Time sharing operation dynamic dispatching method and device
A technology of dynamic scheduling and time-sharing operation, applied in the field of telecommunications, it can solve the problems of inability to adjust the order of task execution, execution efficiency and low resource utilization, so as to improve experience and satisfaction, reduce waiting time, and improve work efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
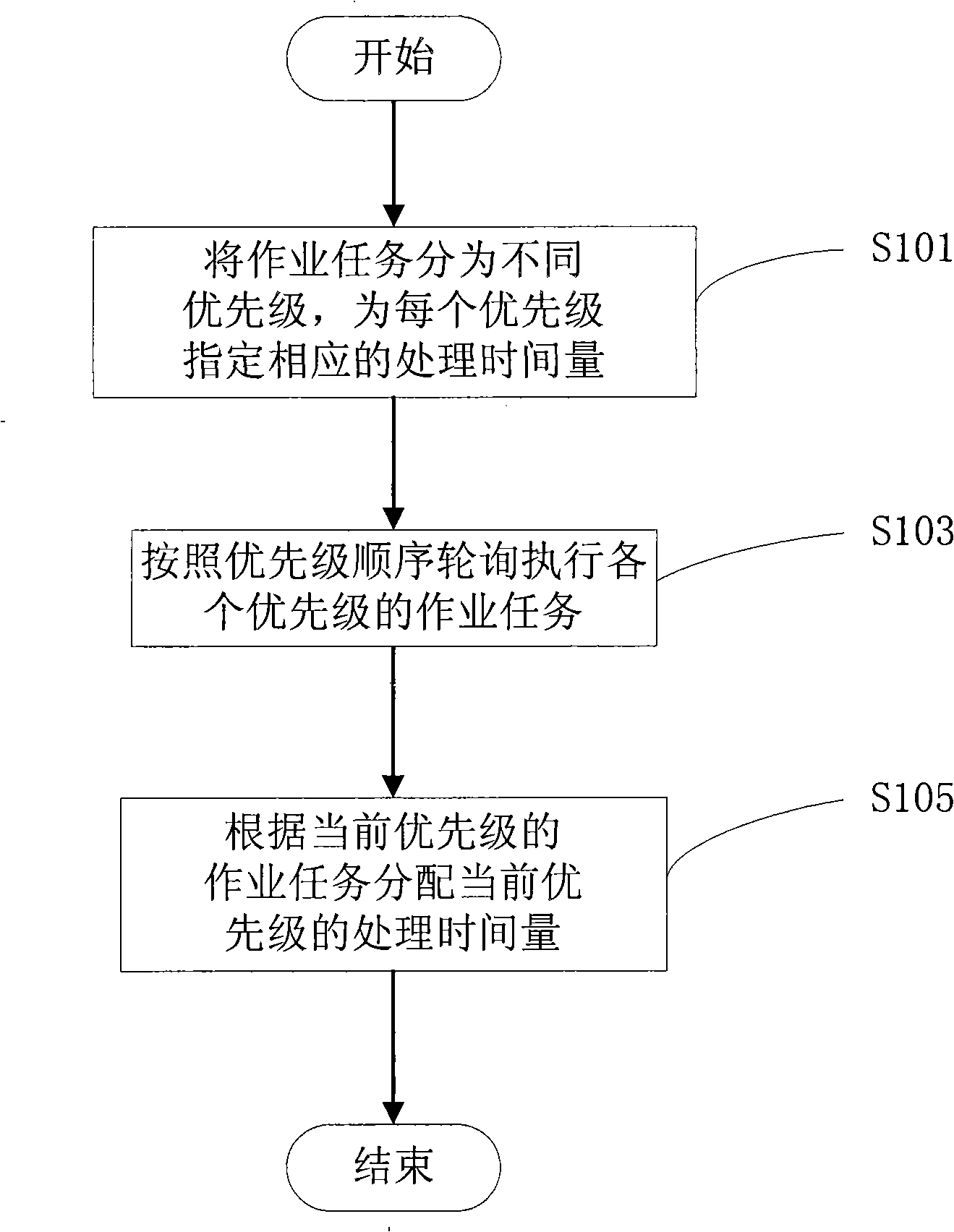
[0035] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the time-sharing job dynamic scheduling method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and Embodiment 1 of the present invention specifically includes:
[0036] Step S101, dividing the job tasks into different priority levels, and specifying a corresponding amount of processing time for each priority level;
[0037] Step S103, polling and executing job tasks of each priority level according to the order of priority;
[0038] Step S105, allocating the processing time of the current priority according to the job task of the current priority.
[0039] Wherein, the amount of processing time mentioned in the specific implementation manner of the present invention is specifically the amount of record processing in the memory buffer.
[0040] First, judge the current priority memory buffer record, if the current priority L has a memory buffer record, then read C (when the priority remaining memory record M>=C) or M (when M< During C) the recor...
Embodiment 3
[0051] image 3 It is a flow chart of the time-sharing job dynamic scheduling method in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and Embodiment 3 of the present invention specifically includes:
[0052] Step S301, classify job tasks into different priorities, and set corresponding memory buffers for the priorities. When processing memory buffer records, start processing from priority 1, and execute job tasks in order of different priorities, assuming that the previous processing priority is L 0 (initial runtime L 0 =0), then the current processing priority L=L 0 +1 (when L is greater than the last priority L M , L=1, that is, restart from the first priority);
[0053] Step S303, get the memory buffer record of the current priority L, if there is no record in the memory buffer, go to step S305 for processing, otherwise get C or M records from the memory buffer for processing, and turn to step S301 for polling processing after the obtained records are completed next priority;...
Embodiment 4
[0061] Figure 4 It is a flowchart of a time-sharing job dynamic scheduling method in Embodiment 4 of the present invention, and Embodiment 4 of the present invention specifically includes:
[0062] Step S401, classify job tasks into different priorities, and set corresponding memory buffers for the priorities. When processing memory buffer records, start processing from priority 1, and execute job tasks in order of different priorities, assuming that the previous processing priority is L 0 , then the current processing priority L=L 0 +1;
[0063] Step S403, read the memory buffer record of the current priority L, if there is no record in the memory buffer, go to step S405 for processing, otherwise obtain C or M records from the memory buffer for processing, and turn to step S401 for polling when the obtained records are completed Handle the next priority;
[0064] Step S405, read the number of buffered records N and the time T1 of the last access to the database read by t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com