Resistive memory device and stack structure of resistive random access memory device
A resistive memory, resistive random technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, magnetic field controlled resistors, etc., can solve problems such as difficult sensing, and achieve the effect of improving resistivity and increasing coherence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
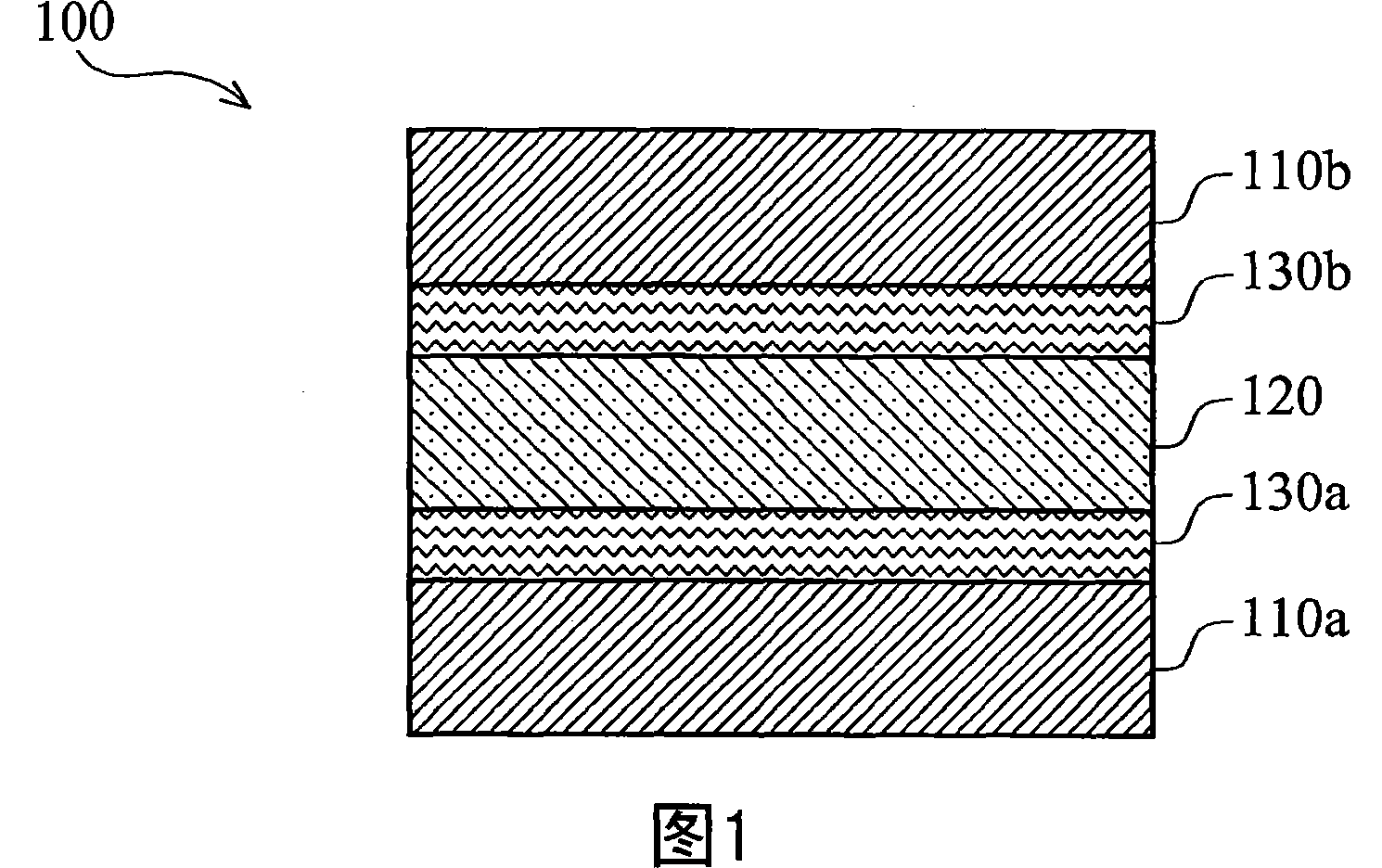
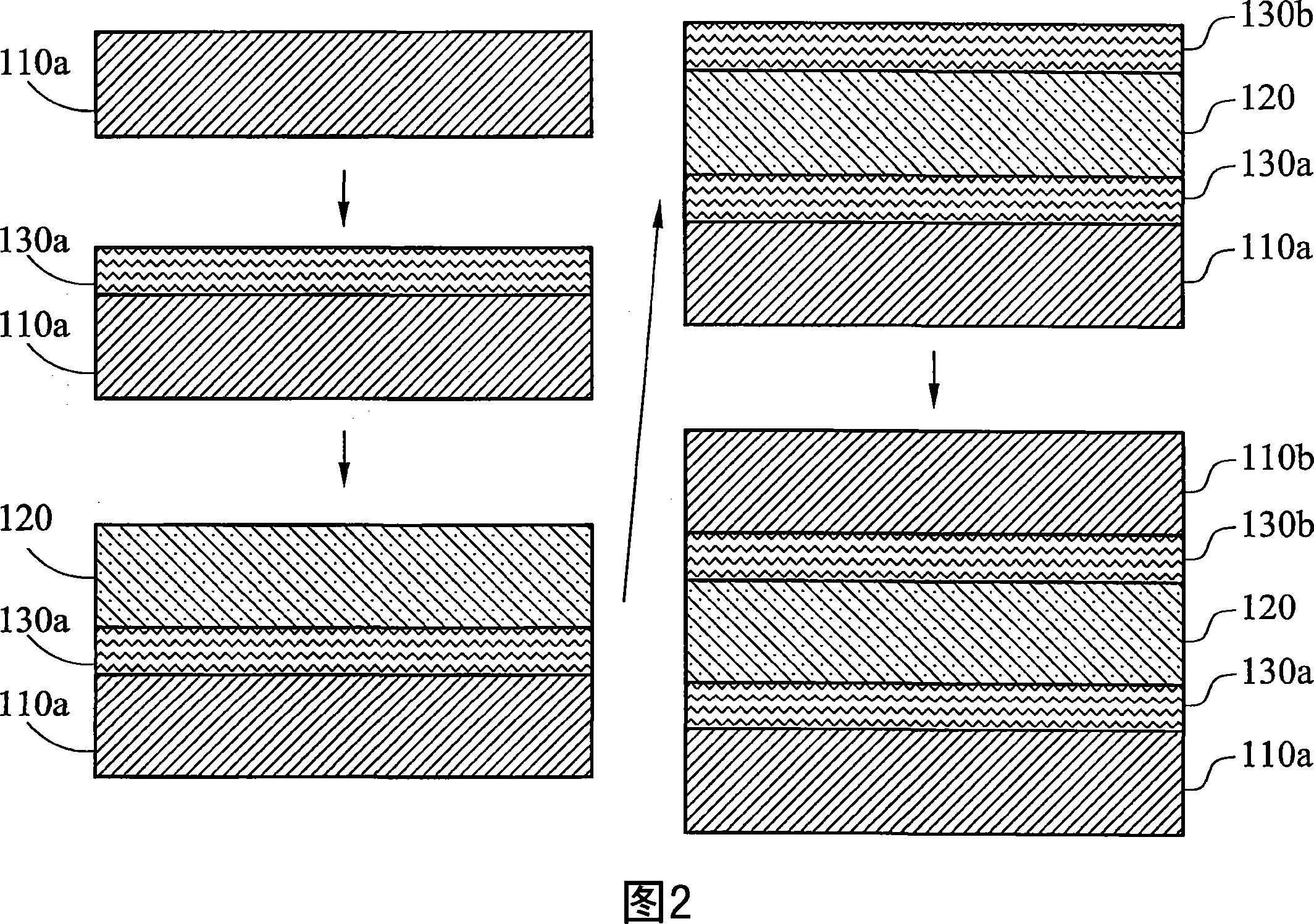
[0040] Please refer to the embodiment shown in FIG. 1, which shows the RRAM stacked layer 100 used in a resistive random access memory (RRAM) monolithic structure, and its method of processing according to the principles disclosed herein. As previously understood, the RRAM stack 100 includes bottom and top electrode layers 110a, 110b. In an exemplary embodiment, the bottom and top electrode layers 110a, 110b may be composed of conductive materials. For example, the bottom and top electrode layers 110a, 110b can be composed of platinum (Pt) or any useful conductive material.
[0041] The RRAM stack 100 also includes an intermediate dielectric layer 120 between the bottom and top electrode layers 110a, 110b. In the representative embodiment, the intermediate dielectric layer 120 is composed of a Colossal Magnetoresistive (CMR) material. In a specific embodiment, the dielectric layer 120 is made of a dielectric material Pr 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (PCMO). Of course, any dielectric material...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com