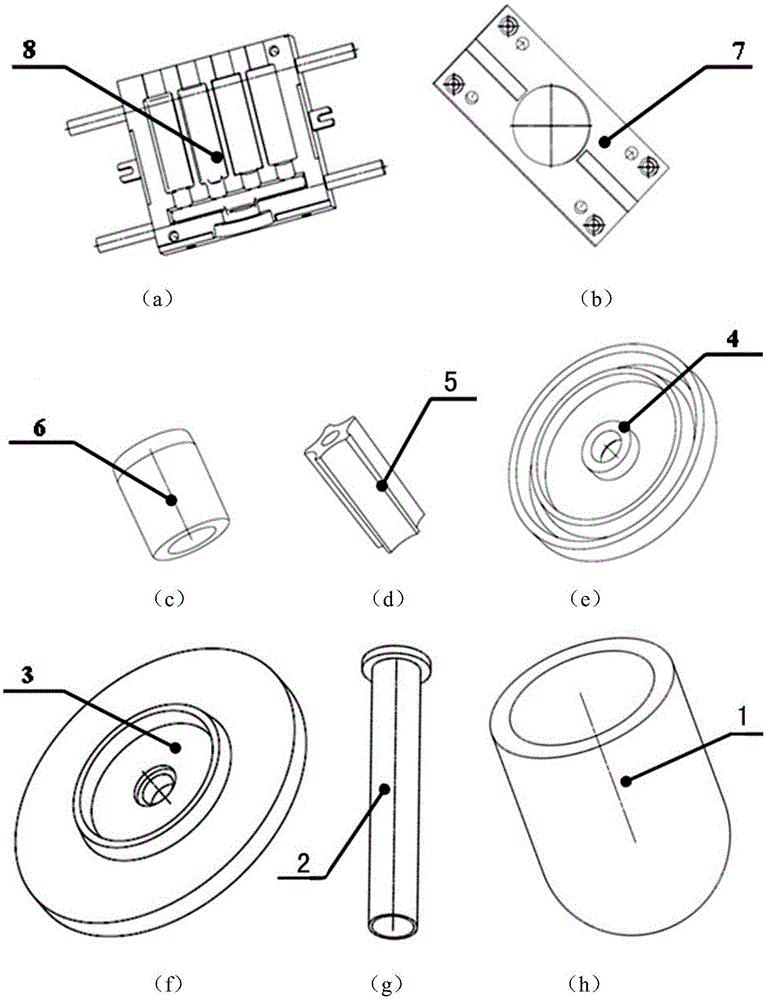
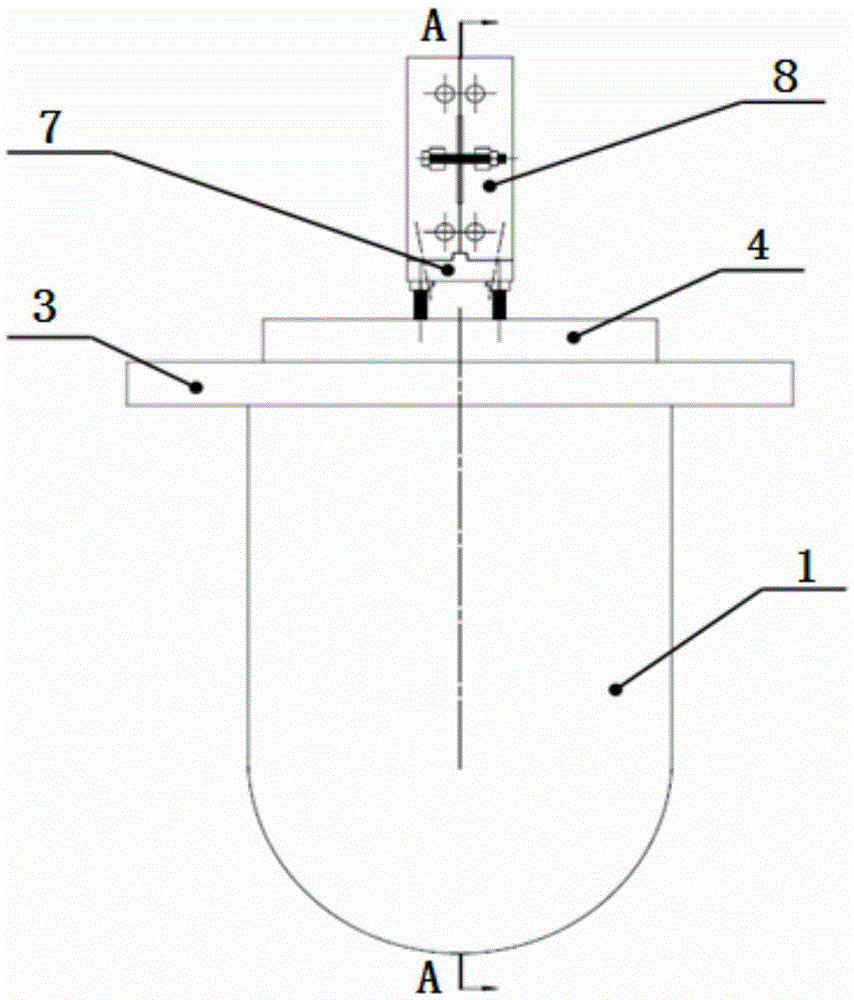
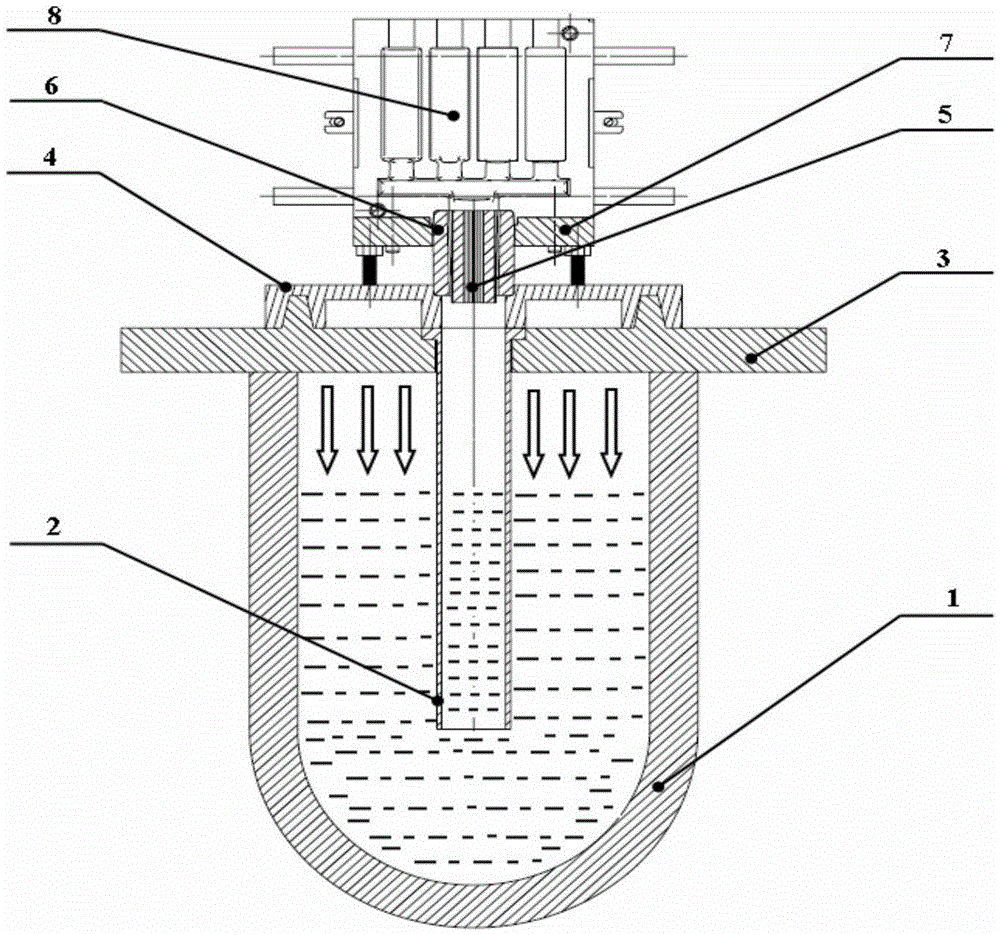
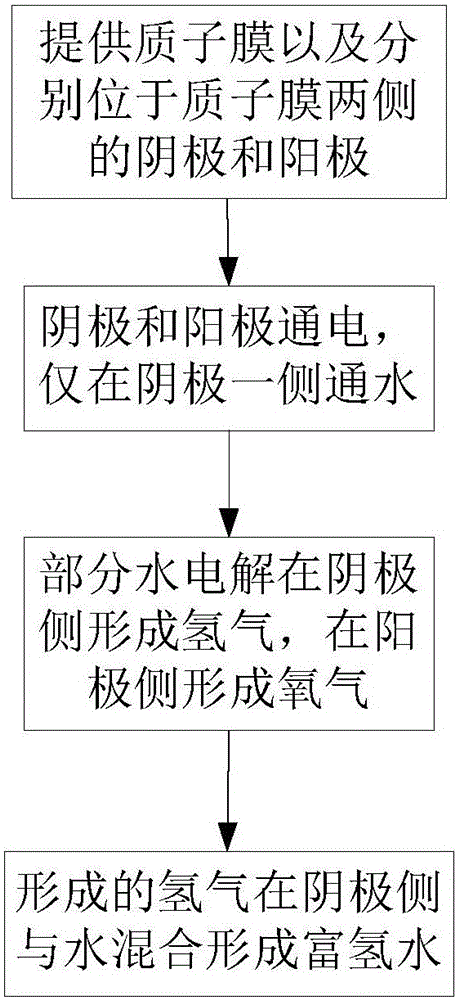
Patents
Literature
382results about How to "Manufacturing flexibility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
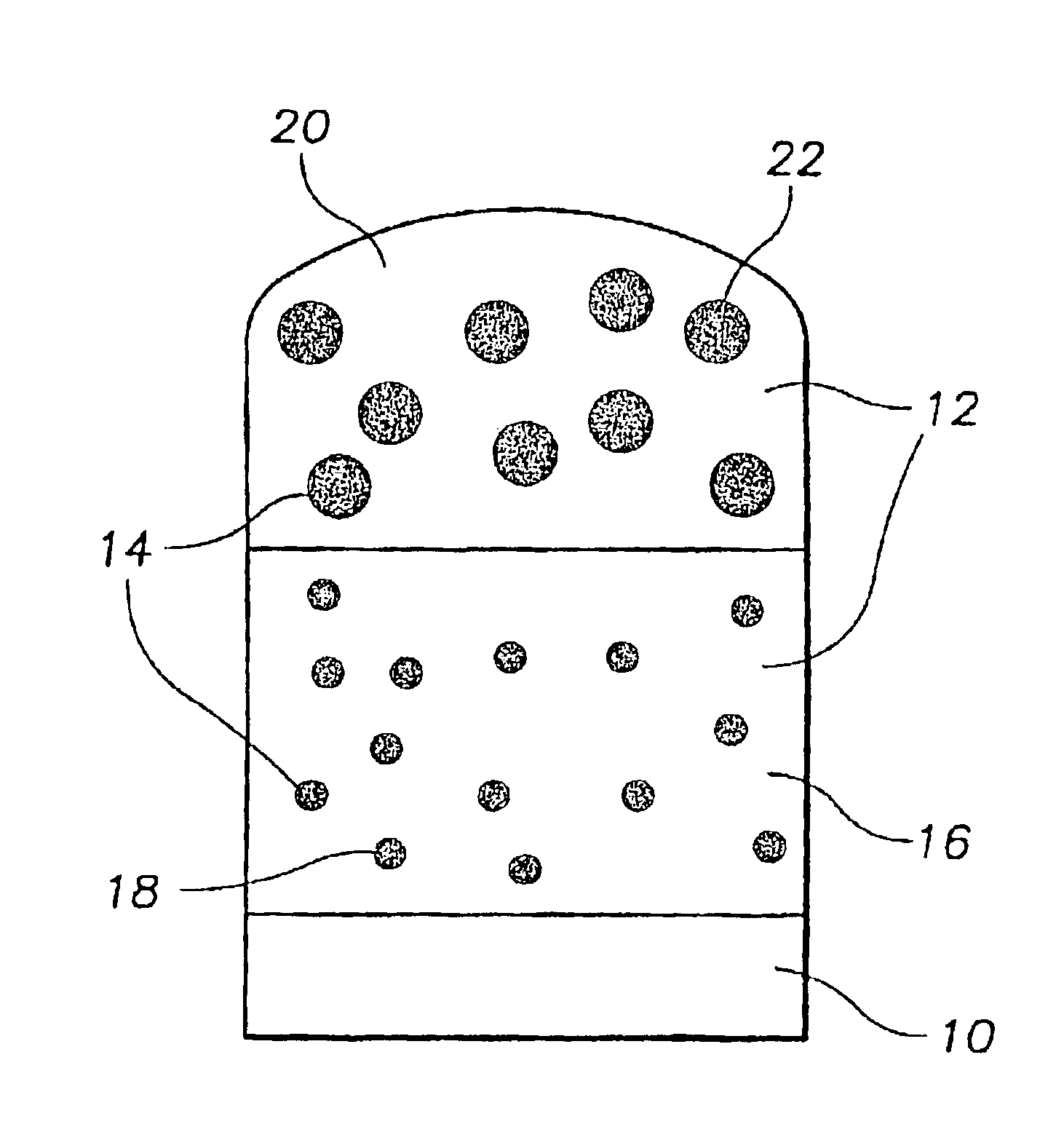
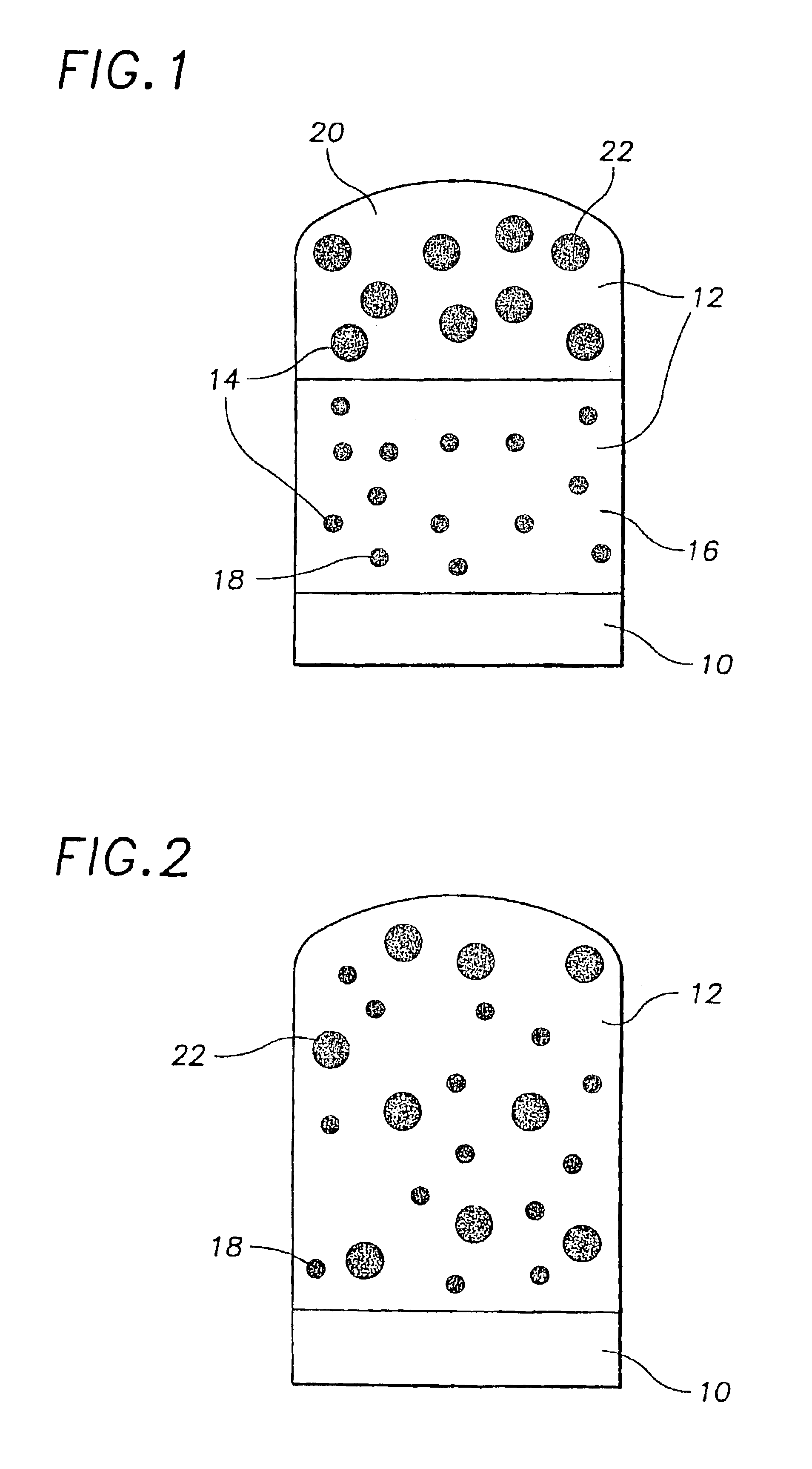
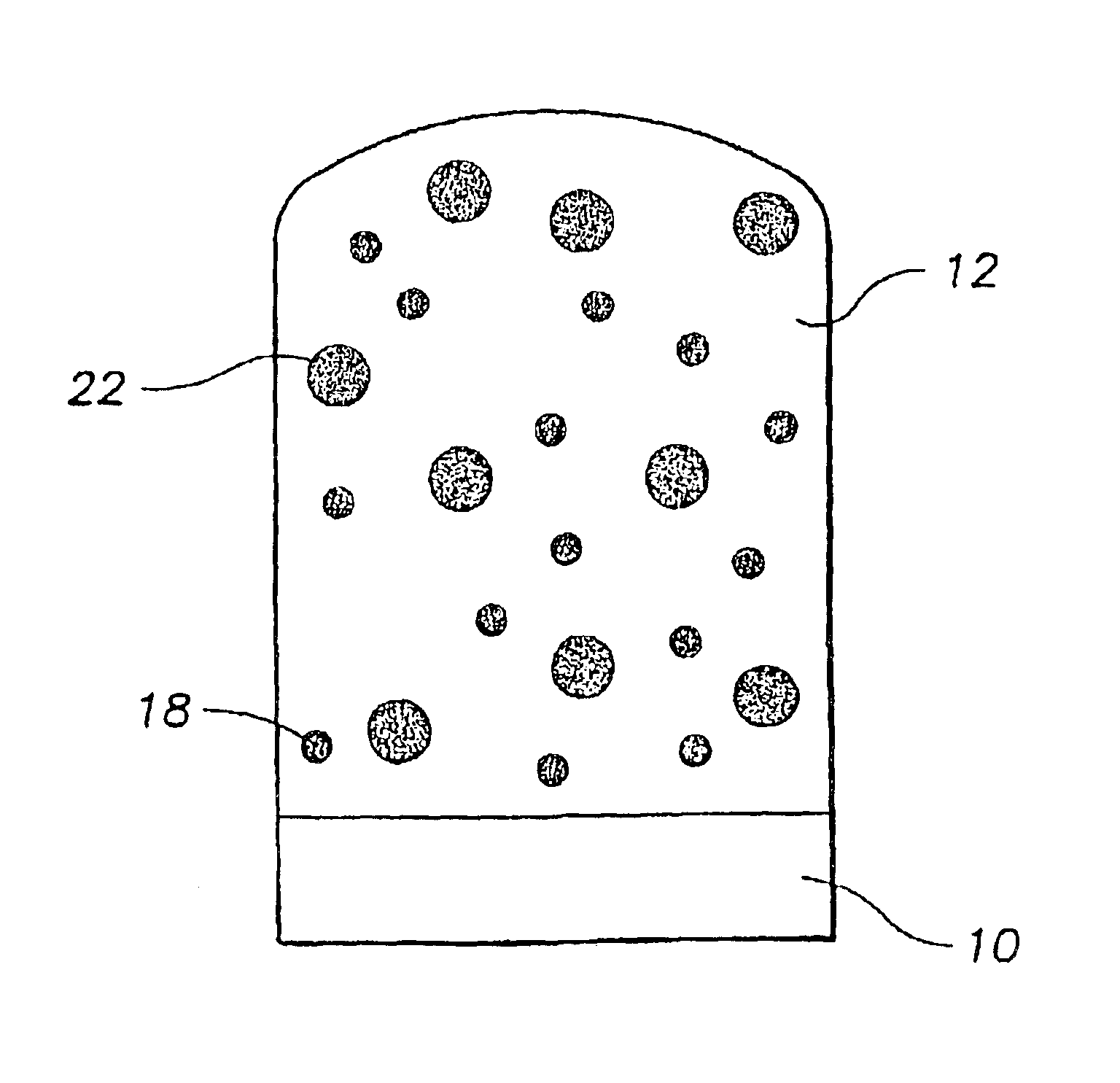
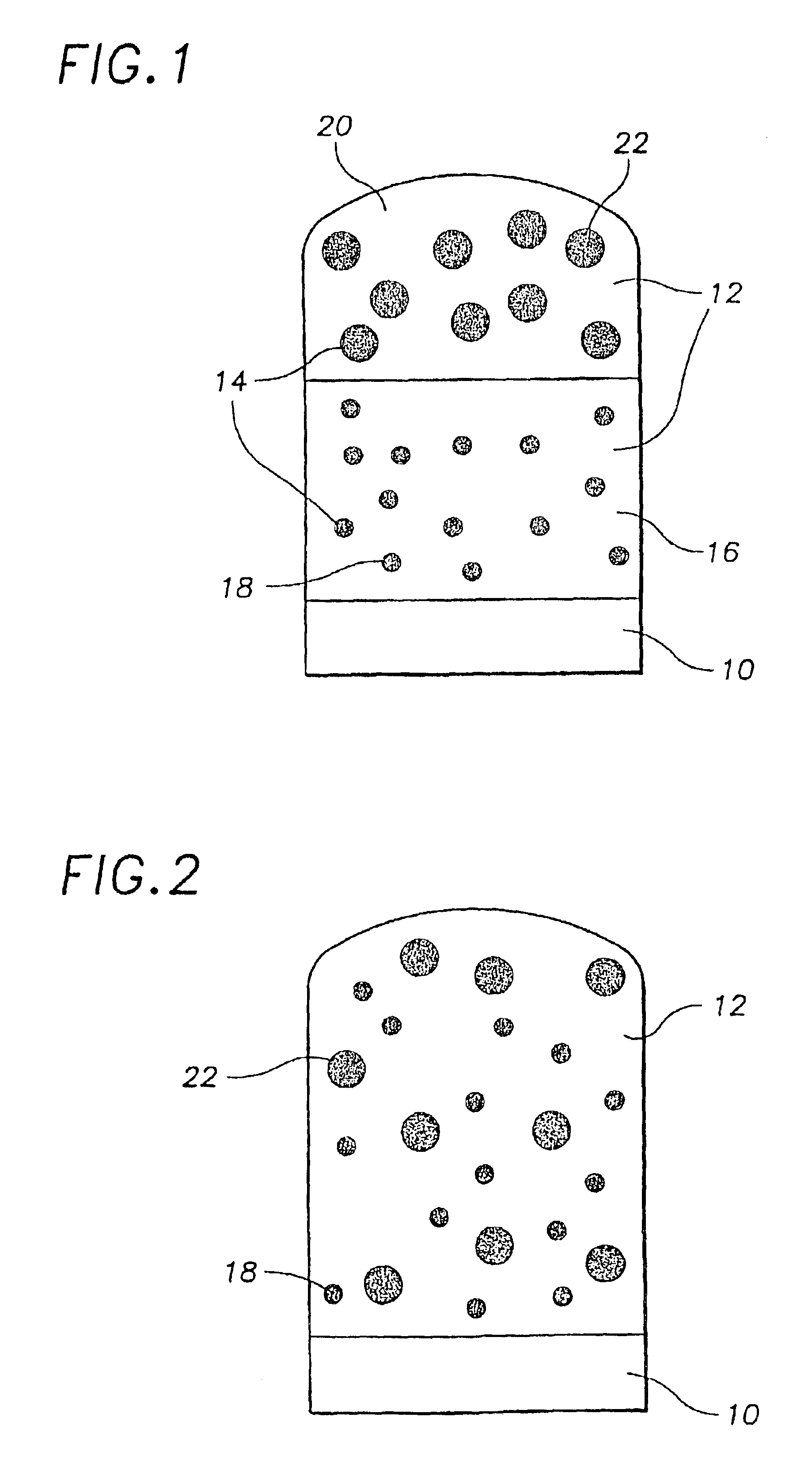
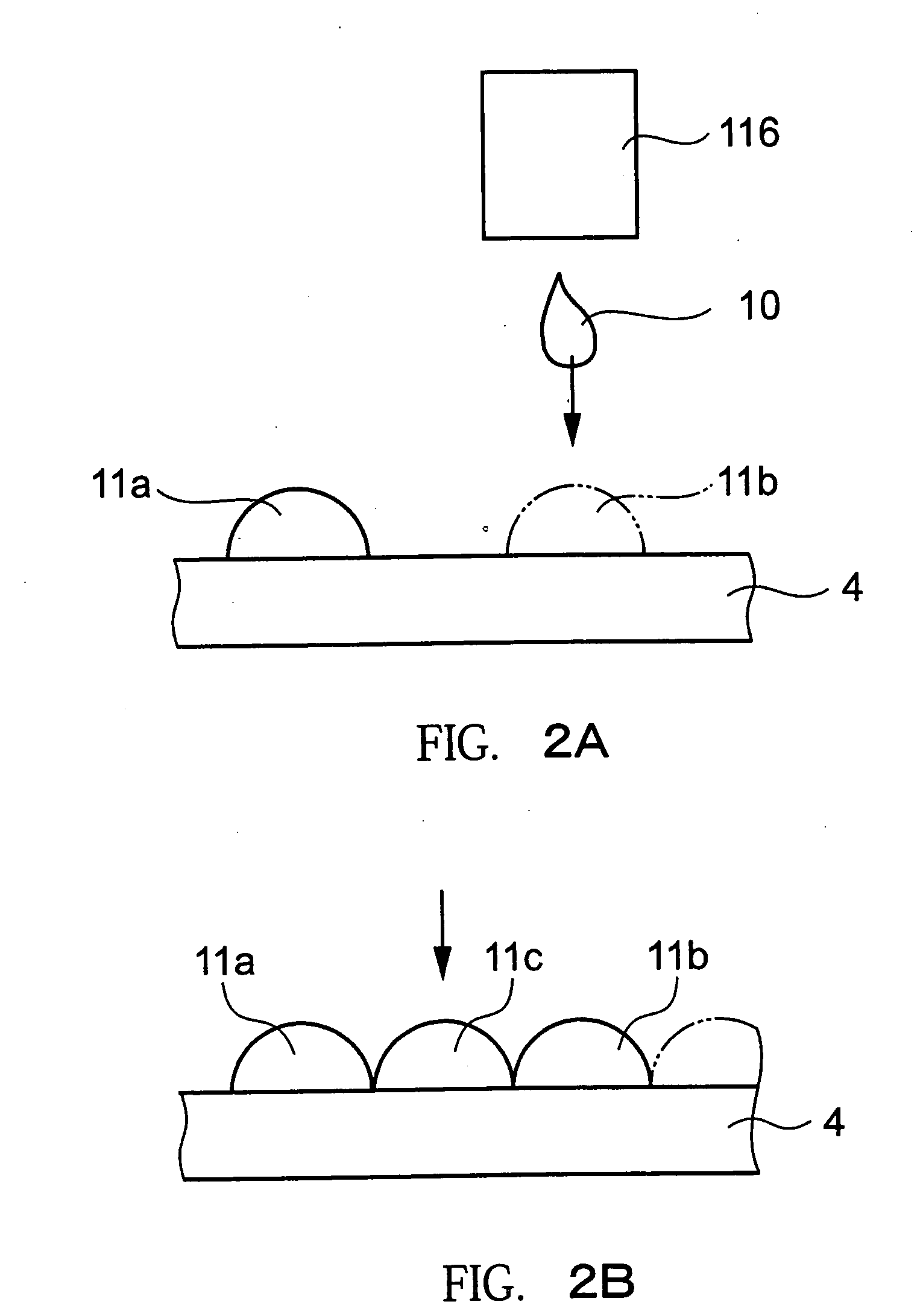
Quantum dot white and colored light emitting diodes
InactiveUS6890777B2Manufacturing flexibilityDesired colorLaser detailsNanoinformaticsPhotoluminescenceColored light
An electronic device comprising a population of quantum dots embedded in a host matrix and a primary light source which causes the dots to emit secondary light of a selected color, and a method of making such a device. The size distribution of the quantum dots is chosen to allow light of a particular color to be emitted therefrom. The light emitted from the device may be of either a pure (monochromatic) color, or a mixed (polychromatic) color, and may consist solely of light emitted from the dots themselves, or of a mixture of light emitted from the dots and light emitted from the primary source. The dots desirably are composed of an undoped semiconductor such as CdSe, and may optionally be overcoated to increase photoluminescence.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Quantum dot white and colored light emitting diodes
InactiveUS6914265B2Manufacturing flexibilityIncrease brightnessLaser detailsDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhotoluminescenceQuantum dot
An electronic device comprising a population of quantum dots embedded in a host matrix and a primary light source which causes the dots to emit secondary light of a selected color, and a method of making such a device. The size distribution of the quantum dots is chosen to allow light of a particular color to be emitted therefrom. The light emitted from the device may be of either a pure (monochromatic) color, or a mixed (polychromatic) color, and may consist solely of light emitted from the dots themselves, or of a mixture of light emitted from the dots and light emitted from the primary source. The dots desirably are composed of an undoped semiconductor such as CdSe, and may optionally be overcoated to increase photoluminescence.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Wide wale papermaking fabrics
InactiveUS6998024B2Manufacturing flexibilitySimplifying inventoryNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperMedicinePaper towel
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Integrated center rail dispenser
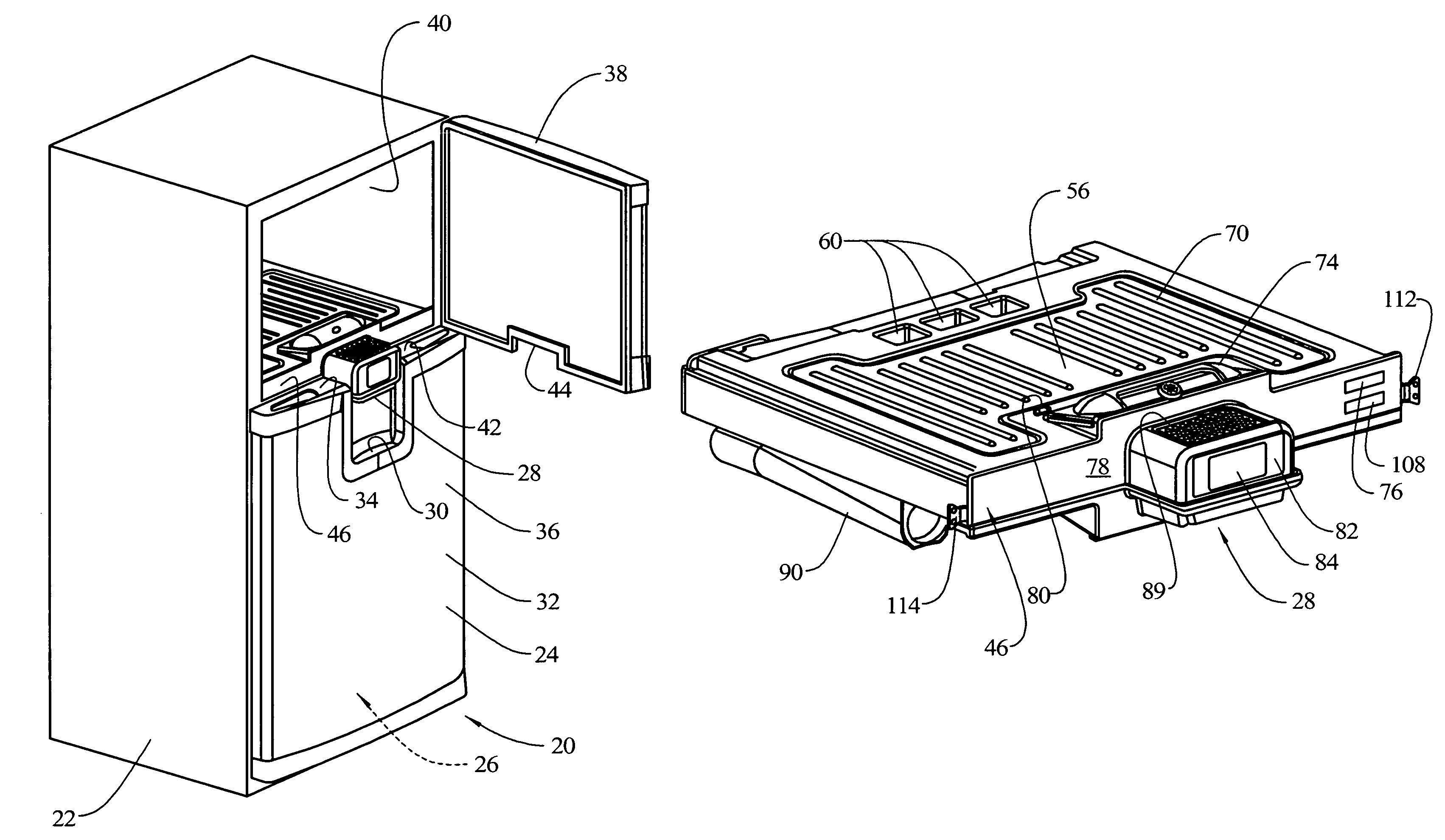
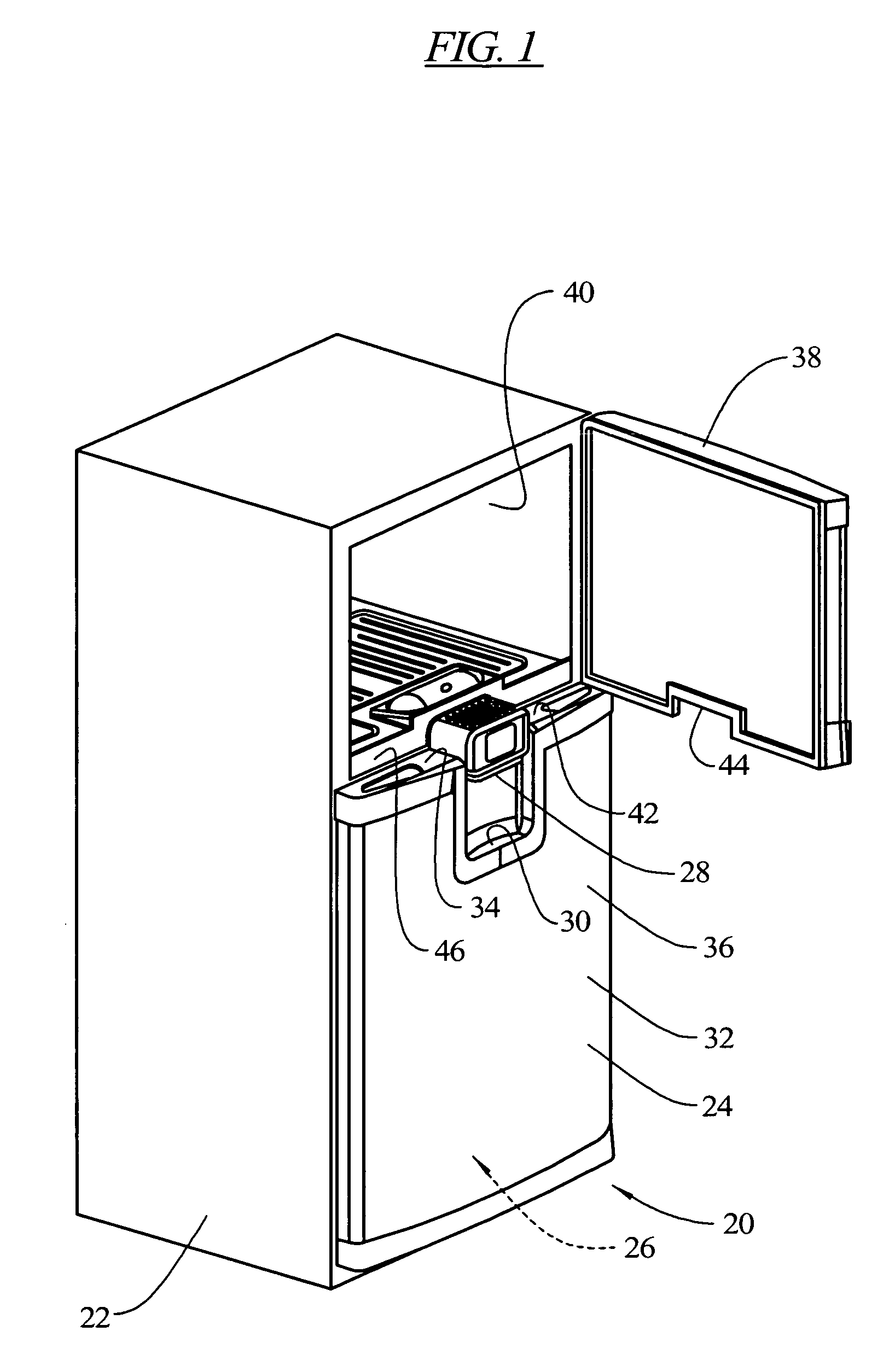
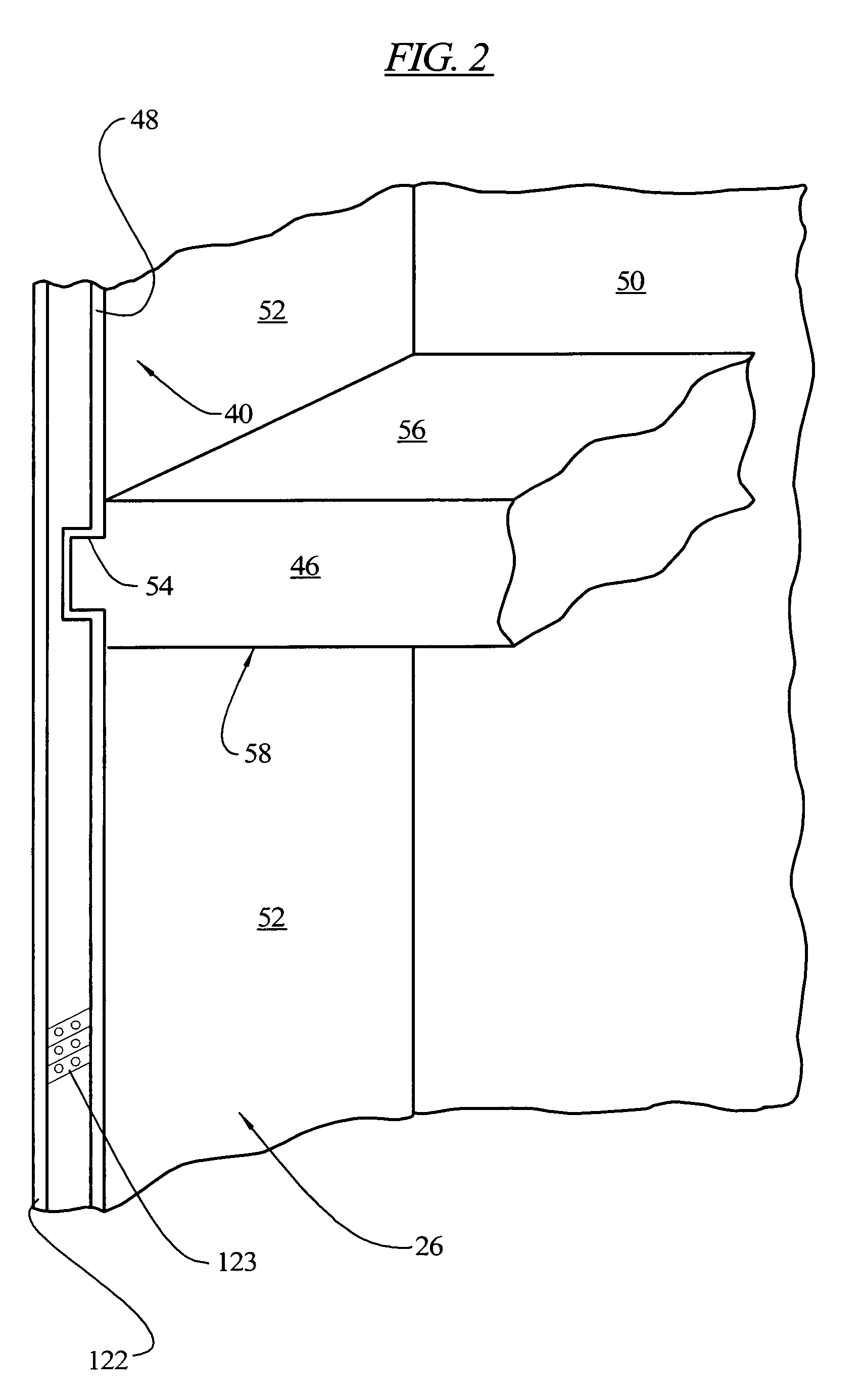
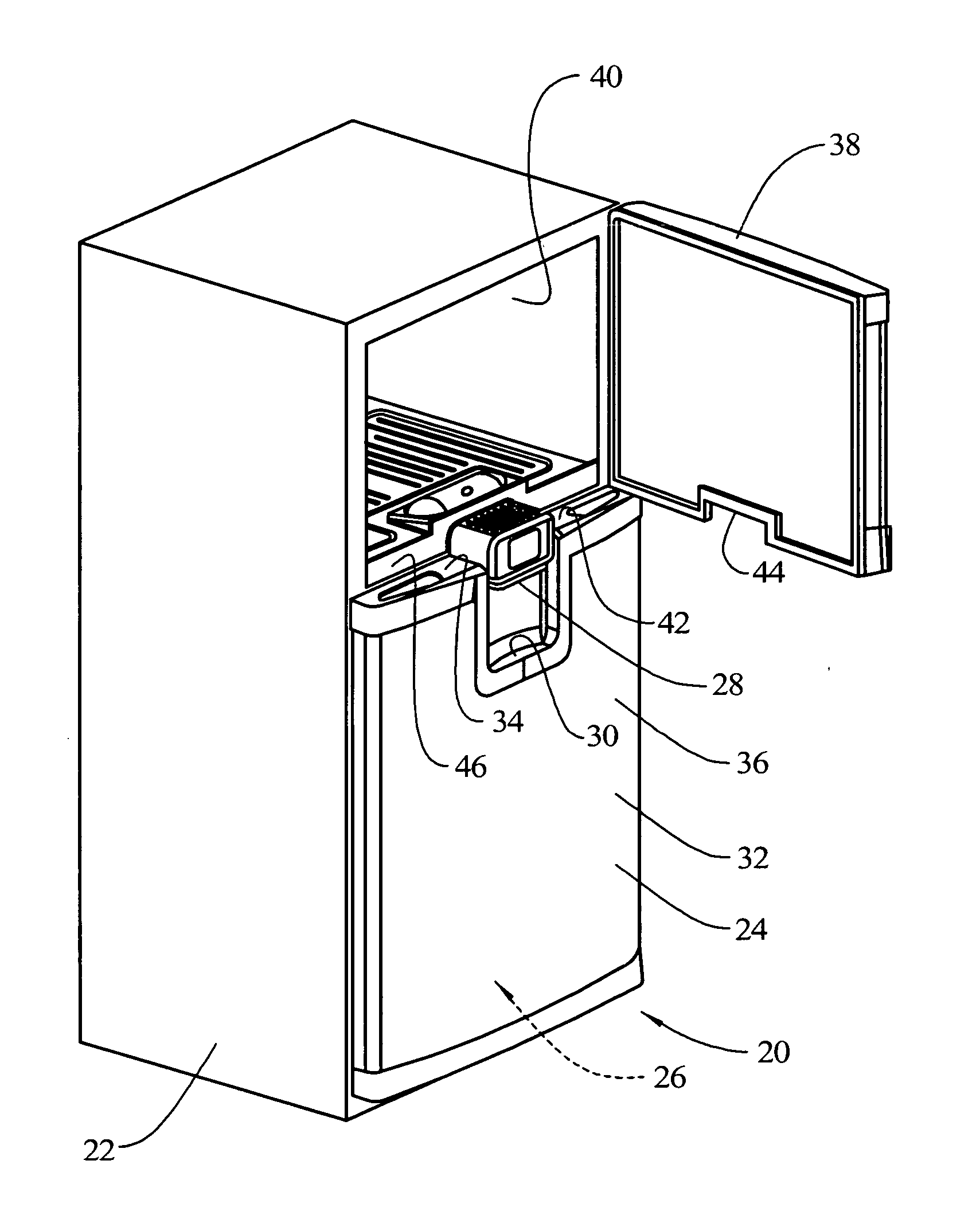
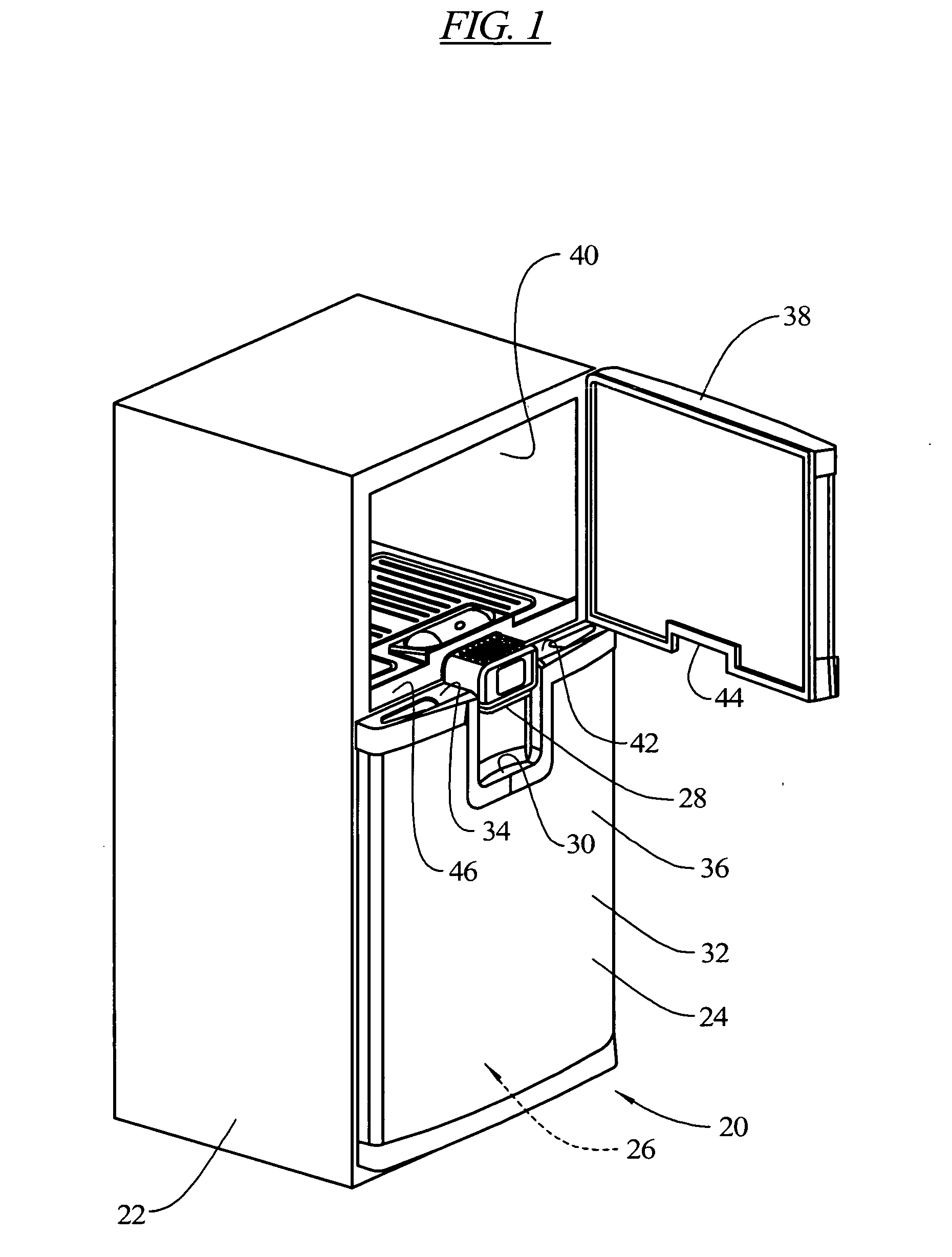
InactiveUS7343757B2Reduce wiring and plumbing complexityManufacturing flexibilityLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsCold storeRefrigeration
A refrigeration appliance is provided which includes a cabinet with a first openable door providing access to a first refrigeration compartment and a second openable door providing access to a second refrigeration compartment. The second openable door has a portion thereof positioned below a portion of the first openable door. A rail separates the first refrigeration compartment and the second refrigeration compartment. A water dispenser is contained in the rail, as well as electronic controls for the refrigeration appliance. The dispenser is arranged to be stationary relative to the refrigeration appliance while the doors are open or closed. The rail may be removed and replaced, and with the water and electronic controls located in the rail, repairs are performed more efficiently and flexibility in manufacturing is enhanced. A drip tray is formed in an exterior side of the second openable door below the dispenser. When the door is opened, the drip tray moves away from the dispenser, permitting the dispenser to be used with larger receptacles than can be accommodated with the drip tray under the dispenser.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Embedded semiconductor memory devices and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080145985A1High density data storageEasy to useNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesGate dielectricSemiconductor
