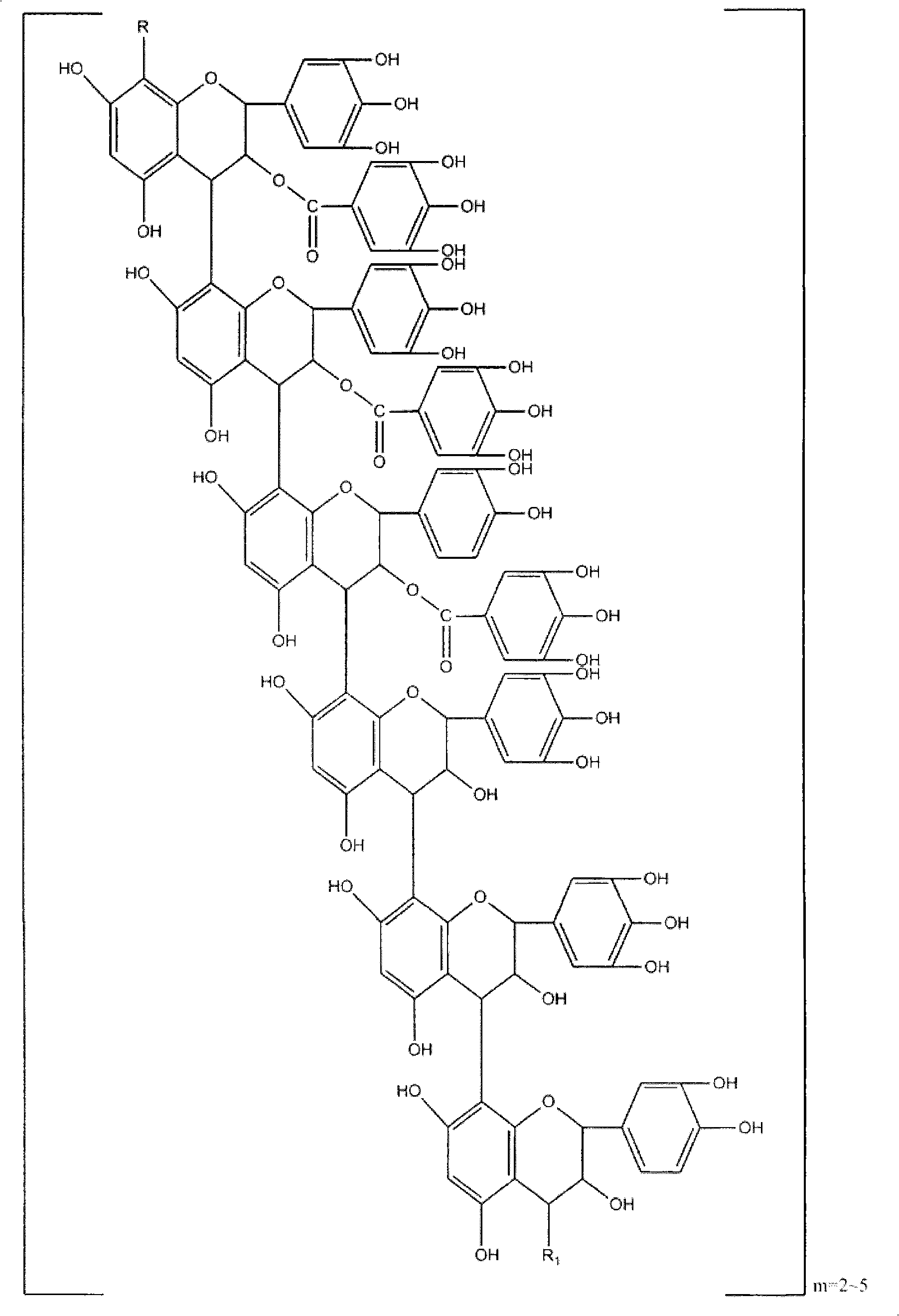
Preparation of low free monomer, degradable persimmon tannin modified phenolic resin
A phenolic resin, low free technology, applied in the field of preparation of modified phenolic resin to reduce pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
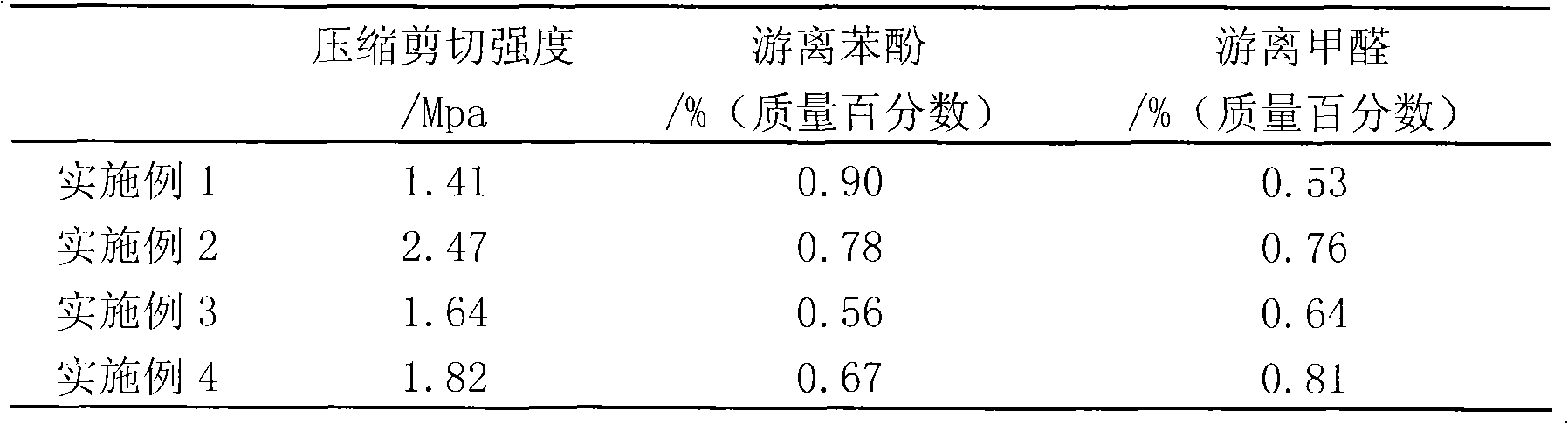
[0021] Take 28.5g of phenol and 8g of persimmon tannin solution (mass concentration of tannin≥3wt%), add them into a reaction vessel equipped with a reflux condenser and an electric stirrer, stir evenly and add 0.85g of oxalic acid. The temperature was raised to 90° C., and 15.5 g of formaldehyde solution was added dropwise (the mass concentration of formaldehyde in the formaldehyde solution was 38%, at this time, the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol was 0.64). After 50 minutes, the formaldehyde solution was added dropwise. Then heat to 95°C to reflux the reactants for 60 minutes, depressurize (pressure 0.04Mpa) for dehydration, stop dehydration when the viscosity of the resin reaches 110cPa.s, cool down to 30°C and collect the materials to obtain low free monomer and degradable Persimmon tannin modified phenolic resin. The test results of the obtained resin are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Take 28.5g of phenol and 14g of persimmon tannin solution (mass concentration of tannin≥3wt%), add them into a reaction vessel equipped with a reflux condenser and an electric stirrer, stir evenly and add 0.85g of oxalic acid. The temperature was raised to 95° C., and 24.85 g of formaldehyde solution was added