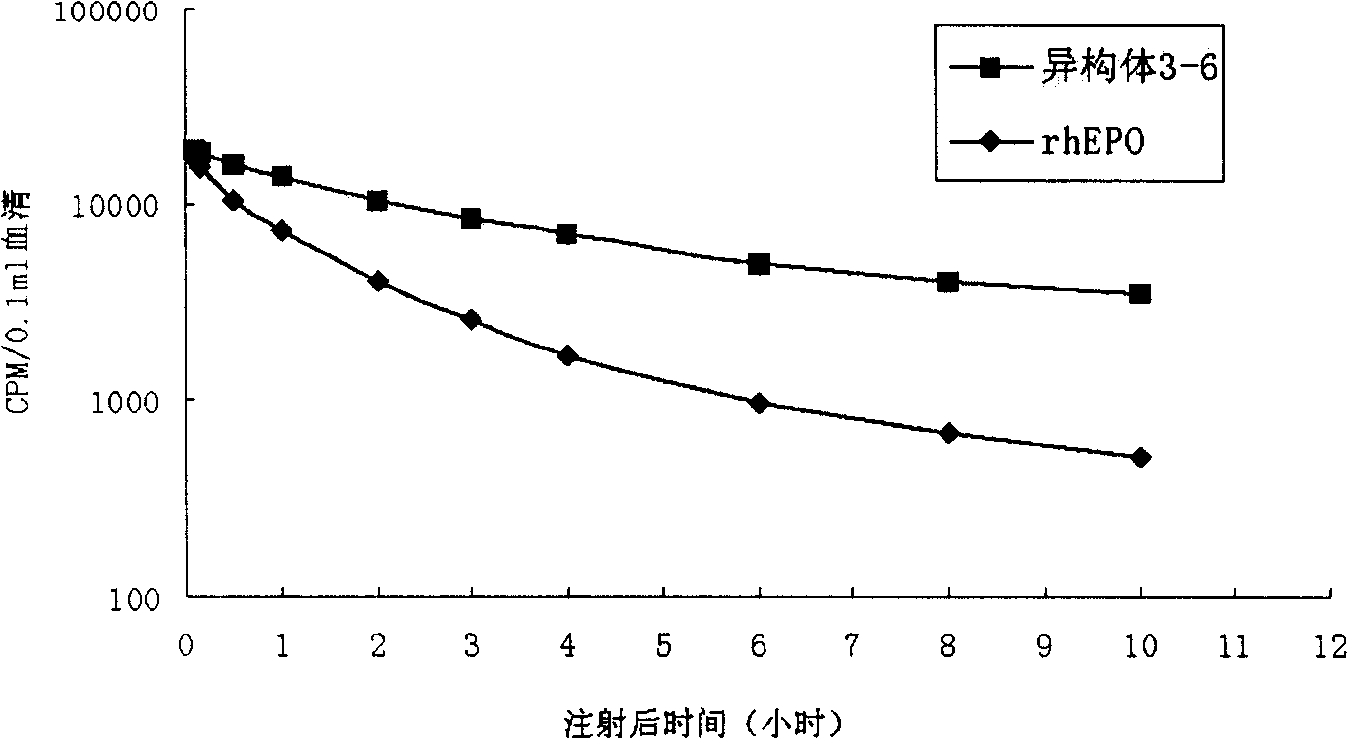
New erythrocyte-stimulating factor analogues
A technology of erythropoietin and analogs, which is applied in the field of recombinant plasmids and host cells, erythropoietin analogs or variants, and can solve the problem of decreased activity in vitro
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
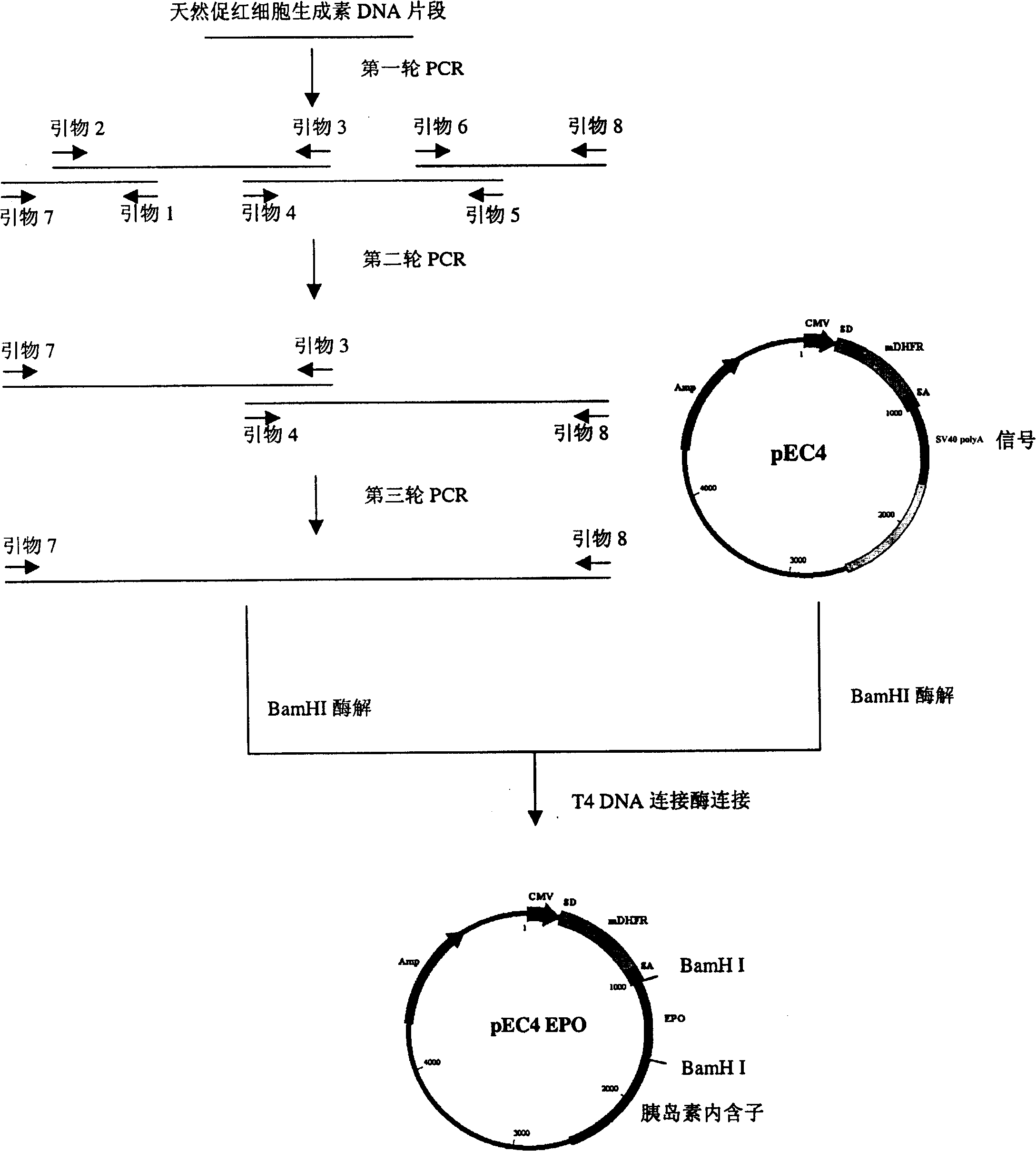
[0046] Example 1: Construction of human erythropoietin analog DNA fragments
[0047] There are 3 natural N-glycosylation sites in the amino acid sequence of human erythropoietin, which are located at positions 24, 38 and 83, respectively. 28, 30, 88 (see figure 1 ).
[0048] Combinations between mutation groups are performed on the above sites, such as constructing [Asn 2 Gly 3 Thr 4 ], [Asn 28 Thr 30 ], [Asn 88 Gly 89 Ser 90 ], adding N-glycosylation sites at positions 2, 28, and 88, and enhancing the glycosylation at this position by changing the amino acid sequence of the middle position or the position before the glycosylation site.
[0049] See SEQ ID NOS: 2-85 for primers that additionally add N-glycosylation site mutant moieties. Using these primers, the erythropoietin analog DNA fragment after mutation can be obtained by performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with erythropoietin DNA as a template. Template DNA was derived from a native EPO cDNA library. ...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Example 2: Asn 2 Gly 3 Thr 4 Preparation of EPO
[0134] A. Construction, screening and culture of engineered cells