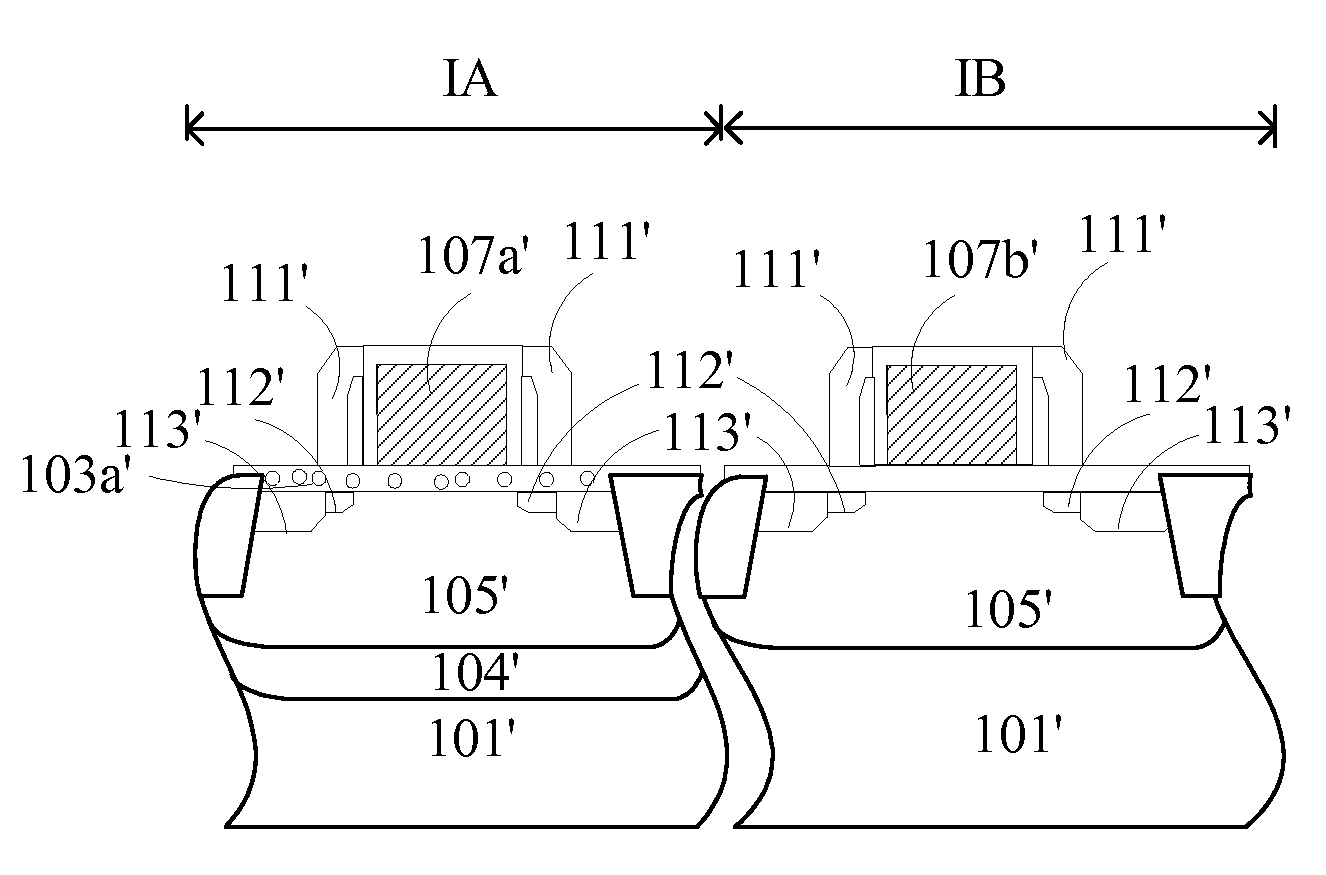
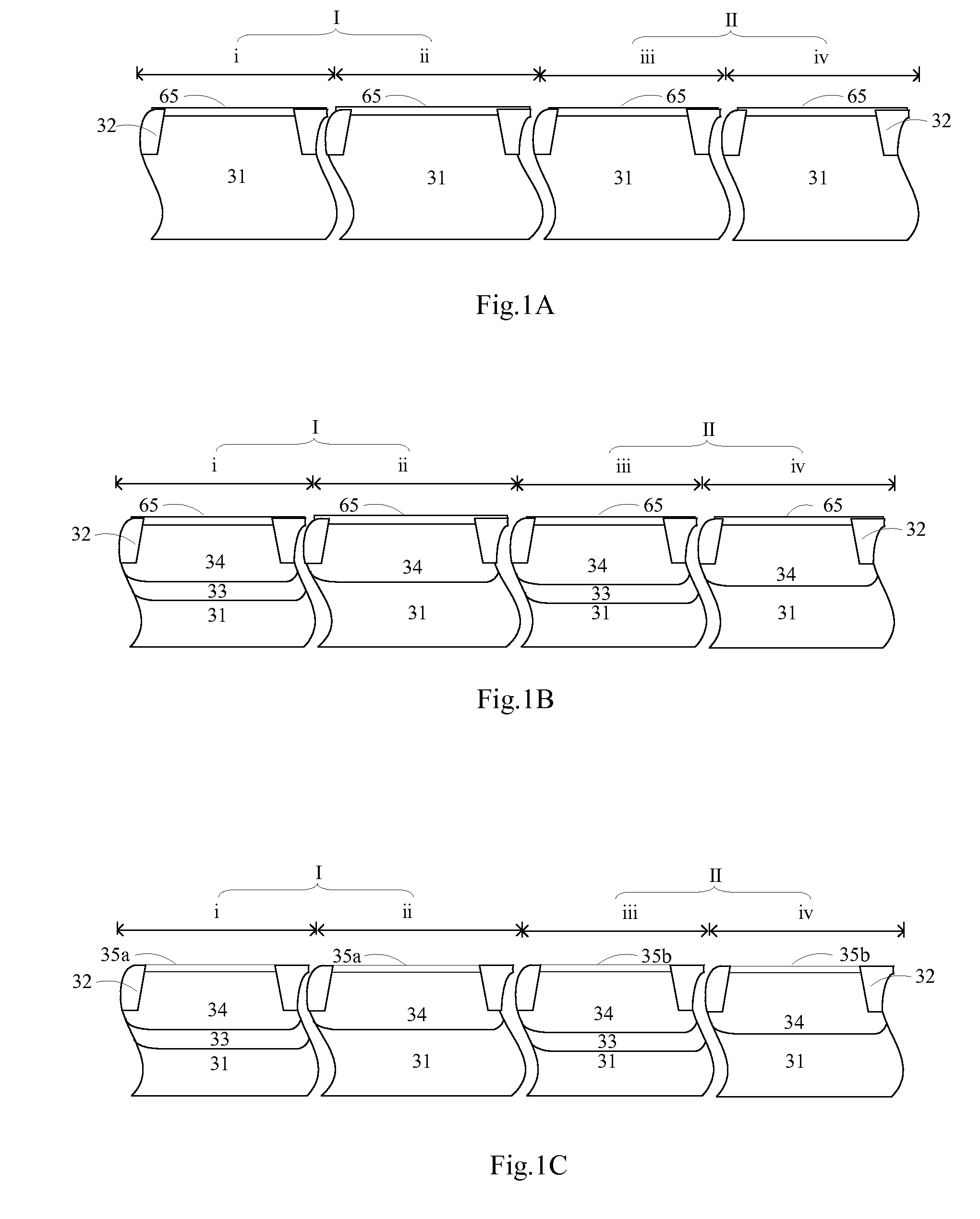
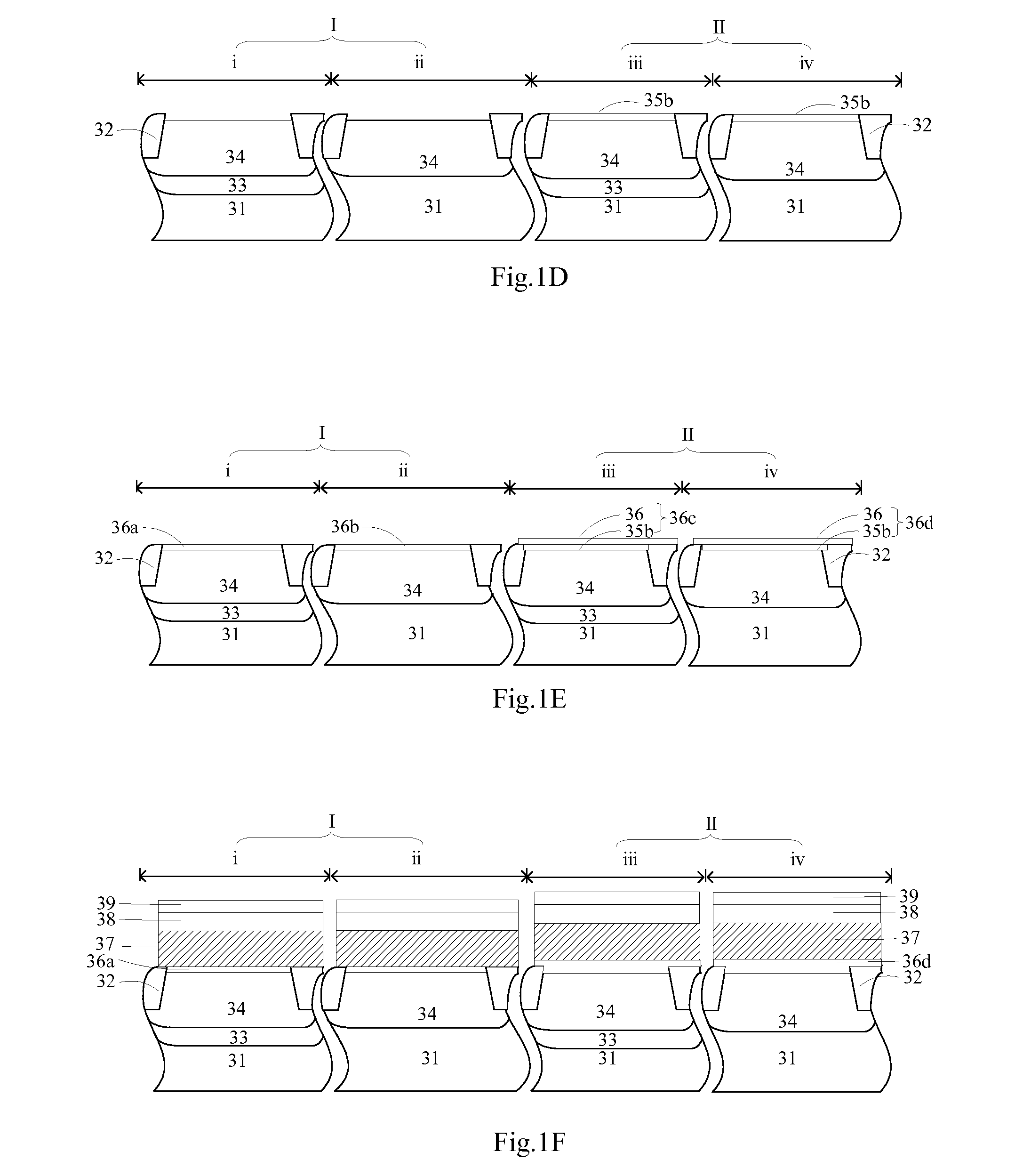
The invention discloses a method for fabricating an embedded semiconductor memory device, comprising: preparing a semiconductor substrate comprising a region IA and a region IB; forming gate dielectric layers and gate structures sequentially on the semiconductor substrate, with the gate dielectric layer in region IA being a charge trap region, and the gate dielectric layer in region IB being a non-charge trap region; forming source / drain extension regions in region IA and region IB of the semiconductor substrate; and forming source / drain regions in region IA and region IB of the semiconductor substrate. There is provided correspondingly an embedded semiconductor memory device. The invention also provides an embedded semiconductor memory device and a method for fabricating the same. A two-bit storage operation can be enabled for the embedded semiconductor memory device according to the invention so as to achieve high-density storage. Furthermore, the process for forming a logic circuit can be compatible with that for forming a memory device circuit according to the invention.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
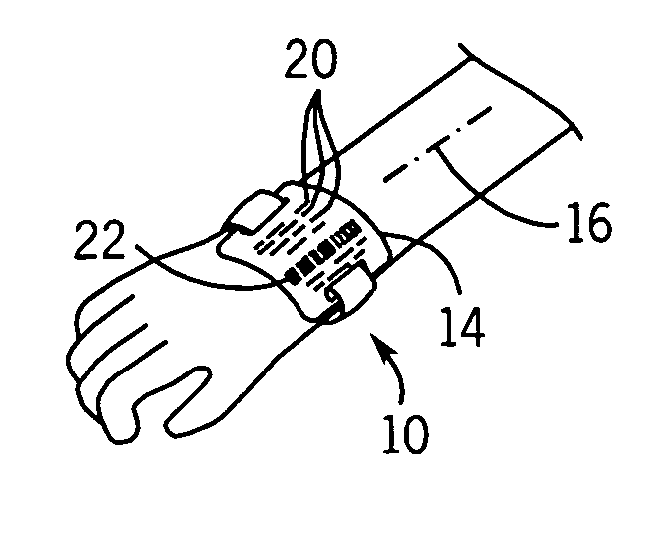
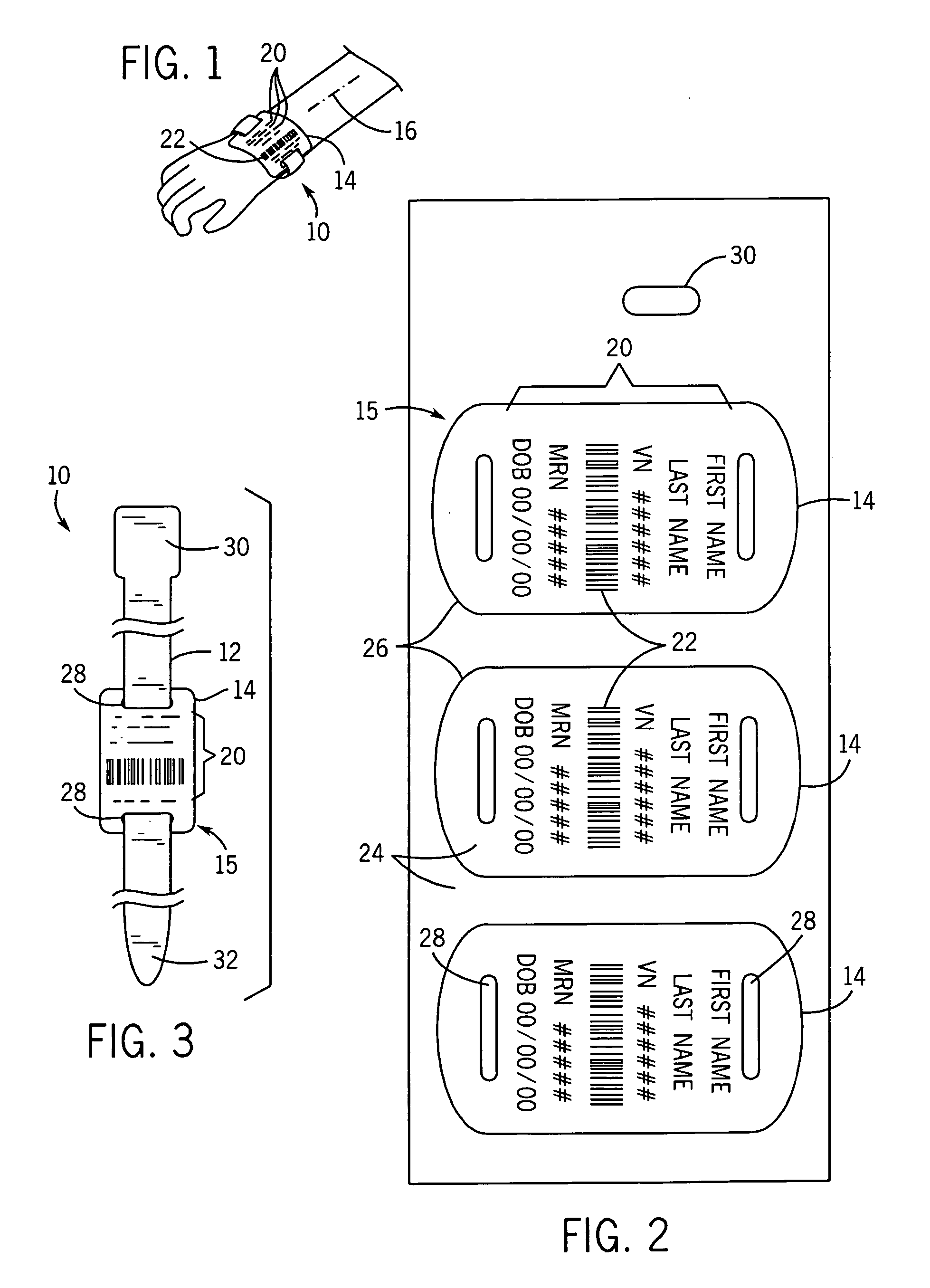
Pediatric patient identification wristband tag
InactiveUS20060242875A1High tensile strengthManufacturing flexibilityPerson identificationBraceletsPediatric patientBarcode
A wristband particularly suited for infants, has separate printable tag that may be threaded onto a wristband to provide a widened axial segment for clean printing and scanning of a barcode. The bar code is positioned to extend along the wrist so as to remain relatively flat on a wrist that may be a small as an adult's thumb.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL & HEALTH SYST
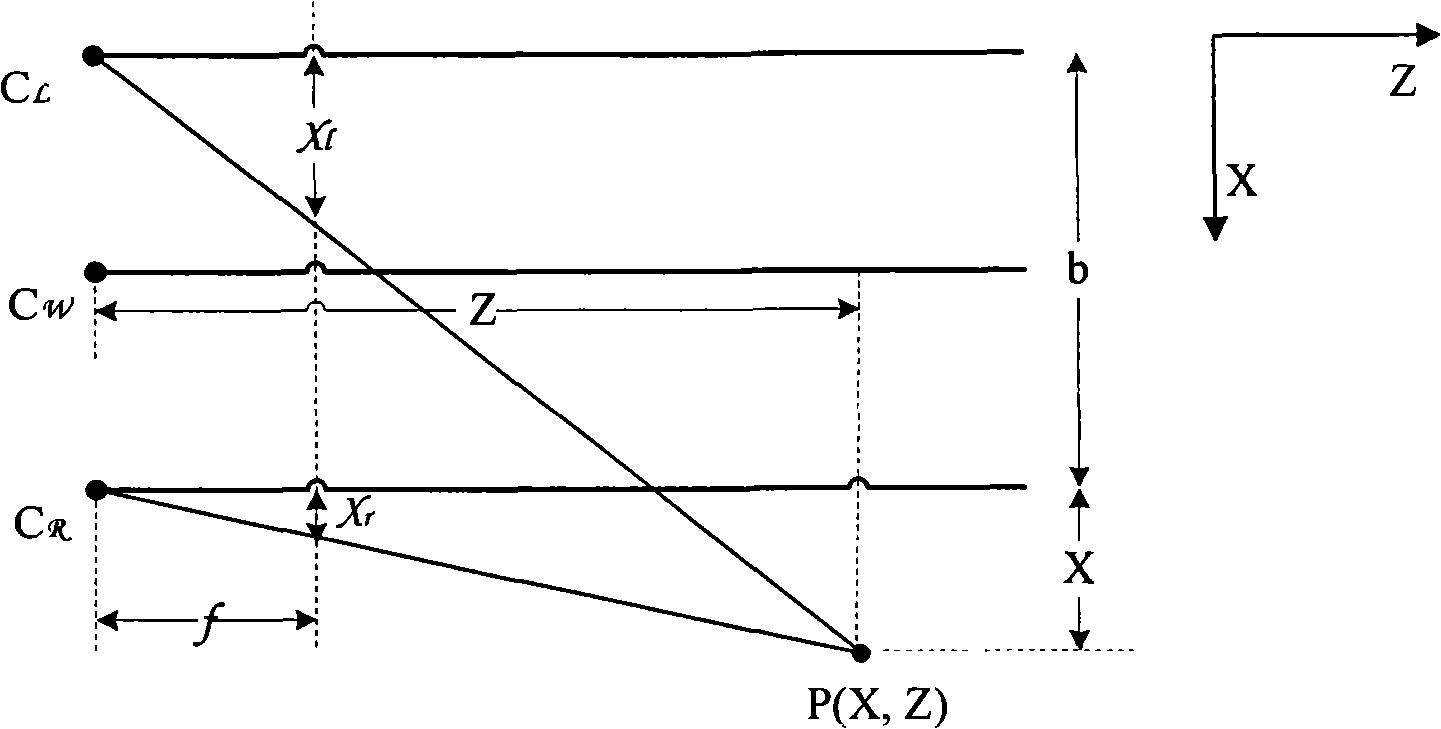
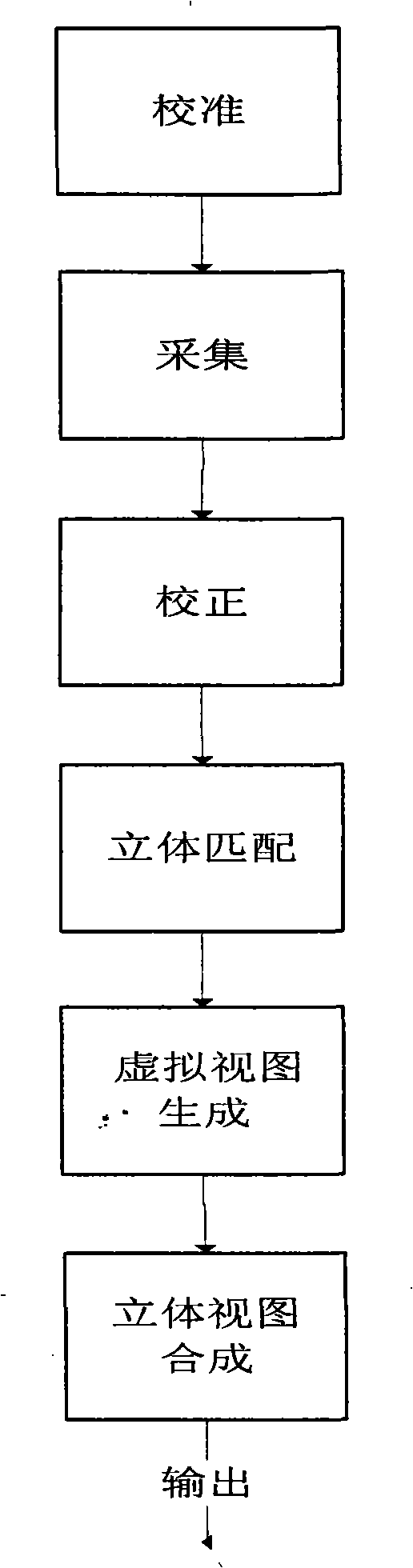
Method for generating real time tridimensional video based on binocular camera
InactiveCN101277454ANo human intervention requiredLow costSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoStereo matching
The invention relates to a real-time three-dimensional video generation method that belongs to the acquisition and processing technology field of the three-dimensional video. The method involves the following steps of calibration, collection, regulation, stereo match, virtual view generation and three-dimensional view synthesis. The invention is convenient, simple and rapid, particularly suitable for some situations needing real-time processing.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
MEMS (Micro-Electromechanical System) sensor encapsulation structure and encapsulation method thereof
ActiveCN103950886ACompact structureReduce electrical connectionsDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesHigh densityThermal expansion
The invention relates to an MEMS sensor encapsulation structure and an encapsulation method thereof, which are used for encapsulating an MEMS sensor. The MEMS sensor encapsulation structure is characterized by comprising a ceramic base, a side wall and a top cap, wherein a plurality of metal bonding pads are respectively arranged on a top layer and a bottom layer of the ceramic base; the metal bonding pads on the top layer of the ceramic base are connected with leads of the MEMS sensor; the MEMS sensor is arranged on the ceramic base; the metal bonding pads on the bottom layer of the ceramic base are connected with an external circuit; the ceramic base adopts one-layer or multi-layer perpendicularly interconnected structure; the side wall and the top cap are both made of kovar alloy. According to the invention, the ceramic base of which coefficient of thermal expansion is approximate to that of the MEMS sensor material is selected as the encapsulation material, in order to reduce influence of the base expansion stress to the MEMS sensor; meanwhile, the ceramic base can be utilized to realize one-layer perpendicular interconnection or multi-layer perpendicular interconnection; the system-level integration between the MEMS sensor and the peripheral circuit can be realized within a small area; high-density system-level encapsulation can be realized; the encapsulation flexibility and the expansibility of the MEMS sensor can be realized.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