dropwise (the mass concentration of formaldehyde in the formaldehyde solution was 39%, and at this time, the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol was 1.06). After 60 minutes, the formaldehyde solution was added dropwise. Reheat to 95°C and react for 70 minutes, then dehydrate under reduced pressure (pressure is 0.03Mpa), stop dehydration when the viscosity of the resin reaches 200cPa.s, cool down to 30°C and collect materials, and obtain low free monomer, degradable persimmon tannin Modified phenolic resin. The test results of the obtained resin are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Get 28.2g of phenol, 14g of persimmon tannin solution (mass concentration of tannin ≥ 3wt%), add in the reaction vessel that reflux condenser, electric stirrer are housed, after stirring evenly, add the hydrochloric acid 0.5g that mass concentration is 20%. The temperature was raised to 95° C., and 20.62 g of formaldehyde solution was added dropwise (the mass concentration of formaldehyde in the formaldehyde solution was 39%, and at this time, the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol was 0.89). After 60 minutes, the formaldehyde solution was added dropwise. Reheat to 95°C and react for 70 minutes, dehydrate under reduced pressure (pressure is 0.05Mpa), stop dehydration when the viscosity of the resin reaches 300cPa.s, cool down to 30°C and collect the material, and obtain low free monomer, degradable persimmon tannin Modified phenolic resin. The test results of the obtained resin are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com