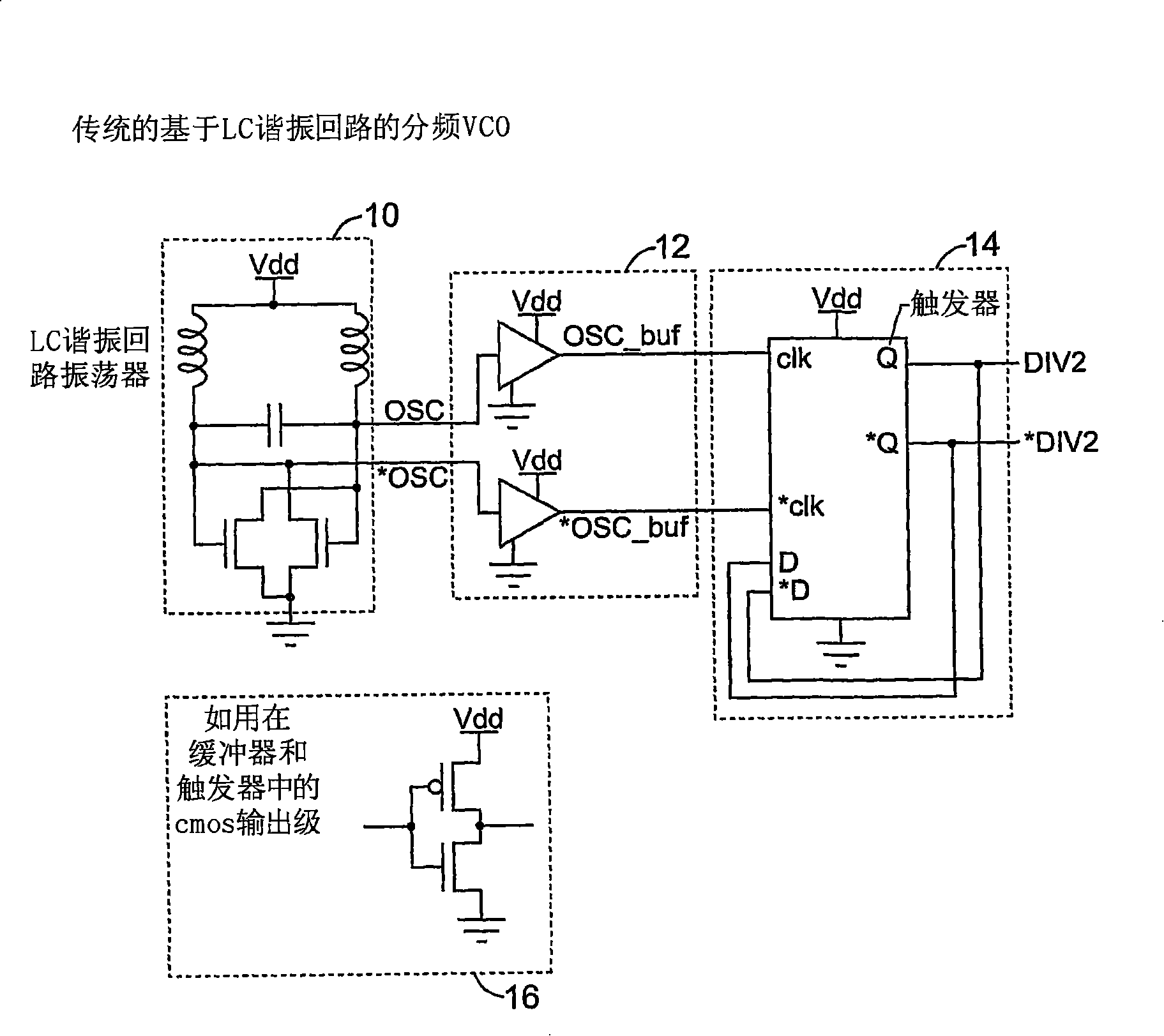
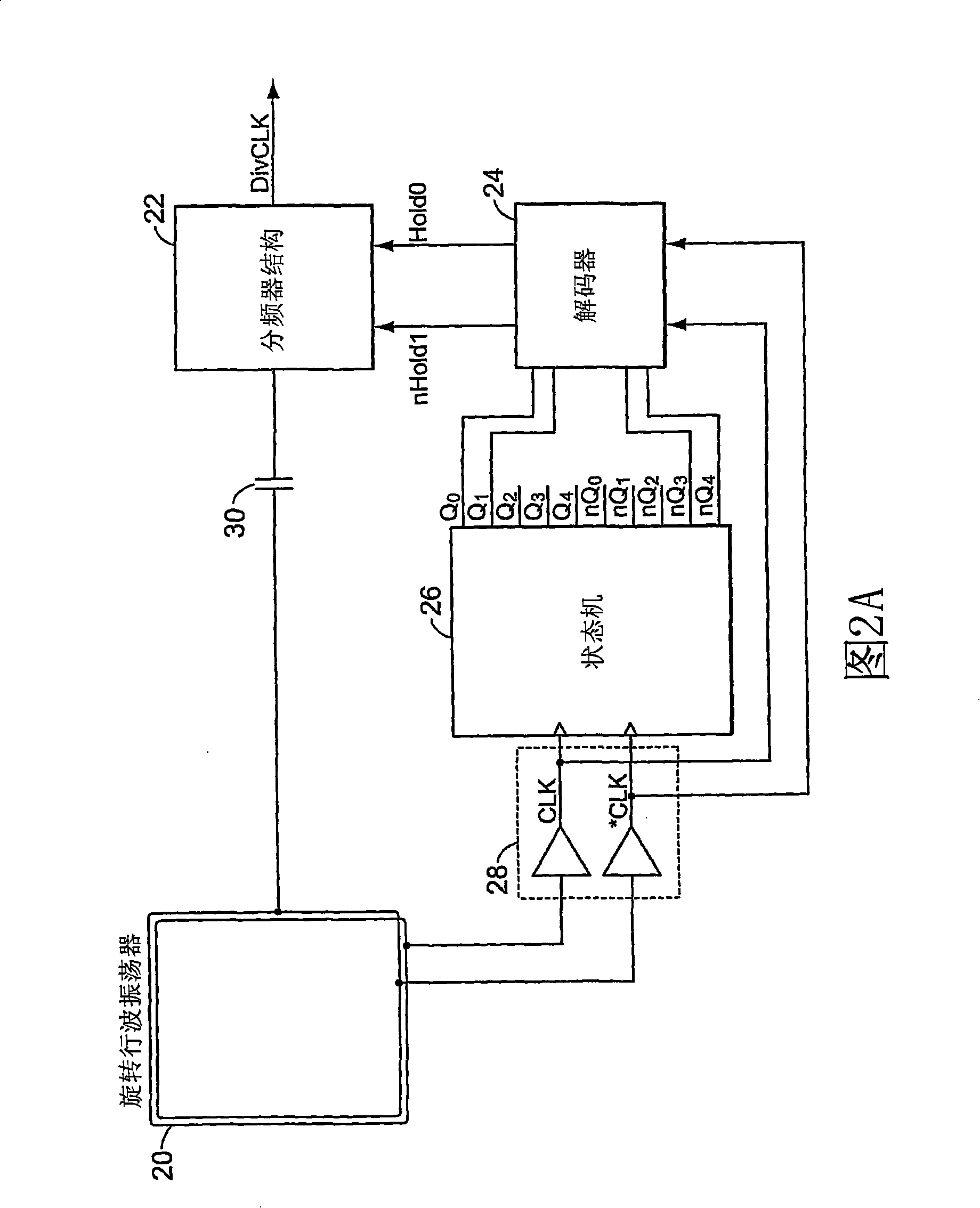
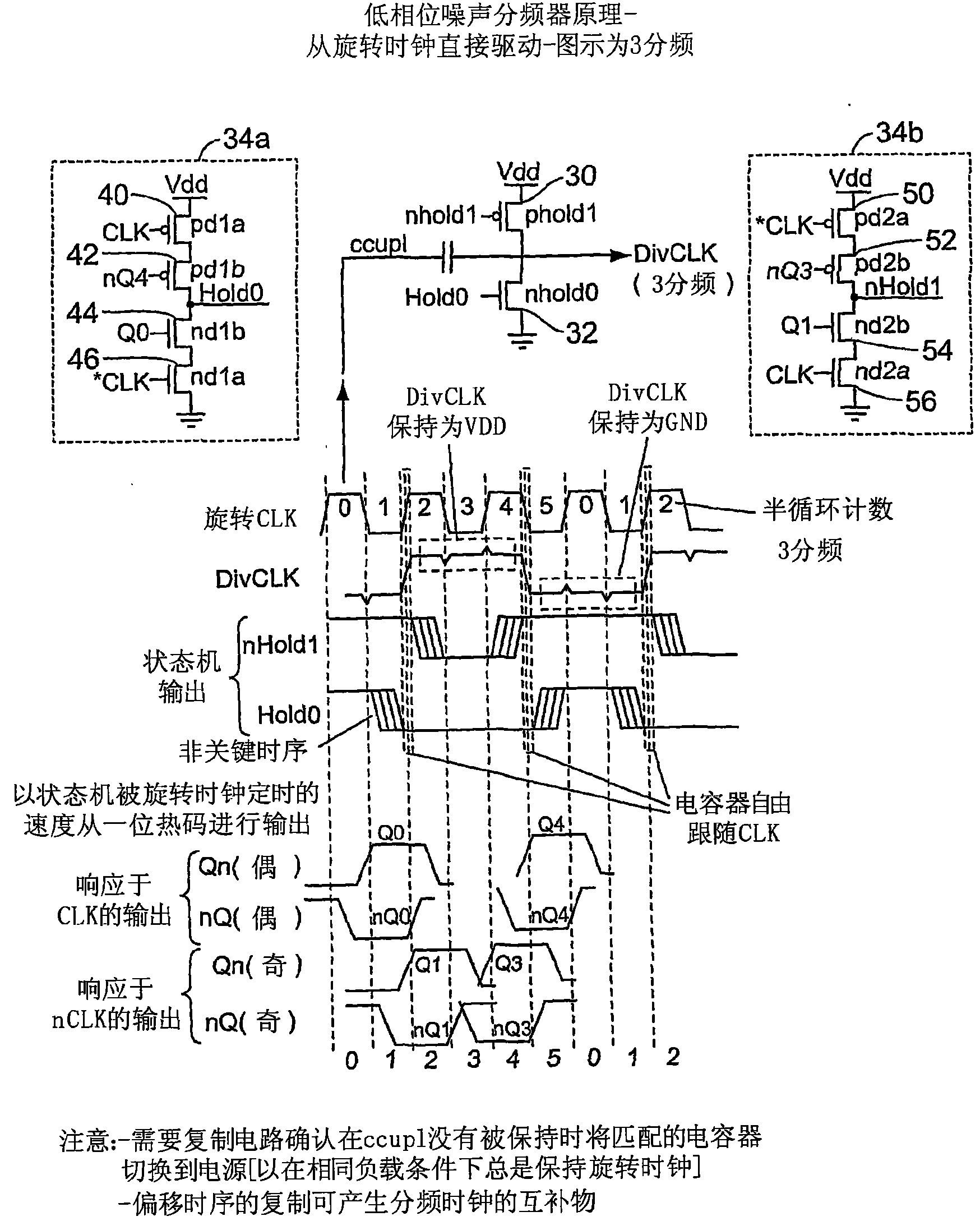
[0025] Figure 2A shows a block diagram of one embodiment of a low noise clock divider. The block diagram includes a multiphase oscillator 20 (such as the rotating traveling wave oscillator of U.S. Patent No. 6,556,089 (incorporated by reference)), a frequency divider structure 22, a decoder 24, a state machine 26, and a clock buffer 28. One branch of the multiphase oscillator is directly connected to the frequency divider structure 22 via capacitor 30, the output of which is DIVCLK. Divider structure 22 receives a pair of signals nHold1 and Hold0 from decoder 24 , which determine when the DIVCLK output is allowed to follow multiphase oscillator 20 . Decoder 24 receives signals from state machine 26 clocked by multiphase oscillator 20 , and receives a clock from multiphase oscillator 20 via clock buffer 28 . State machine 26 is driven by the same pair of clocks as decoder 24 . In one version, the state machine is a "one-hot" state machine, ie, it advances a single "1" (or "0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com