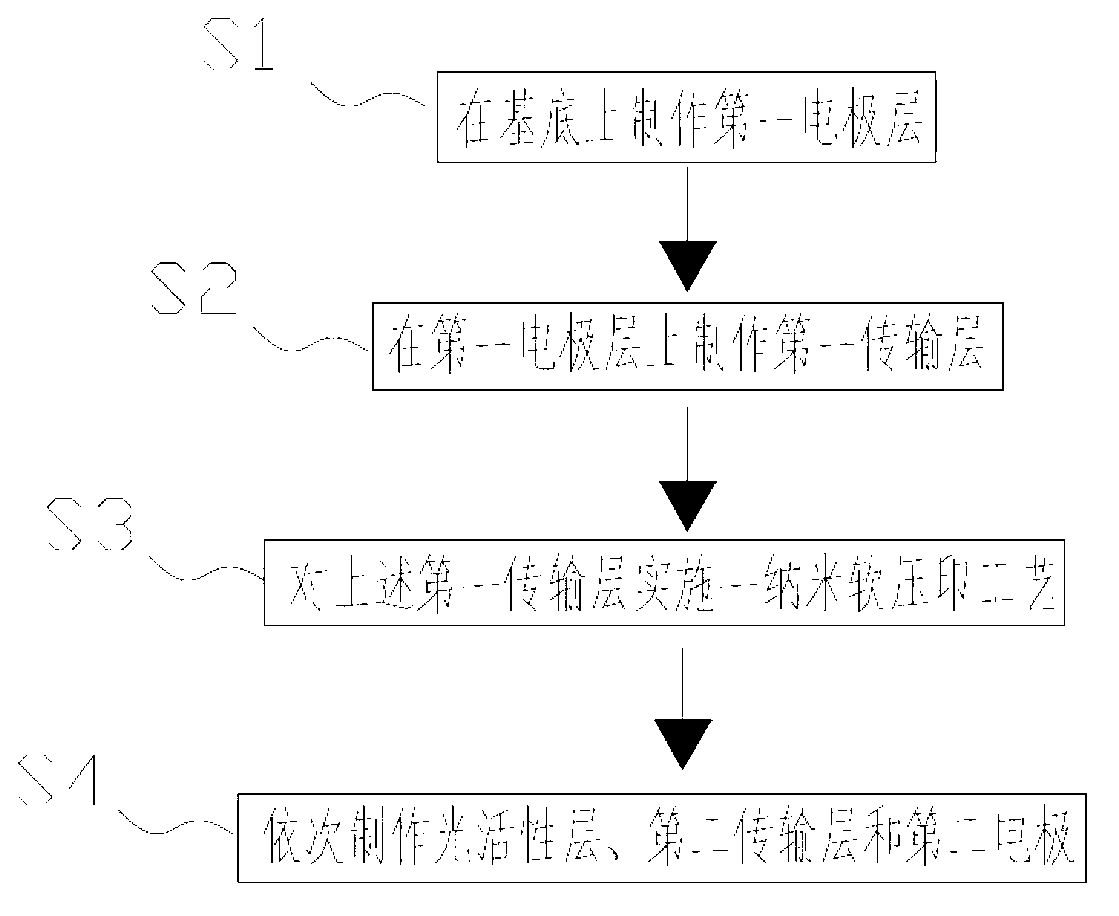
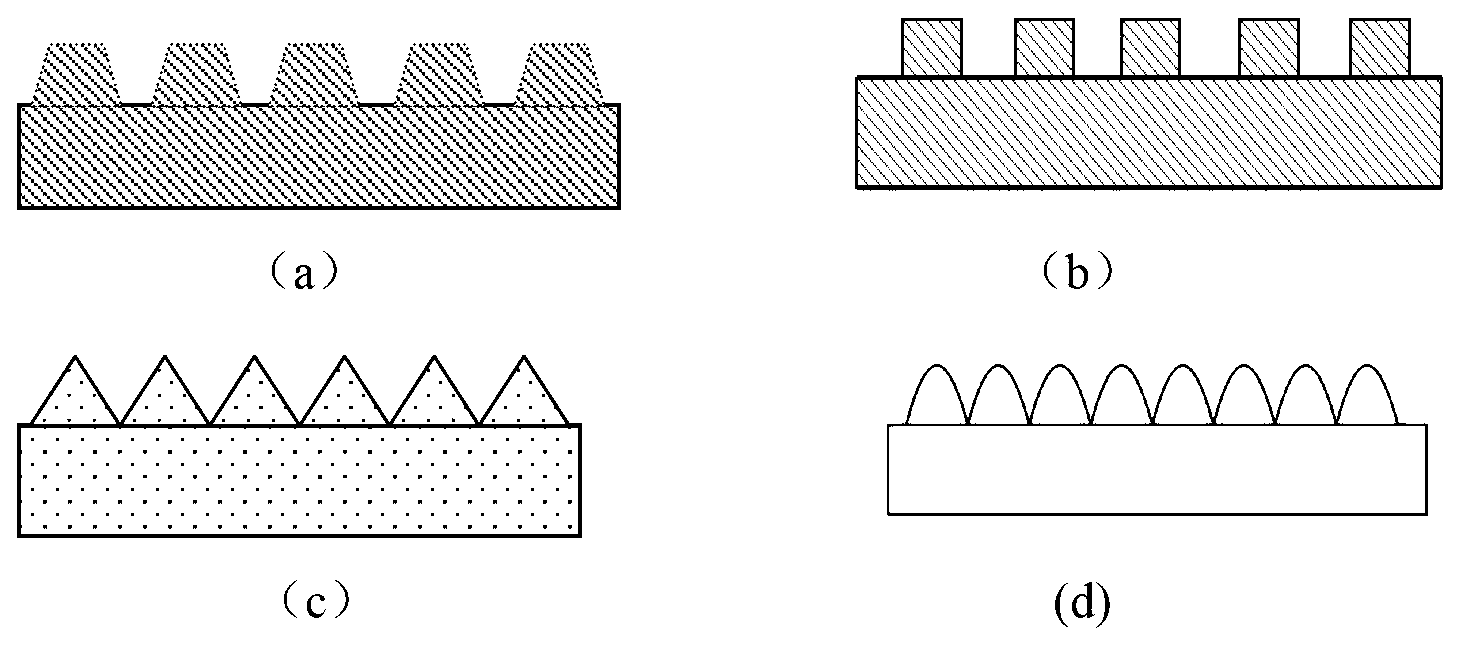
Organic solar battery and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103078057AImprove fidelityLow costFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionTrapping
The invention discloses an organic solar battery and a manufacturing method thereof. The organic solar battery consists of a first electrode, a second electrode, a photoactive layer, an electronic transmission layer and a hole transport layer, wherein a convex or concave nanostructure is formed on the surface of the electronic transmission layer or that of the hole transport layer by soft-nano imprinting and forms a convex-concave complementary light trapping structure with the photoactive layer; and the convex-concave complementary light trapping structure can effectively increase the absorption to light within a wide spectrum range from ultraviolet light to infrared light, and thus the conversion efficiency of the organic solar battery is increased. The manufacturing method has the advantages of high fidelity, one-step forming property, low cost and the like as well as has favorable actual application value.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
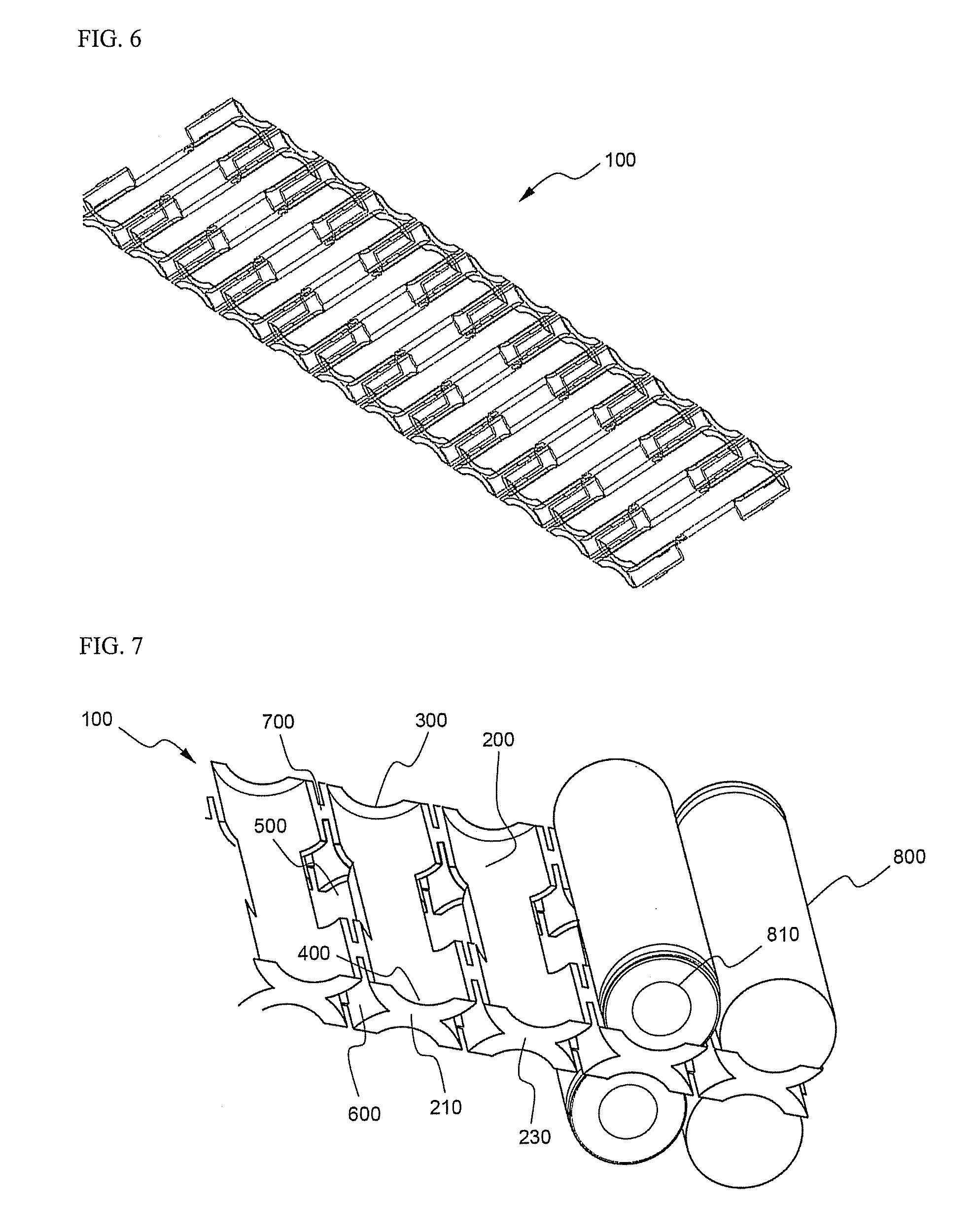
Spacer for production of battery pack
ActiveUS20070190405A1Maximize the effectEasy to installPrimary cell to battery groupingLi-accumulatorsEngineeringSurface structure
Disclosed herein is a spacer for production of a battery pack using cylindrical batteries as unit cells, wherein the spacer is constructed in the form of a rectangular frame, the spacer is provided at opposite side surfaces (opposite faces) of the rectangular frame with a plurality of battery receiving parts having a circumference-type inner surface structure that partially covers the outer surfaces of the cylindrical batteries, each battery receiving part has a horizontal through-hole, which extends between the opposite side surfaces of the frame, and a pair of battery receiving parts (a unit receiving part) formed at the opposite side surfaces of the frame is connected with another adjacent unit receiving part via structures that can be easily cut. Consequently, the spacer according to the present invention has the effect of allowing the production of a structurally stable battery pack using the minimized number of parts, reducing the number of processes, thereby lowering the costs of products, and preventing the occurrence of short circuits between unit cells during the assembly or the use of the battery pack. In addition, the spacer according to the present invention can be cut into various appropriate sizes, as occasion demands. Consequently, the spacer according to. the present invention has the effect of easily adjusting the capacity and output of a battery pack and effectively removing heat generated from unit cells during the charge and discharge of the unit cells.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
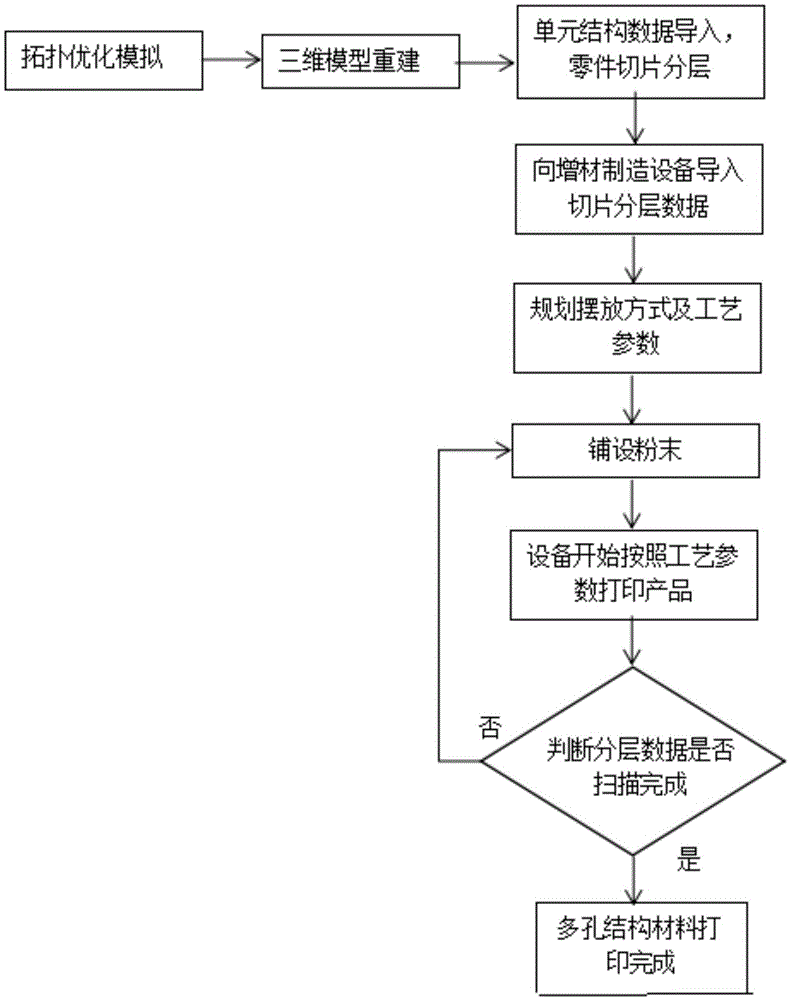
Design and manufacturing method of porous grid structure material
InactiveCN105499575AManufacturing flexibilityImprove performance qualityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationLaser scanningSize ratio
The invention discloses a design and manufacturing method of a porous grid structure material and aims to solve the problems of blindness and uncertainty in traditional manufacturing of a porous material and apply an effective design concept for the porous material to practical manufacturing. The design and manufacturing method comprises the following steps: obtaining a data image based on topological optimization simulation; performing three-dimensional rebuilding on the data image on Solid Works; importing to magics software as a unit grid structure; filling into various three-dimensional models of specific parts which need to adopt the grid structure at any size ratio; afterwards manufacturing the parts. According