[0135] The plasmid pEC4-N1 constructed according to the method of Example 1 was transfected into CHO cells, and the host cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and were dihydrofolate reductase-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO dhfr-). The cells were cultured in a 100mm petri dish, and when the cells were 60-95% full, the cells were rinsed with serum-free medium, and a transfection mixture consisting of 5ml of serum-free medium, 10μg pEC4-N1, and 60μg lipofectamine was added. , cultured at 37°C for 4 hours, aspirated the medium, added MEM medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum, and cultured at 37°C overnight. MTX was then added to the medium, and the culture was continued for 10-14 days until resistant clones appeared. Cells cultured from resistant clones were digested with trypsin, and the concentration of MT...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3: Asn 3 Phe 4 Ser 5 Preparation of EPO
[0145] A. Construction, screening and culture of engineered cells
[0146] The plasmid pEC4-N2 constructed according to the method of Example 1 was transfected into CHO cells, and the host cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and were dihydrofolate reductase-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO dhfr-). The cells were cultured in a 100mm petri dish. When the cells grew to 60-95% full, the cells were rinsed with serum-free medium, and a transfection mixture consisting of 5ml of serum-free medium, 10μg pEC4-N2, and 60μg lipoFectamin was added. , cultured at 37°C for 4 hours, aspirated the medium, added MEM medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum, and cultured at 37°C overnight. MTX was then added to the medium, and the culture was continued for 10-14 days until resistant clones appeared. Cells cultured from resistant clones were digested with trypsin, and the concentration of MTX ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com