Signture dynamic discrimination method
A dynamic and trajectory technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, input/output of user/computer interaction, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult linear velocity identification, great difference in stroke strength, and difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
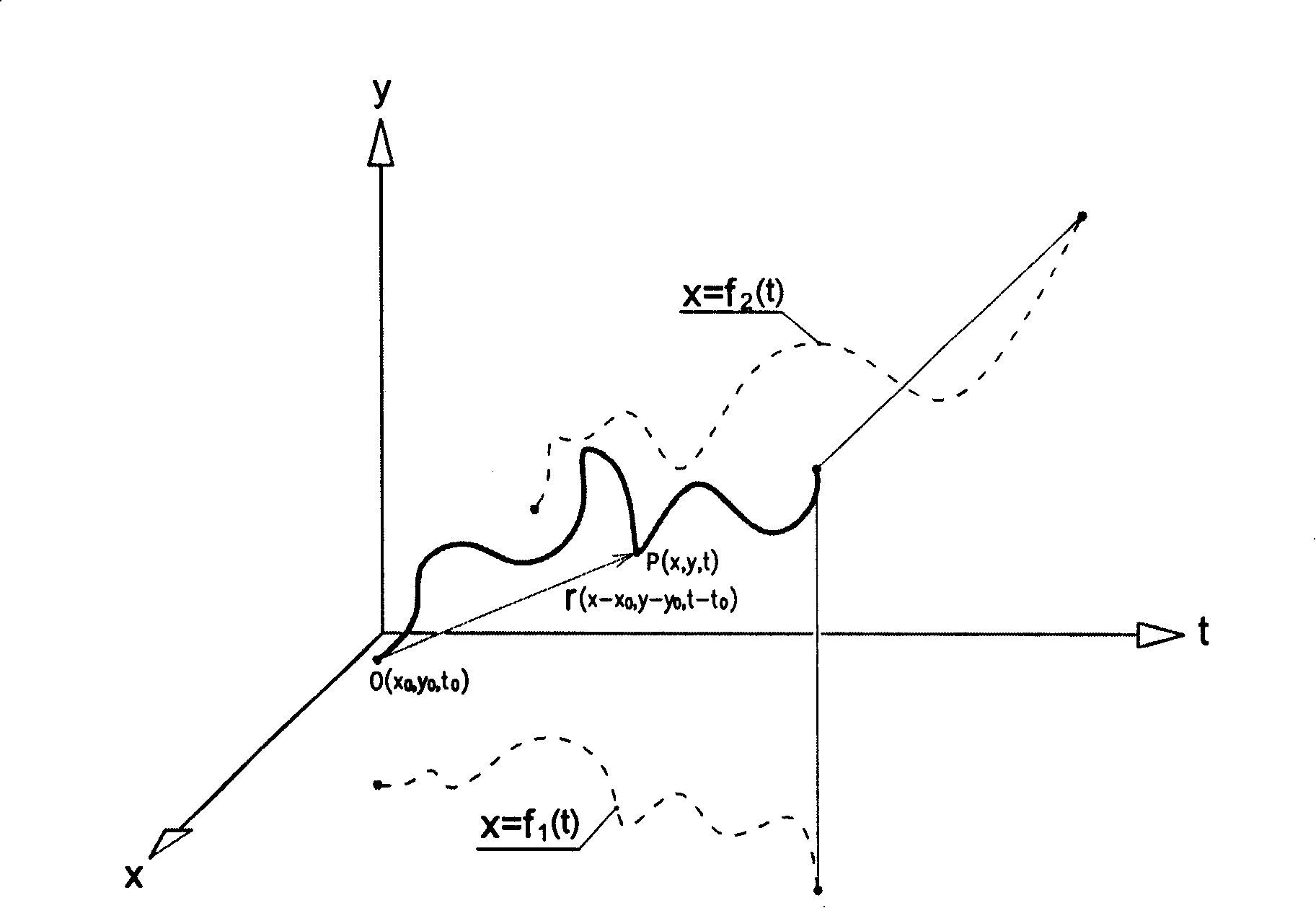
[0032] A scheme for dynamic authentication of signatures, figure 1 Shown is the signature trajectory in the space-time coordinate system x-y-t, the signature trajectory can be expressed as a function of the y-direction position and x-direction position of a pen-down point changing with time t respectively. x=f 1 (t) and y = f 2 (t), and the relationship y=f(x, t) between y and x can be established. The space-time coordinate value of a point P on the signature trajectory is P(x, y, t), and the space-time coordinate value of the initial pen-down point 0 is 0(x 0 ,y 0 , t 0 ). With the initial pen-down point 0 as the starting point and the point P in the signing process as the end point, a set of space-time position vectors r(x-x 0 ,y-y 0 ,t-t 0 ) to describe the spatio-temporal location characteristics of each point on the signature trajectory. The space-time position vector r(x-x 0 ,y-y 0 ,t-t 0 ) group is compared with the space-time position vector group of each co...