to the design and manufacturing method, firstly, the three-dimensional model of each part is imported to a computer on a worktable; the printing angle and the printing position are set according to the three-dimensional graph structure; a powder layer is sintered into a corresponding two-dimensional shape on the layer; powder with the same thickness is repeatedly laid on the worktable on which one layer of graph is sintered; laser scanning is still performed according to the scanning route of the layer until the overall three-dimensional graph is completed. The design and manufacturing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reducing the elasticity modulus of the part and realizing good mechanical properties.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS20070211523A1Reduce power consumptionGate delay have been decreasedDigital storageStatic random-access memoryHemt circuits
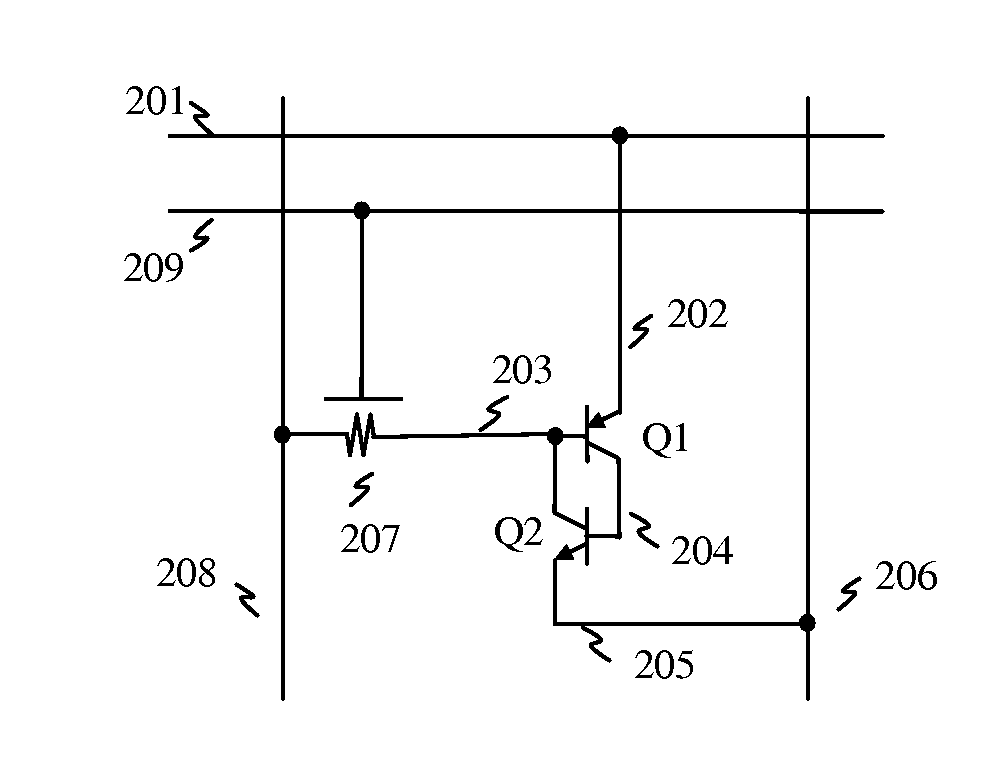
A magnetic memory includes a diode as an access device instead of MOS transistor and a magnetoresistive storage serves as a storage element, wherein the diode has four terminals, the first terminal is connected to a read word line, the second terminal serves as a storage node, the third terminal is floating, the fourth terminal is connected to a bit line, and wherein the magnetoresistive storage includes MTJ (magnetic tunnel junction) stack, the first electrode of the stack is connected to the storage node, the second electrode of the stack is connected to a free magnetic layer which serves as a resistor line, those electrodes are isolated by insulation layer, and the stack is coupled to a pinned magnetic layer which serves as a write word line. The diode also serves as a current amplifier with controlling the storage node through the storage element when the resistor line is asserted to measure the resistance of the storage element during read. And current-to-voltage converter receives the current output of the current amplifier, and transfers voltage output to the sense amp which amplifies the received voltage from the (main) memory cell and the reference voltage from the dummy memory cell(s). After latching data, the sense amp output cuts off the current path of the bit line. In the present invention, the memory cells are formed in between the routing layers. Hence the memory cells can be stacked over the peripheral circuits and alternatively multiple cells can be stacked.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
Electric arc additive manufacturing method of conformal cooling passage with circular cross section
ActiveCN108480821AIncrease profitShorten the timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusManufacturing cost reductionCircular dichroism
The invention relates to an electric arc additive manufacturing method of a conformal cooling passage with a circular cross section. According to the method, the inner surface of a rough machined moldis used as an additive datum plane, a consumable electrode inert gas protection electric arc additive process is adopted, an internal conformal passage with a circular cross section is manufactured through a specific conformal additive path and a specific angle, a cooling medium flows in the passage, and a flowing direction is parallel to the inner surface of a mold cavity. The method comprises the following steps of S1, designing a structure of a three-dimensional conformal passage with the circular cross section; S2, partitioning the passage structure, and milling the datum plane of a basebody; S3, carrying out additive manufacturing on the lower half part of the passage; S4, carrying out additive manufacturing on an inner wall structure and other structures of the upper half part of the passage; and S5, machining the inner surface of the mold cavity. The electric arc additive manufacturing method of the conformal cooling passage with the circular cross section provided by the invention adopts a low-cost electric arc additive manufacturing process technology for realizing high-efficient manufacturing of the complicated conformal cooling passage of the large-size mold, and has the characteristics that raw materials are saved, the manufacturing cost is reduced, the mold cooling efficiency is high, the cooling uniformity is good, and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Integrated center rail dispenser
