A semiconductor device and a method of manufacture thereof
一种半导体、器件的技术,应用在光电子半导体器件及其制造领域,能够解决不适于制备量子点有源区、器件加工复杂、器件复杂等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0071] The following will refer to Figure 2a -2d, according to the first embodiment of the present invention, explain a light emitting device and a method of manufacturing the light emitting device.
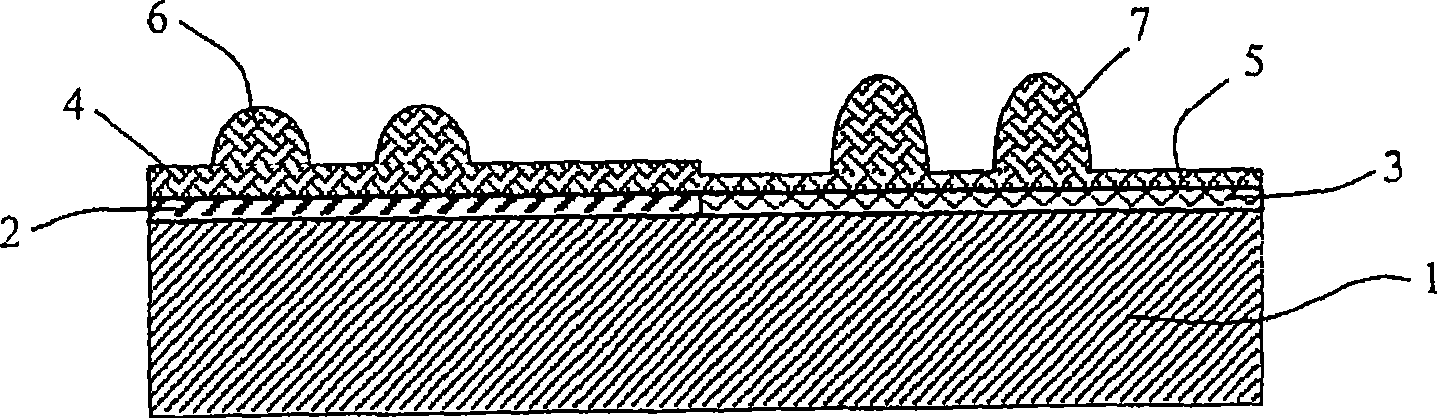
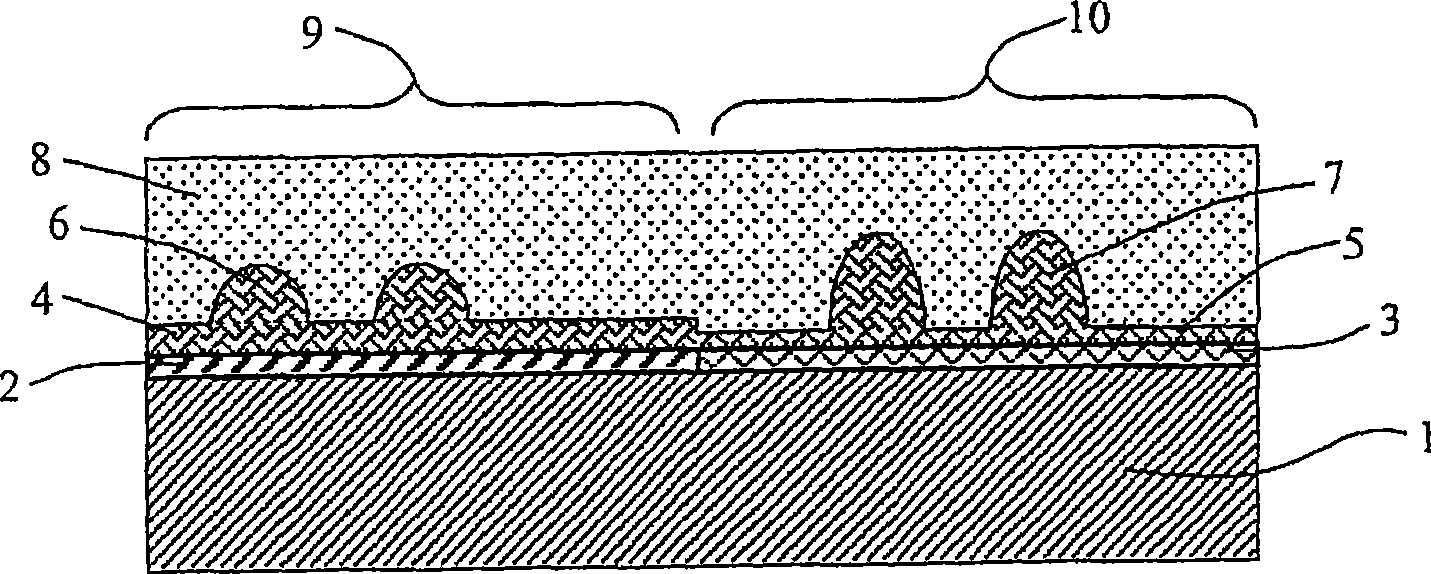
[0072] In this example, MBE is used to deposit a heterostructure with an elastically strained surface layer on a substrate. exist Figure 2a A schematic cross-sectional view of the heterostructure is shown in . In this embodiment, the substrate 12 is a template substrate comprising an n-type doped GaN layer 13 grown over a sapphire substrate 14 . In this order, n-type GaN buffer layer 15 and n-type Al x Ga 1-x An N (0<x≦1) (hereinafter referred to as AlGaN) layer 16 is grown covering the substrate 12 . Because the AlGaN layer is partially or completely strained onto the GaN buffer layer 15 in a plane parallel to the substrate surface, and because the ASLP of the released AlGaN is not equal to the ASLP of the GaN buffer layer (because GaN layers grown on sapphire are usually...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com