specific Embodiment approach 2
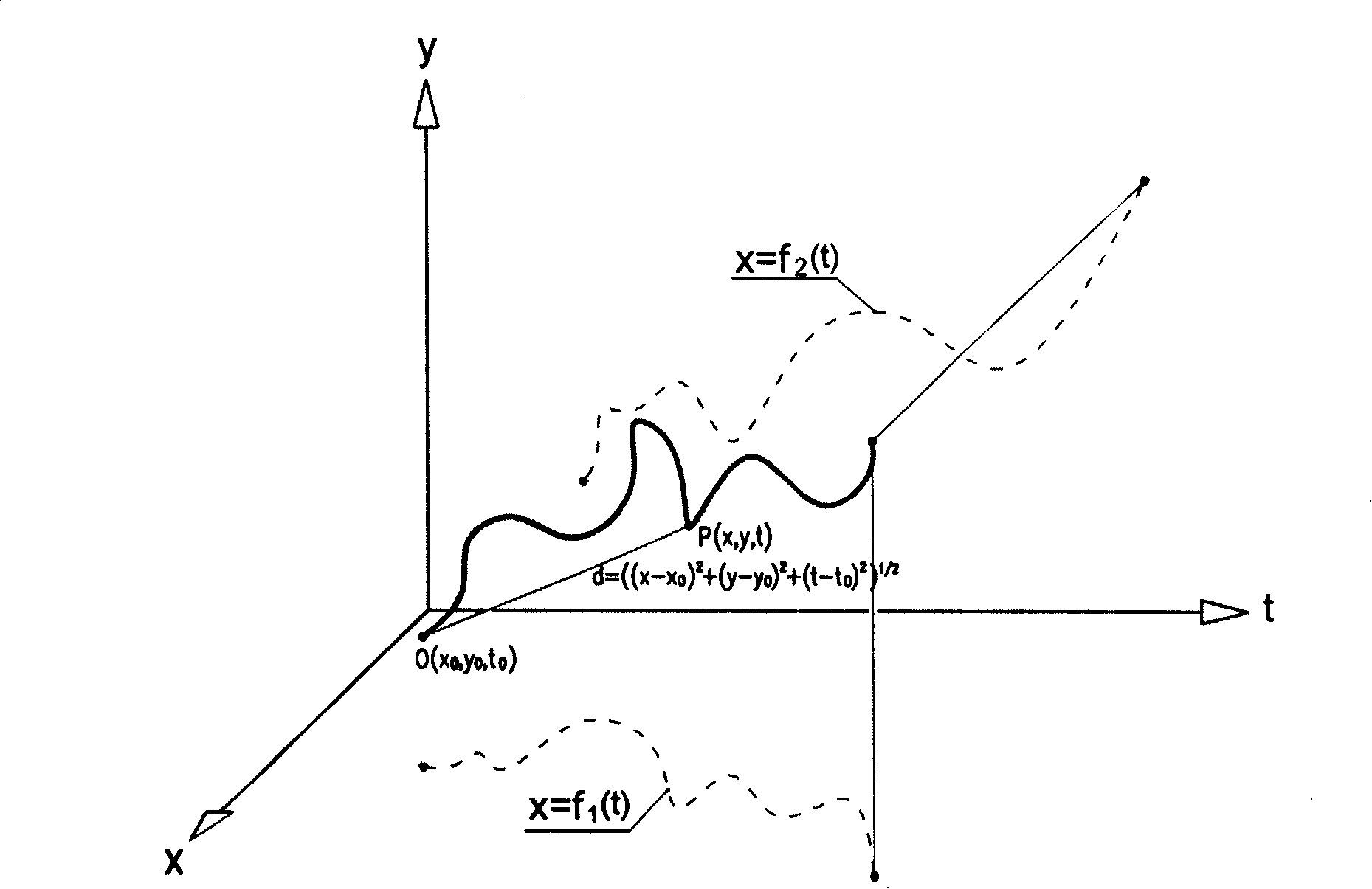
[0034] A scheme for dynamic authentication of signatures, figure 2 Shown is the signature trajectory in the space-time coordinate system x-y-t, the signature trajectory can be expressed as a function of the y-direction position and x-direction position of a pen-down point changing with time t respectively. x=f 1 (t) and y = f 2 (t), and the relationship y=f(x, t) can be established. The space-time coordinate value of a point P on the signature trajectory is P(x, y, t), and the space-time coordinate value of the initial pen-down point 0 is 0(x 0 ,y 0 , t 0 ). Taking the initial pen-down point 0 as one end point and point P in the signing process as the other end point, the space-time distance d=((x-x 0 ) 2 +(y-y 0 ) 2 +(t-t 0 ) 2 ) 1 / 2 , to describe the spatio-temporal location characteristics of each point on the signature trajectory. The space-time distance d=((x-x 0 ) 2 +(y-y 0 ) 2 +(t-t 0 ) 2 ) 1 / 2 The group is compared with the time-space distance group...