InactiveUS20070033960A1Reduce wiringReduce plumbing complexityLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsEngineeringCold store
A refrigeration appliance is provided which includes a cabinet with a first openable door providing access to a first refrigeration compartment and a second openable door providing access to a second refrigeration compartment. The second openable door has a portion thereof positioned below a portion of the first openable door. A rail separates the first refrigeration compartment and the second refrigeration compartment. A water dispenser is contained in the rail, as well as electronic controls for the refrigeration appliance. The dispenser is arranged to be stationary relative to the refrigeration appliance while the doors are open or closed. The rail may be removed and replaced, and with the water and electronic controls located in the rail, repairs are performed more efficiently and flexibility in manufacturing is enhanced. A drip tray is formed in an exterior side of the second openable door below the dispenser. When the door is opened, the drip tray moves away from the dispenser, permitting the dispenser to be used with larger receptacles than can be accommodated with the drip tray under the dispenser.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Technique and device for simultaneously removing malodor of multiple gas mixture
InactiveCN101259367AManufacturing flexibilityFlexible assemblyDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementFiltrationEngineering
The invention discloses an odor biological treatment process and a device in environmental engineering, meanwhile, the invention discloses a process for removing a plurality of mixed obnoxious gases and a device, which is characterized in that a trickling bio-filter A is arranged, the gas to be treated is pressurized by a draught fan to be delivered to an air pretreatment device, then the gas enters into a gas distributor at the lower part of the trickling bio-filter A, thereby carrying out the reactions of filtration, adsorption, degrading and biochemical when passing through a biological carrier and removing H2S; a trickling bio-filter B is arranged, the gas comes from the top of the trickling bio-filter A and enters into the trickling bio-filter B from the bottom of the trickling bio-filter A, which can pass through the biological carrier to remove volatile organic compounding exhaust gases; the trickling bio-filter A and the trickling bio-filter B are respectively provided with a spraying liquid A and a spraying liquid B, and the spraying liquid A and the spraying liquid B enter into the biological carrier from top to down. The process and the device have the advantages that the obnoxious gases are removed with different grades; the device is flexible and convenient to manufacture, assembly and disassembly with low cost; the trickling bio-filter B is provided with a multi-grade biological carrier; the trickling bio-filter A and the trickling bio-filter B are respectively sprayed with the spraying liquid A, the spraying liquid B and nutrient fluid thereof, which is convenient to operate, easy to adjust and are capable of removing a plurality of obnoxious gases with good treatment effect and strong ability against load impacts.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of flexible sensor
ActiveCN108007480AWell combinedImprove stabilityRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsSurface modificationAutomatic processing
The invention relates to a preparation method of a flexible sensor, which comprises the following steps: modifying carbonated polymer on part of the surface of a flexible matrix to form a carbonated polymer layer; irradiating at least part of the carbonated polymer layer with laser to realize in-situ carbonization and form a sensing element; and electrically connecting at least two positions of the sensing element to form electrodes, and then, obtaining a flexible sensor. The method of the invention has the advantages of low cost, strong universality, flexible design, simple manufacture, automatic processing and good technological controllability. The flexible sensor prepared is multifunctional and highly sensitive.
Owner:深圳感碳科技有限公司
Copper line-clad aluminum silicon carbide ceramic substrate applicable to radiation of high-power LED
InactiveCN102569625AImprove thermal conductivityImprove thermal stabilitySemiconductor devicesCopperPorous silicon carbide
A copper line-clad aluminum silicon carbide ceramic substrate applicable to radiation of a high-power LED is characterized by consisting of an aluminum silicon carbide layer (1), a copper and aluminum oxide layer (2) and copper lines (3), wherein the copper and aluminum oxide layer (2) is arranged on the alumina layer (1); the copper lines (3) are arranged on the copper and aluminum oxide layer (2); the distance between the copper lines (2) is 0.1-1mm; the widths of the copper lines (2) are 200-1000 microns; the heights of the copper lines (2) are 0.01-2mm; the copper line-clad aluminum silicon carbide ceramic substrate is manufactured by the following steps: weighing SiO2, coke and a fluxing agent, and preparing the raw materials into porous silicon carbide; heating an aluminum block and melting the aluminum block into liquid aluminum, mixing the liquid aluminum with the porous silicon carbide in a certain ratio, and preparing the mixture into aluminum silicon carbide powder and a high-thermal conductivity aluminum silicon carbide substrate; cladding copper on the aluminum silicon carbide substrate, heating at a high temperature to form an eutectic melt, and forming an aluminum silicon carbide ceramic substrate layer, the copper and aluminum oxide layer and a copper layer from the bottom up; and etching conductive copper lines. The ceramic substrate has a good application prospect in the aspect of the radiation of the high-power LED.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
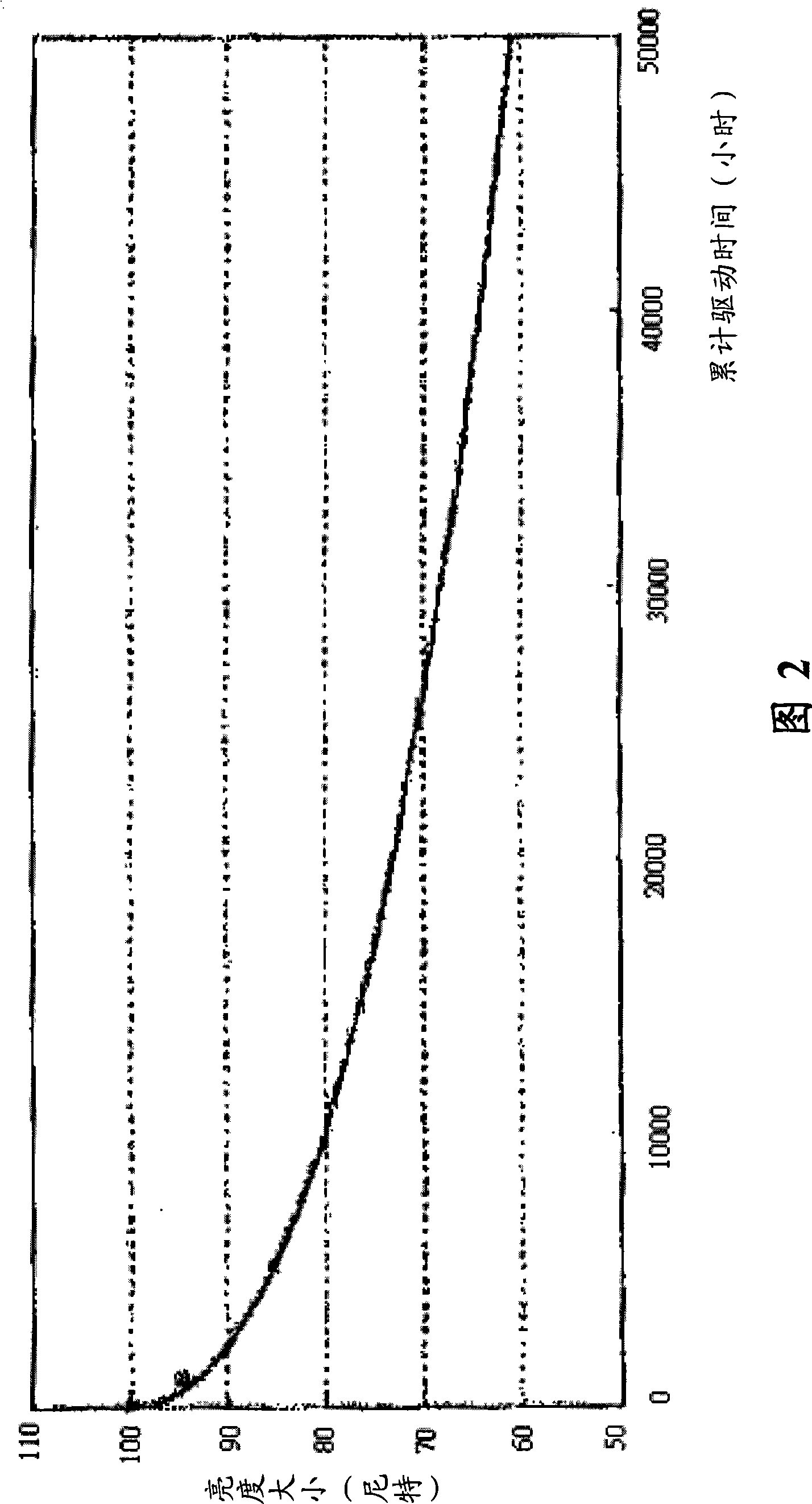
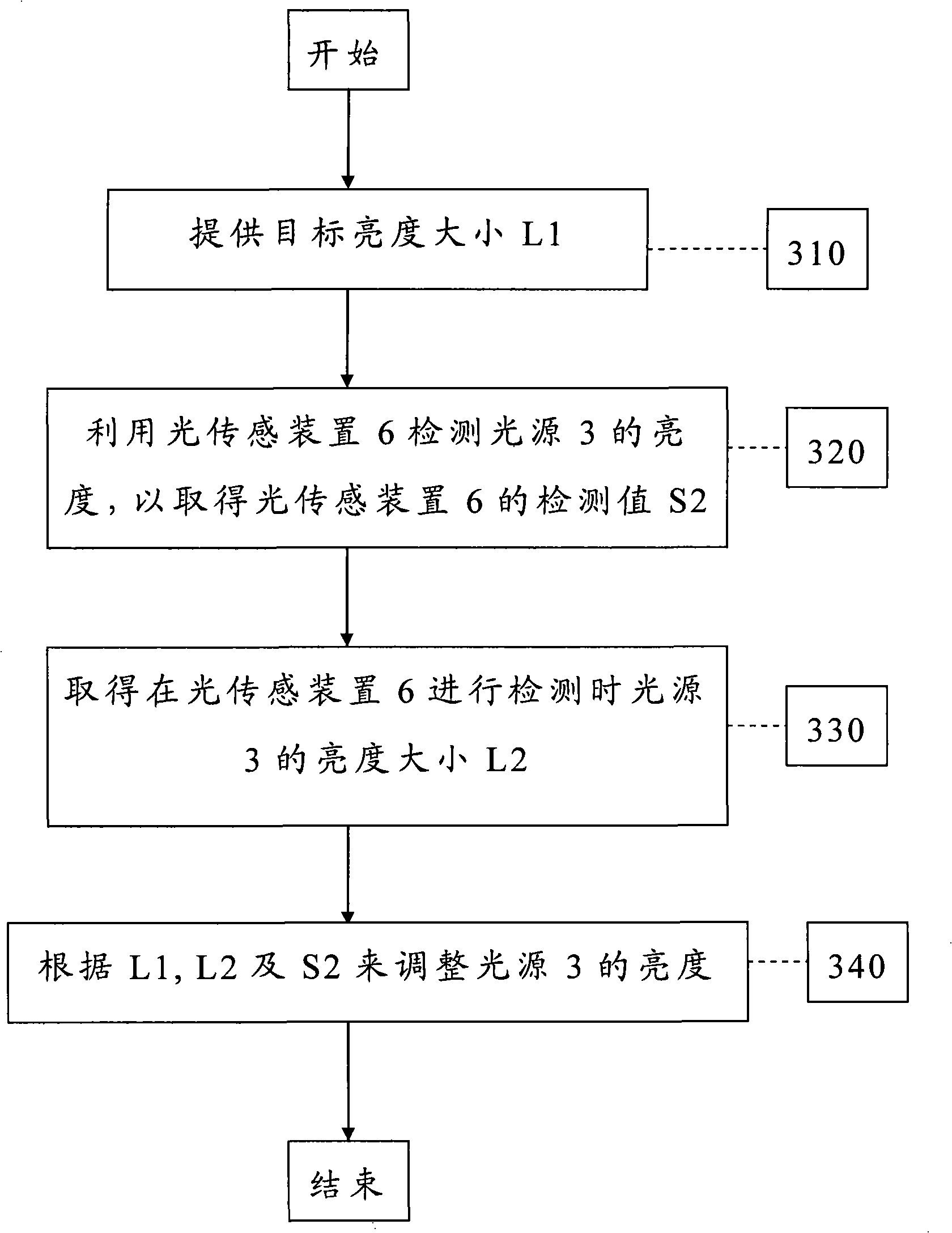
Display apparatus and luminance correction method thereof
InactiveCN101334967AEasy to adjustManufacturing flexibilityElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceCorrection method
The invention relates to a gamma correction method, used for a display device which comprises a light source. First, an object brightness value L1 is provided. Then, an optical sensor is utilized to detect the brightness of the light source so as to obtain a detection value S2 of the optical sensor. Then, a brightness value L2 of the light source when the optical sensor is in the process of detection. Finally, the brightness of the light source is adjusted according to L1, L2 and S2.
Owner:BENQ CORP
Method of manufacturing microlens, microlens, optical film, screen for projection, and projector system
InactiveUS20050088750A1Shape can be reduced and preventedAccurate shapeProjectorsOptical articlesEngineeringMicrolens
Exemplary embodiments of the present invention provide an optimal manufacturing method of a microlens to diffuse light. According to exemplary embodiments, a manufacturing method of microlens includes forming a generally convex shaped lens portions made from a light transmissive resin on a substrate having light transmissivity, and curing the lens portions, forming the lens portions being a process in which a plurality of the lens portions are formed so as to be coupled on the substrate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Automatic awning of automobile
InactiveCN102069700AReduce labor intensityGood shading effectRemovable external protective coveringsEngineering
The invention relates to an automatic awning of an automobile. The awning comprises an awning bracket, an awning remote controller, a power supply, a controller, a blowing device, a furling and stretching motor, a furling main shaft, front sun cloth and rear sun cloth, wherein the power supply, the controller and the blowing device are all arranged on the awning bracket; the power supply is connected with the controller, the blowing device, the furling and stretching motor and the furling main shaft; the awning remote controller is in communication connection with the controller; the furling and stretching motor is in driving connection with the furling main shaft; and one end of the front sun cloth and one end of the rear sun cloth are fixedly connected with the furling main shaft respectively. Compared with the prior art, the awning has the advantages that: the sun cloth of upper and lower layers (one or more layers) is used, and an inflation supporting net with a spatial netlike structure is arranged between the two layers of sun cloth, so that the shape of the sun cloth is determined; because the remote controller, the controller, the motor, the power supply, the blowing device and the like are used, when a driver presses down the remote controller, the awning can be automatically unfolded and fixed to play a good role in sunshade, and labor intensity of workers is greatly lightened.
Owner:程娟萍
Low-pressure casting one-step method for manufacturing semi-solid light alloy castings
The invention discloses a low-pressure casting one-step method for manufacturing semi-solid light alloy castings, and belongs to the field of semi-solid metal processing. A device for the method comprises a crucible resistance furnace, a liquid raising tube, a low-pressure sealing platform, a light alloy crystal leading channel, a sealing barrel, a connecting base, a mold fixing platform and a metal mold. According to the low-pressure casting one-step method, molten alloy with the temperature 15-35 DEG C higher than a liquid phase line flows through the light alloy crystal leading channel with strong chilling capacity under the gas pressure action and then is brought into a casting mold under the gas pressure action, and the castings of a small ball-shaped semi-solid structure are obtained finally. According to the low-pressure casting one-step method, light alloy semi-solid slurry is prepared in the process of mold filling and pouring in a one-step mode; a device special for transporting and preparing the light alloy semi-solid slurry is omitted; and the problems of slurry oxidization in the transportation process and control difficulty of slurry temperature in the process of slurry preparation in a traditional method of manufacturing the semi-solid light alloy castings are solved.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF FOUNDRY
Hydrogen water preparation method and device, bottled water production line and water purifier or water dispenser
ActiveCN105923712AImprove the mixing effectTiny hydrogen bubblesWater/sewage treatment apparatusProduction lineElectrolysis
The invention aims at providing a hydrogen water preparation method and device, a bottled water production line and a water purifier or water dispenser which mainly solve the problems that hydrogen water prepared through an existing preparation method is poor in quality and drinking safety. The hydrogen water preparation method comprises the steps that a proton membrane and a cathode and an anode which are located on the two sides of the proton membrane are supplied; the cathode and the anode are electrified, and water is introduced into only one side of the cathode; part of the water is electrolyzed to generate hydrogen on the cathode side and generate oxygen on the anode side; the generated hydrogen is mixed with the water on the cathode side to form the hydrogen water. The hydrogen water prepared through the hydrogen water preparation method has the advantages of being fine in hydrogen bubble, high in hydrogen-enriched level and free of introduced contaminants; meanwhile, due to the fact that the generated hydrogen is uniformly distributed on the electrodes making contact with the water, the water-hydrogen mixing effect is good, and hydrogen enriching is better promoted; in addition, hydrogen generated through electrolysis has more activity and not only can be used for preparation in a large hydrogen water plant but also can be used for site production of small household water dispensers.