specific Embodiment approach 3
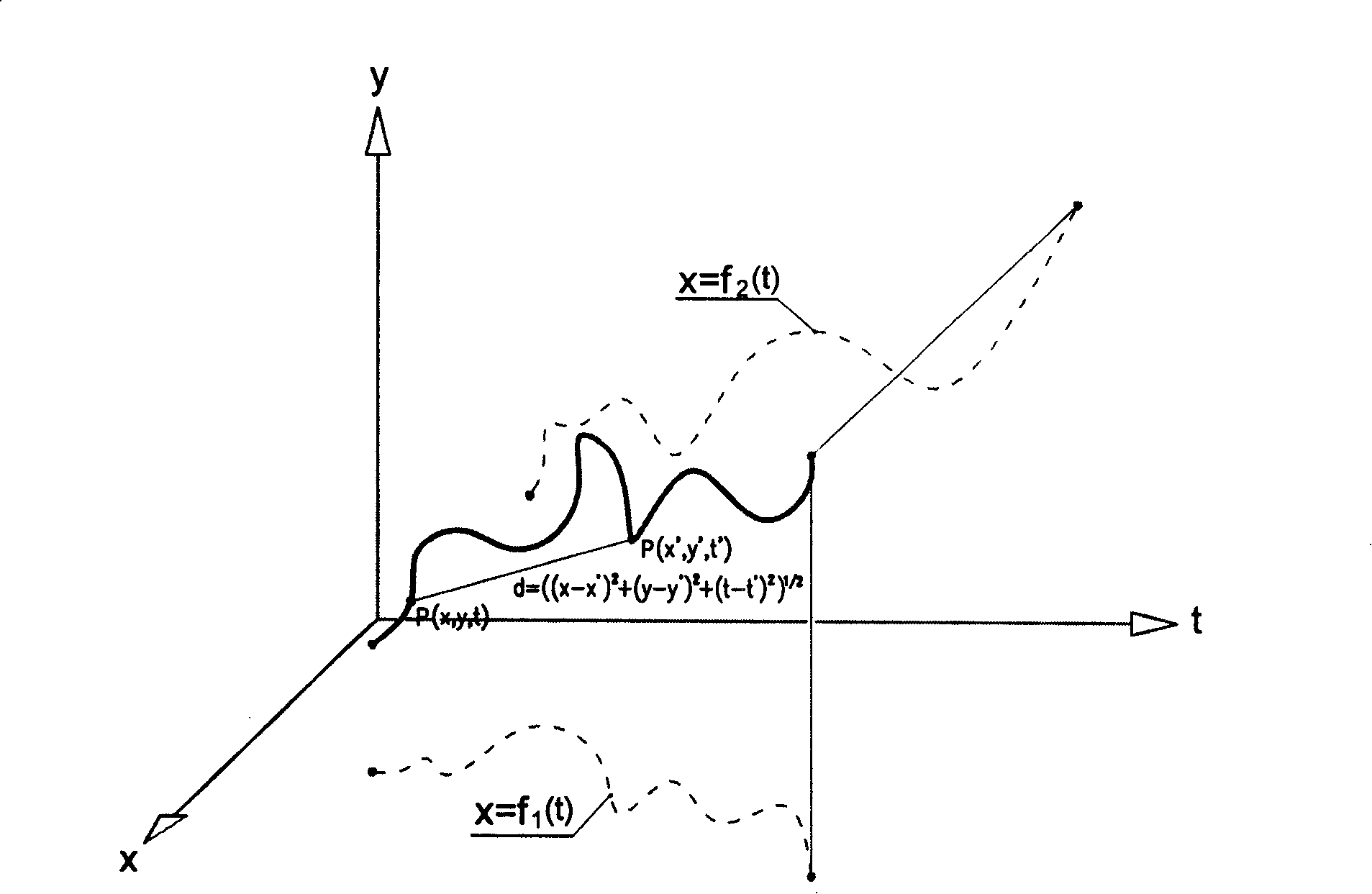
[0036] A scheme for dynamic authentication of signatures, figure 2 Shown is the signature trajectory in the space-time coordinate system x-y-t, the signature trajectory can be expressed as a function of the y-direction position and x-direction position of a pen-down point changing with time t respectively. x=f 1 (t) and y = f 2 (t), and the relation y=f(x, t) can be established. The space-time coordinate value of a point P on the signature trajectory is P(x, y, t), and the space-time coordinate value of the initial pen-down point 0 is 0(x 0 ,y 0 , t 0 ). Taking the initial pen-down point 0 as one end point and point P in the signing process as the other end point, the space-time distance d=((x-x 0 ) 2 +(y-y 0 ) 2 +(t-t 0 ) 2 ) 1 / 2 To describe the spatio-temporal location characteristics of each point on the signature trajectory. In the space-time coordinate system x-y-t, the partial derivative of signature trajectory function y to x ∂ y ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com