Owner:合肥高新区太空科技研究中心 +1
Electronic label reading and writing device antenna and a RFID system
ActiveCN101359767AEasy to installReduce the impactAntenna arraysAntenna supports/mountingsEnvironment effectRadio frequency signal
The invention discloses an electronic tag reader antenna and an RFID system, wherein, the antenna is used to be connected with a reader, and the reader transmits ultra high frequency radio frequency signals through the antenna for activating an electronic tag to communicate with the reader; the antenna can be composed of an antenna radiating element or a plurality of antenna radiating elements connected in series, the front face of each antenna radiating element is provided with a micro-strip line, and the back face thereof is equipped with a ground plane. The antenna is less influenced by installation environment, and facilitates the flexible making and installation, and is simple and practical, and the antenna can be placed in an extreme narrow space, and the reader can communicate with a plurality of passive UHF frequency band RFID electronic tags placed in the extreme narrow space via the antenna stably and correctly. The antenna and the system particularly solve the problem that the plurality of passive UHF frequency band RFID electronic tags in the narrow space can not be read stably and correctly under the condition that the extreme narrow space is enclosed by large area of metal.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 7 RES INST
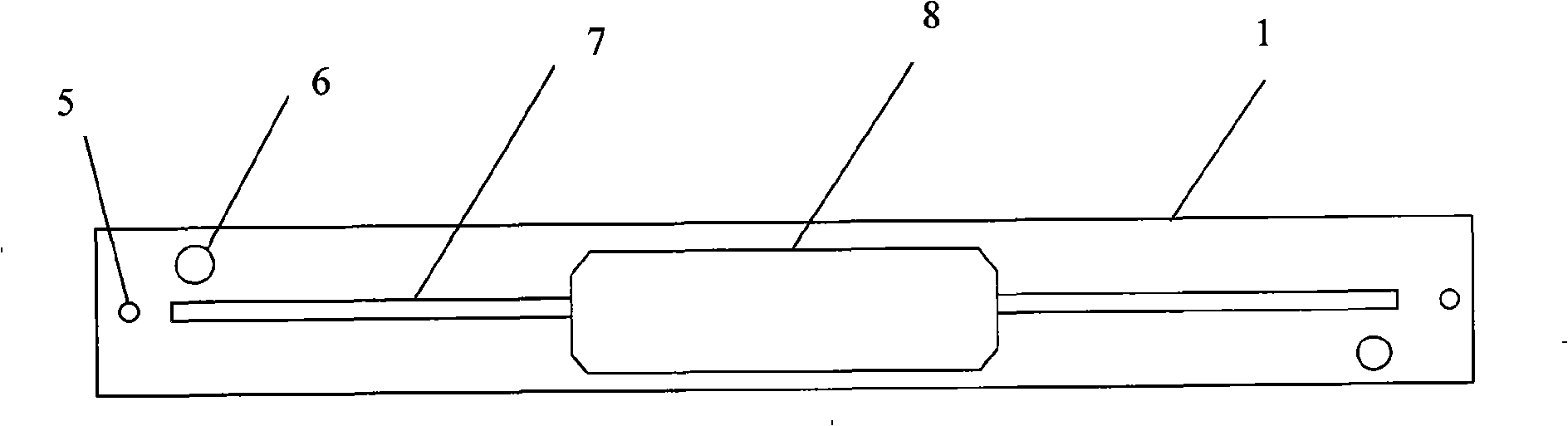
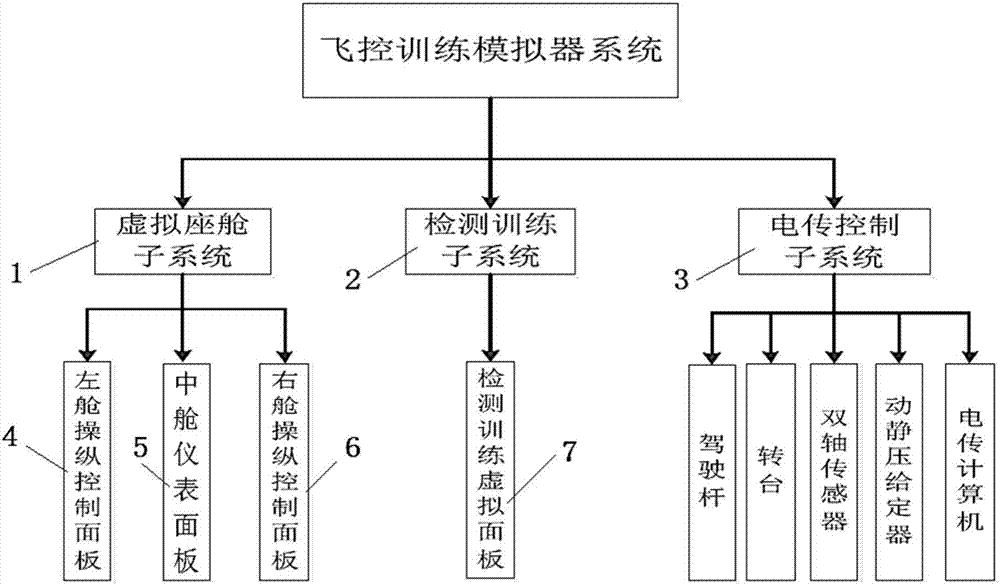
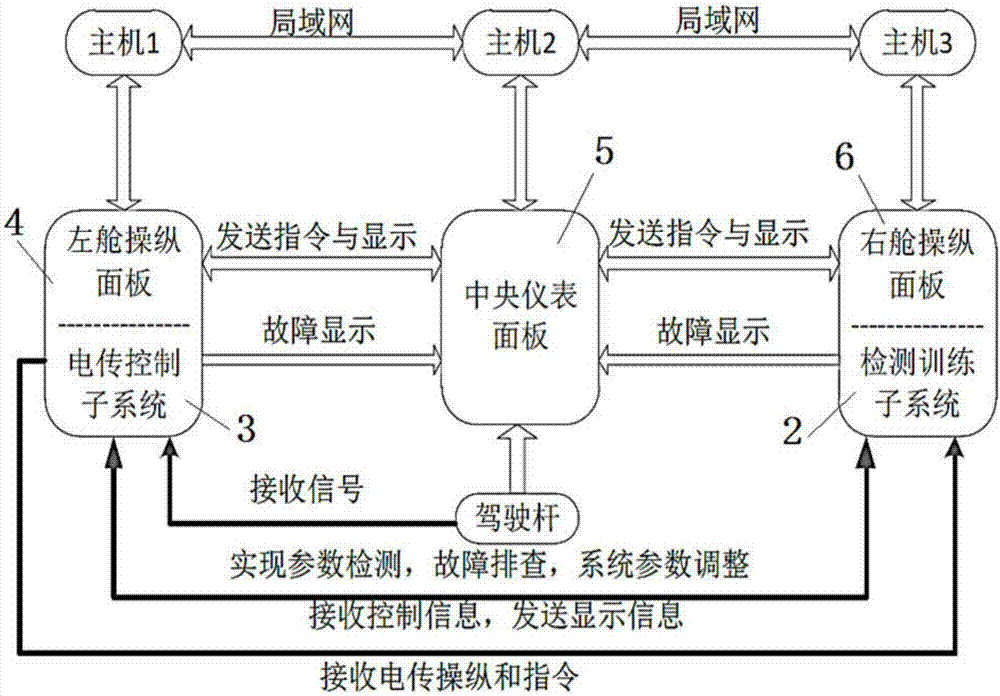
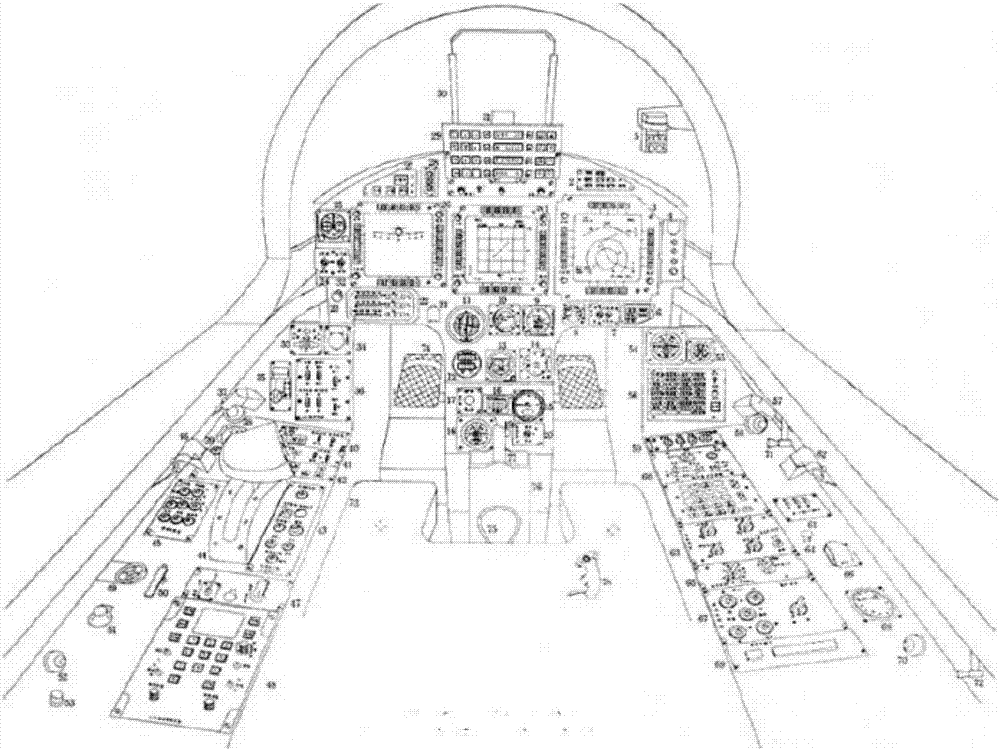
Piloting simulator system and simulation method
InactiveCN106934132AImprove real-time performanceImprove reliabilityGeometric CADCosmonautic condition simulationsTelexReusability
The invention discloses a piloting simulator system and a simulation method. The system consists of a virtual cabin subsystem, a detection training subsystem and a telex control subsystem, wherein the virtual cabin subsystem comprises a left cabin steering control panel, a middle cabin instrument panel and a right cabin steering control panel around a piloting seat; a telex control subsystem is carried on the left cabin steering control panel; the telex control subsystem comprises a steering rod and a plurality of virtual sensors; a detection training subsystem is carried on the right cabin steering control panel; the middle cabin instrument panel sends instructions to the left cabin steering control panel and the right cabin steering control panel, and displays the instructions; parameter adjustment and detection and troubleshooting are realized between the detection training subsystem and the telex control subsystem; and fault information is displayed through the middle cabin instrument panel. The simulation method comprises the steps of setting attributes for controls, respectively compiling behavior codes and realizing all the basic functions, so that the expandability of system functions and the reusability of codes can be ensured.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of manufacturing plastic metallized three-dimensional circuit
InactiveUS20130126465A1Reduce material costsManufacturing flexibility3D rigid printed circuitsPrinted circuit aspectsMiniaturizationEngineering
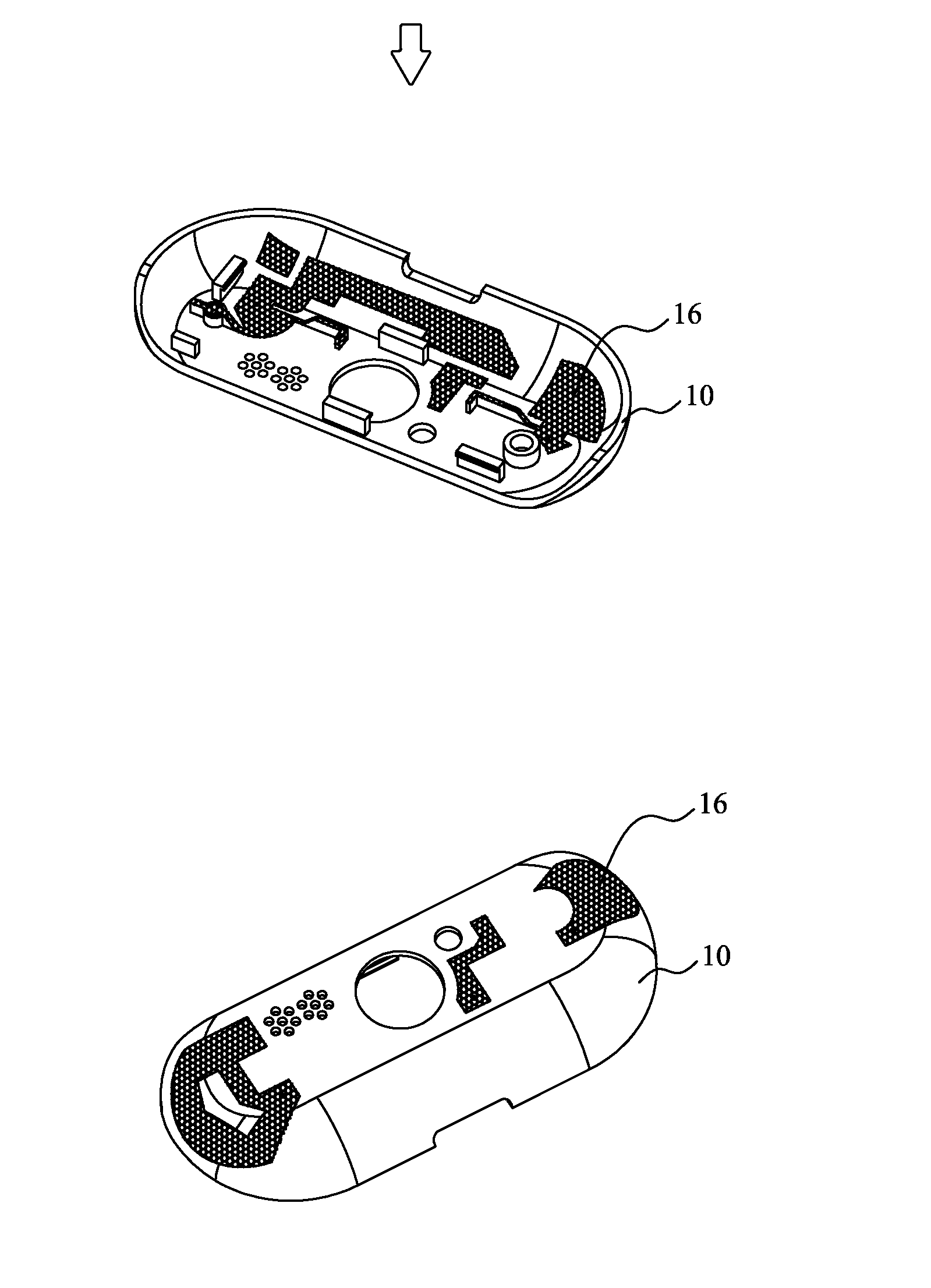
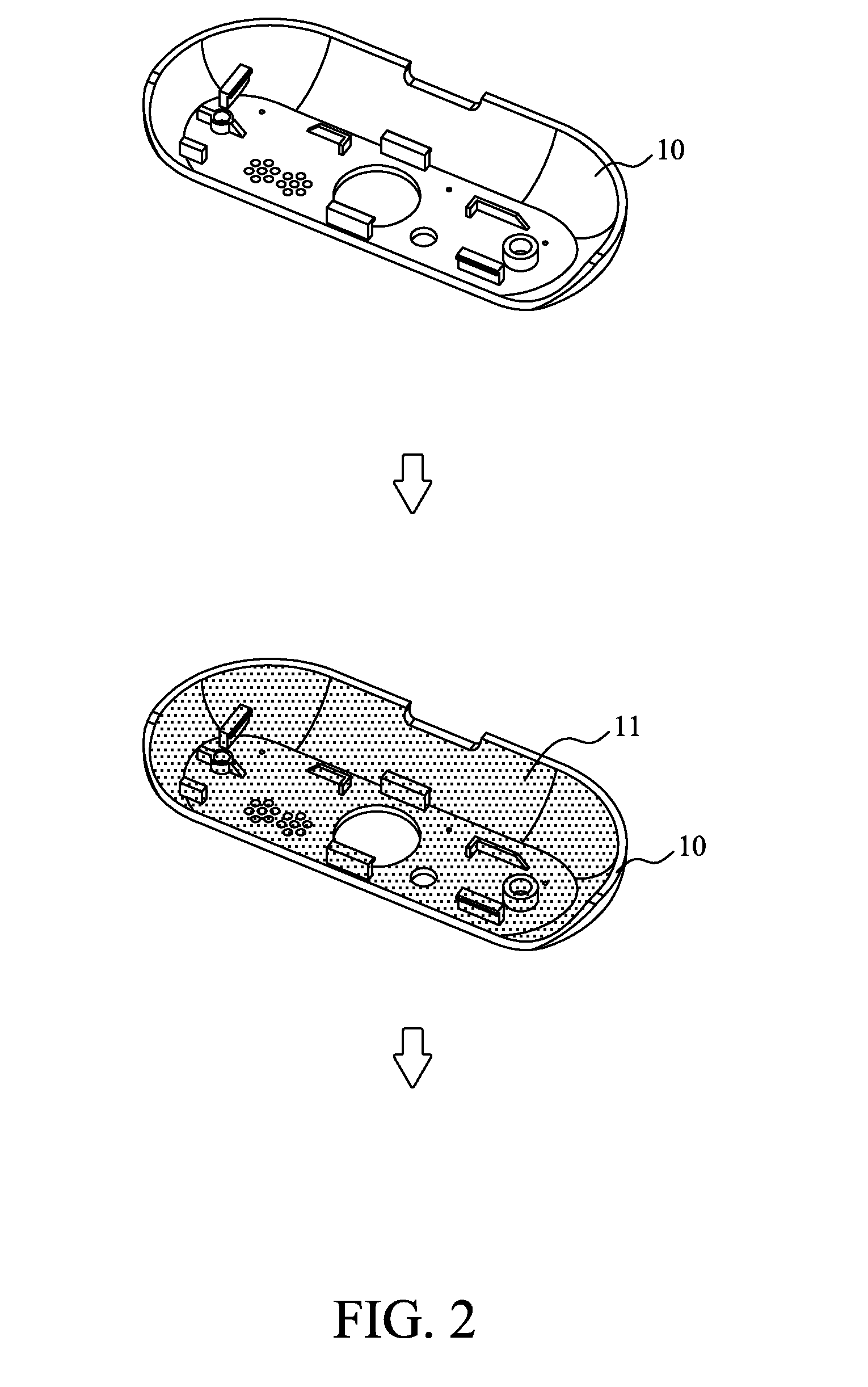
A method of manufacturing plastic metallized 3D circuit includes the steps of providing a 3D plastic main body; performing a surface pretreatment on the plastic main body; performing a metallization process on the plastic main body to deposit a thin metal film thereon; performing a photoresist coating process to form a photoresist protective layer on the thin metal film; performing an exposure and development process on the photoresist protective layer to form a patterned photoresist protective layer; performing an etching process on the exposed thin metal film to form a patterned metal circuit layer; stripping the patterned photoresist protective layer; and performing a surface treatment on the patterned metal circuit layer to form a metal protective layer. With the method, a 3D circuit pattern can be directly formed on a 3D plastic main body without providing additional circuit carrier to thereby meet the requirement for miniaturized and compact electronic devices.
Owner:CHUAN LING HU +1
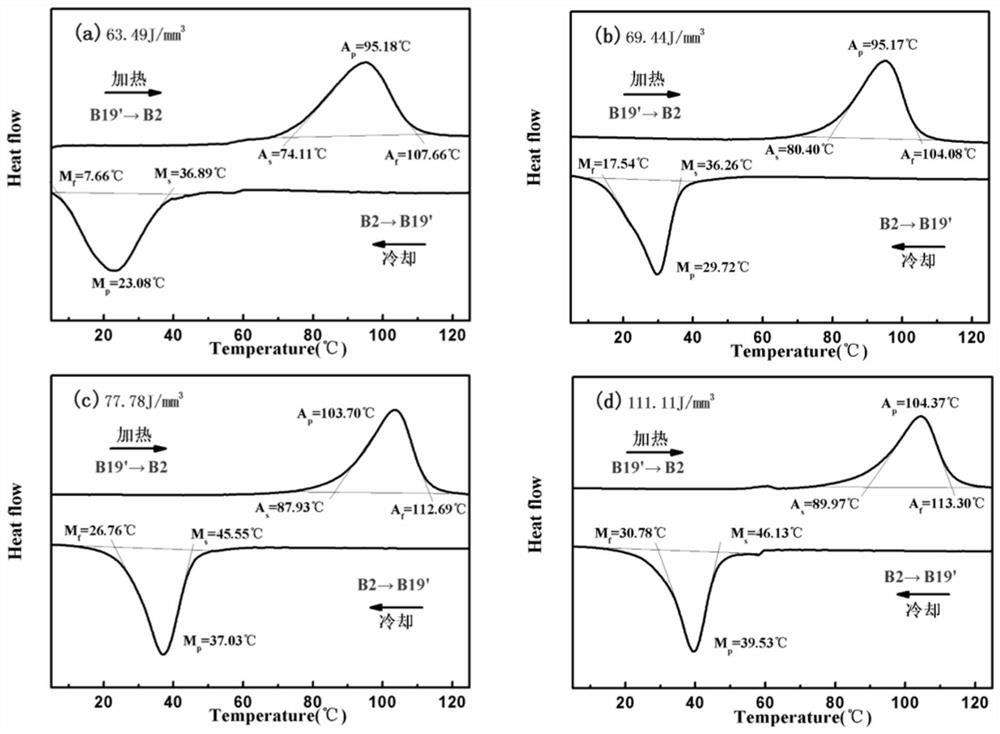
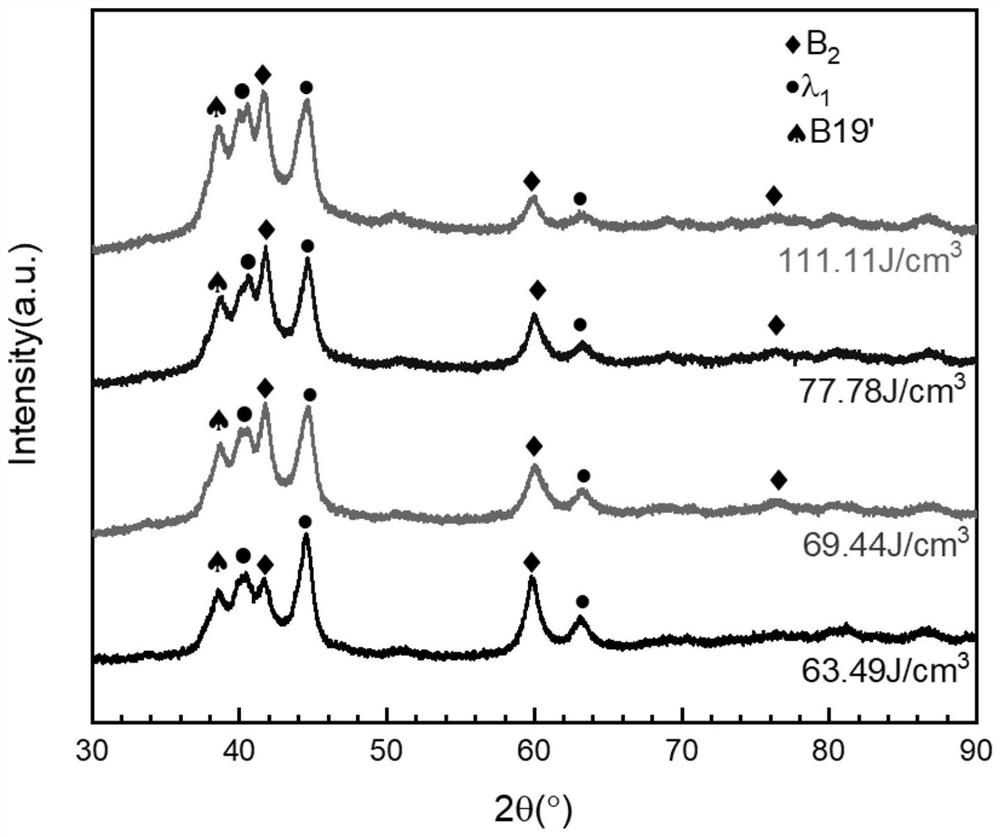
4D printing method of nickel-titanium-based ternary shape memory alloy
InactiveCN111842888AHas shape memory effectRaise the transition temperatureAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingBinary alloy
The invention belongs to the technical field of 4D printing additive manufacturing, and discloses a 4D printing method of a nickel-titanium-based ternary shape memory alloy. The 4D printing method ischaracterized in that a selective laser melting technology is adopted for printing gas atomized prefabricated NiTiZr ternary alloy powder, and a component obtained through printing has the shape memory function; and the laser energy density is changed by changing the technological parameters adopted in the selective laser melting technology, and therefore the changes of the structure and performance of the printed piece are regulated and controlled. According to the 4D printing method, the ternary component Zr is introduced into an existing nickel-titanium binary alloy, the martensite phase transformation temperature is obviously increased, the selective laser melting technology is adopted for forming, and complex parts uniform in structure and high in density can be obtained while the excellent shape memory performance and mechanical performance are guaranteed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser engraving and 3D printing integrated advertising character manufacturing equipment and manufacturing method
InactiveCN105665939AThe production process is simpleManufacturing flexibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusLaser engravingEngineering
The invention provides a laser engraving and 3D printing integrated advertising character manufacturing equipment and manufacturing method. The manufacturing equipment comprises a framework, first linear guide rails, a second linear guide rail, a printing spray head component, a laser engraving device, an X-axis driving mechanism, a Y-axis driving mechanism, a Z-axis driving mechanism and a working table, wherein the first linear guide rails are distributed in the Y-axis direction and mounted on the left side and the right side of the framework respectively; the second linear guide rail is distributed in the X-axis direction and arranged on the first linear guide rails in a sliding manner; the printing spray head component is arranged on the second linear guide rail in a sliding manner; the laser engraving device comprises a laser tube and a laser head component; the X-axis driving mechanism drives the printing spray head component and the laser head component to slide along the second linear guide rail; the Y-axis driving mechanism drives the second linear guide rail to slide along the first linear guide rails; the working table is positioned below the printing spray head component and the laser head component correspondingly; the Z-axis driving mechanism drives the working table to move along the Z-axis. The advertising character manufacturing equipment provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple and flexible in manufacturing process.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method for copper oxide nano line array film
InactiveCN102181831ABroaden the field of applicationExpand scopeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAir atmosphereMaterials preparation
The invention belongs to low-dimensional nano material preparation and application field of nano technology, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a copper oxide nano line array film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sputtering a metal copper film on an FTO substrate by adopting a magnetron sputter plating method, and then annealing the prepared film under air atmosphere, thus obtaining the copper oxide nano line array film. In the preparation method, the controllability is good, the preparation is flexible, the preparation method is not limited to prepare substrate materials, the scale production in the industry can be conducted conveniently, and the application field and scope of nano line array film can be expanded to a greater degree.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Box type indoor power distribution control device
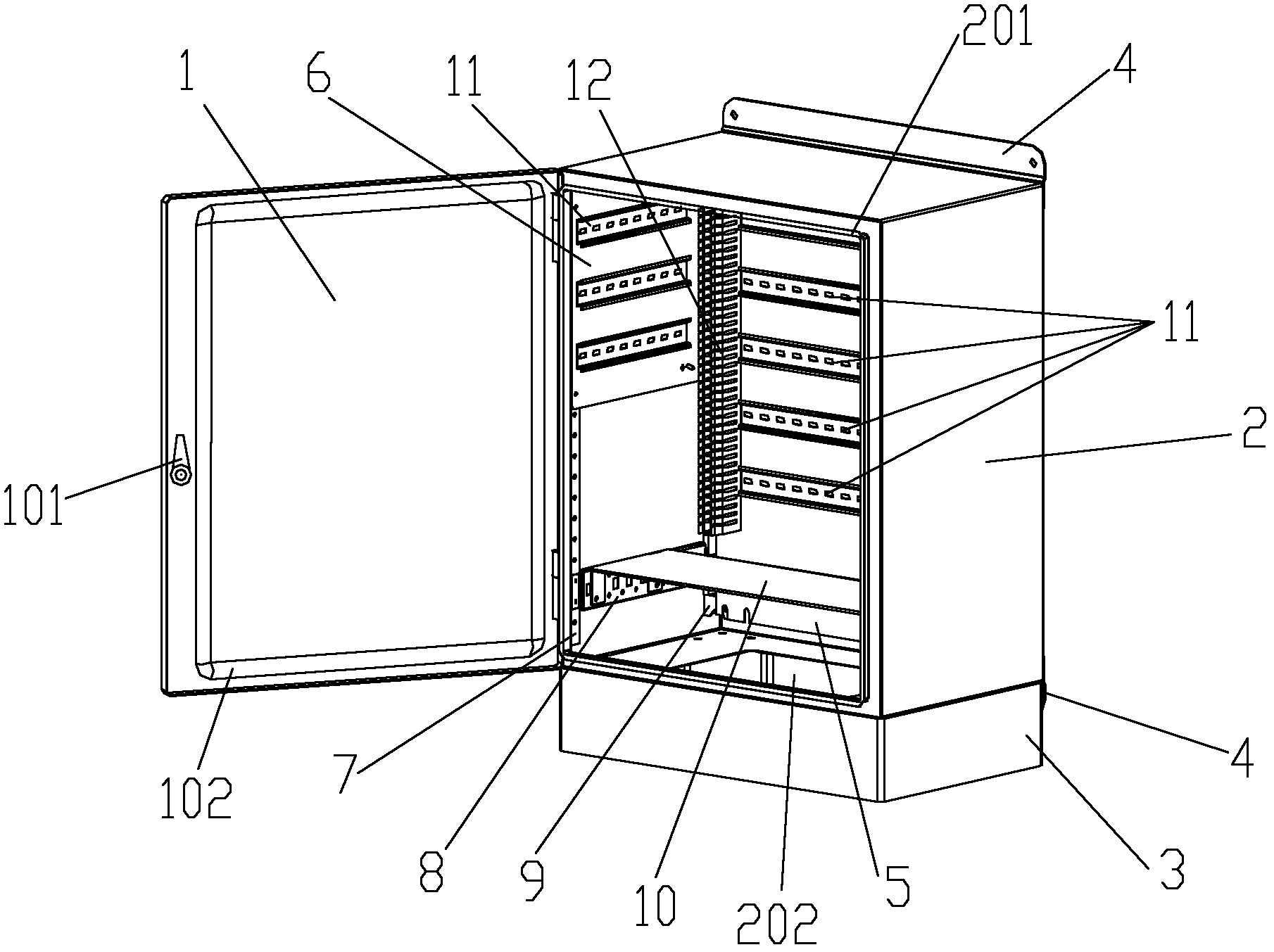
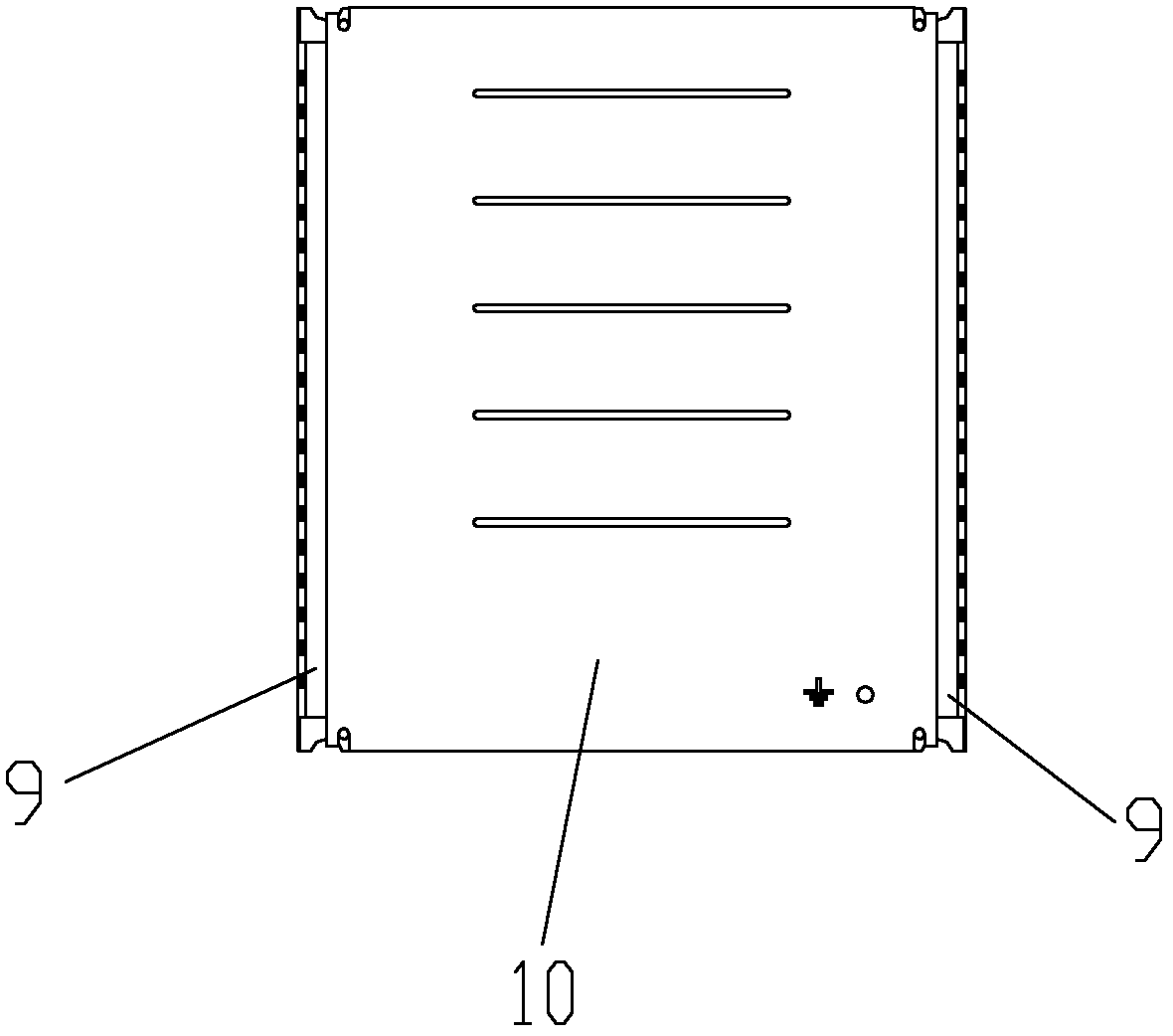
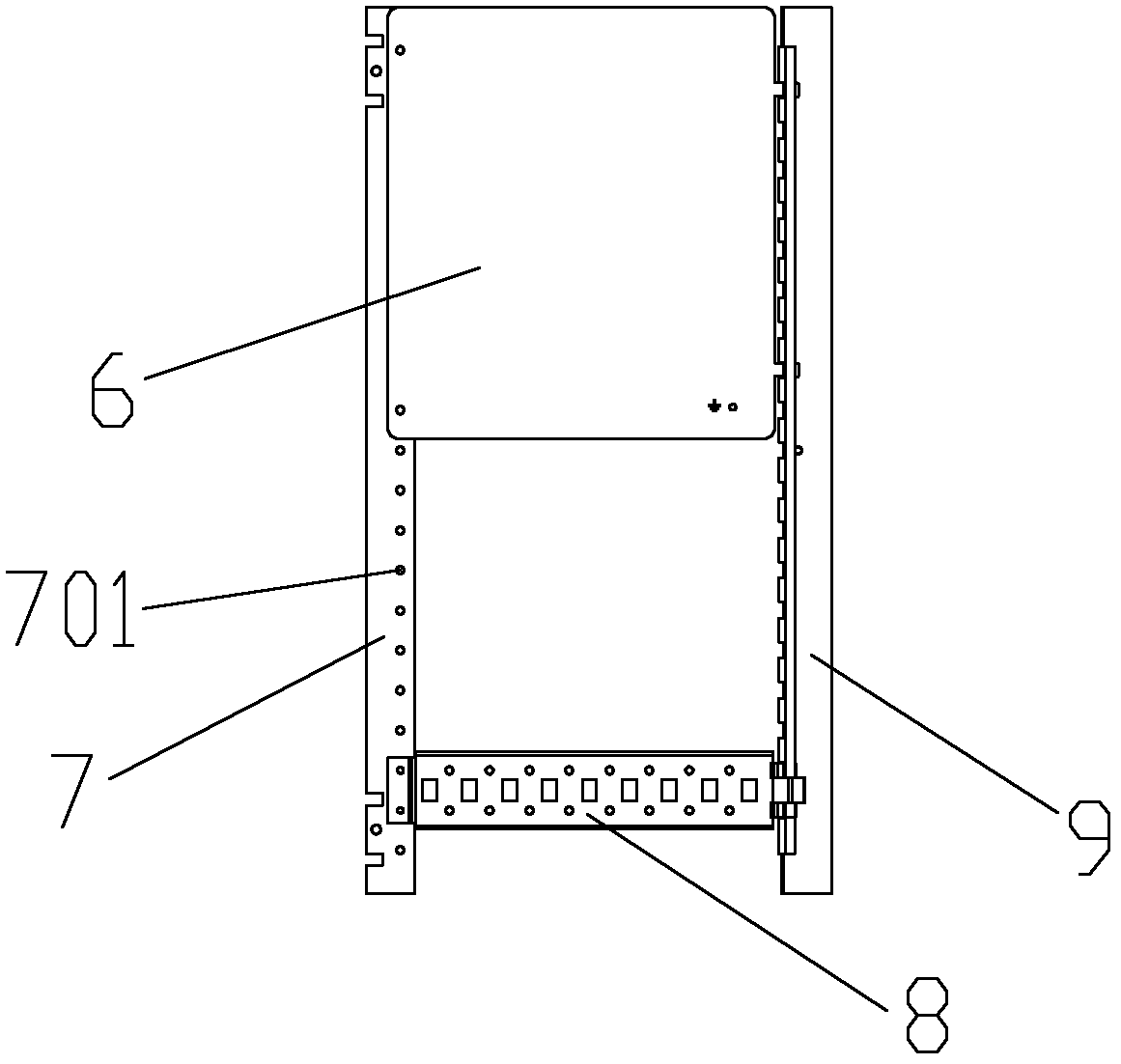
ActiveCN102623907ANovel and flexible installation methodThe mounting plate is simple and reliableSubstation/switching arrangement detailsFastenerDistribution control
The invention belongs to the technical field of power distribution equipment and relates to a power distribution control cabinet arranged and used in a power distribution room, in particular to a box type indoor power distribution control device which is a control cabinet applied to various indoor power distribution occasions for power distribution application. According to the indoor power distribution control device, a full-height rear mounting plate is fixed on a rear vertical mounting rail; both transverse ends of a half-height side mounting plate are clamped and fixed on the rear vertical mounting rail and a front vertical mounting rail; a horizontal separation plate is fixed on a side mounting guide rail; a base is fixed at the bottom of a box body; an outer mounting frame is respectively fixed on the rear bottom and the top of the body of a control box; a hook at one end of the half-height side mounting plate is clamped and fixed in a clamping port of the rear vertical mounting rail, while the other end of the half-height side mounting plate is fixed on a through hole of the front vertical mounting rail by using a fastening piece; and an element guide rail and a grounding bolt are transversely and vertically fixed on the half-height side mounting plate. The indoor power distribution control device has the advantages of simplicity in the integral structure, flexibility in preparation, use and mounting, good adaptability, stability in structural safety, simplicity and convenience in an assembly process and man power and financial resource saving and is suitable to be arranged in various indoor occasions.
Owner:QINGDAO ITECHENE TECH CO LTD
Electronic circuit device and method for manufacturing same
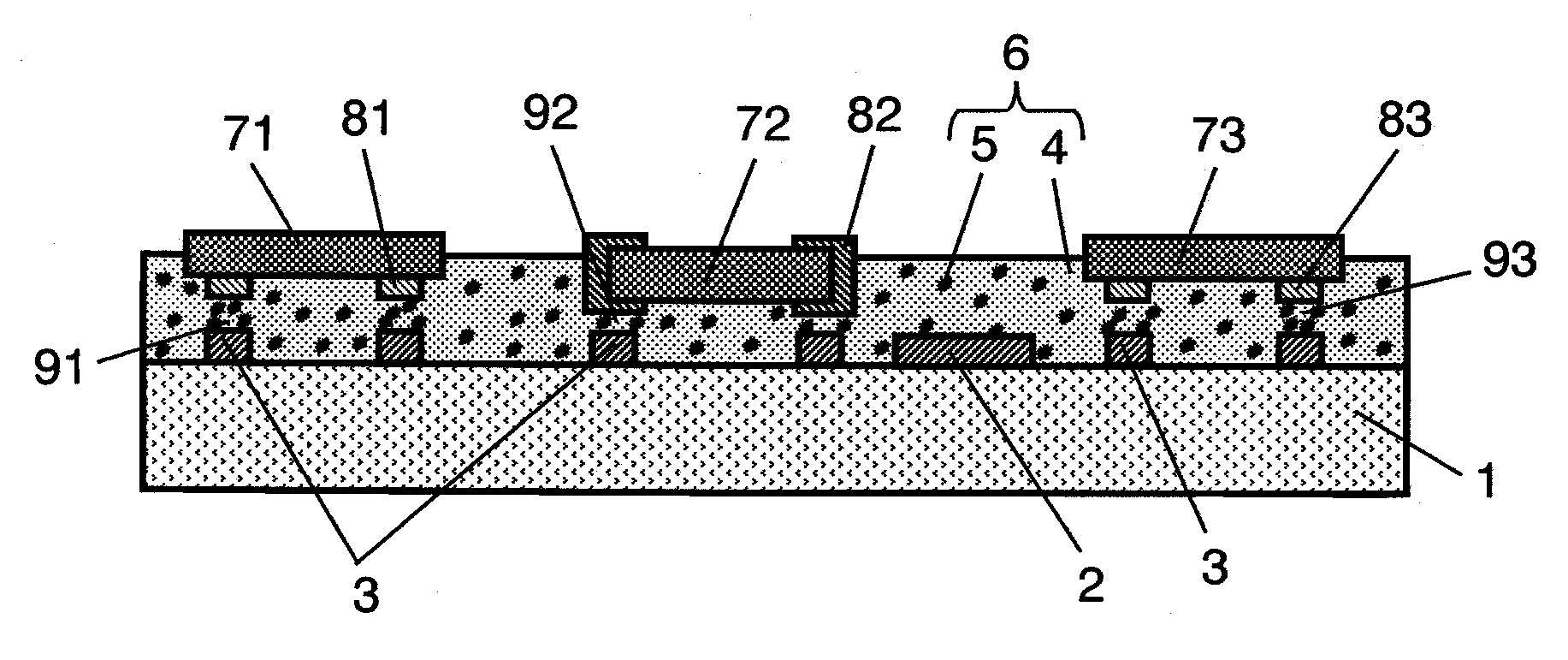
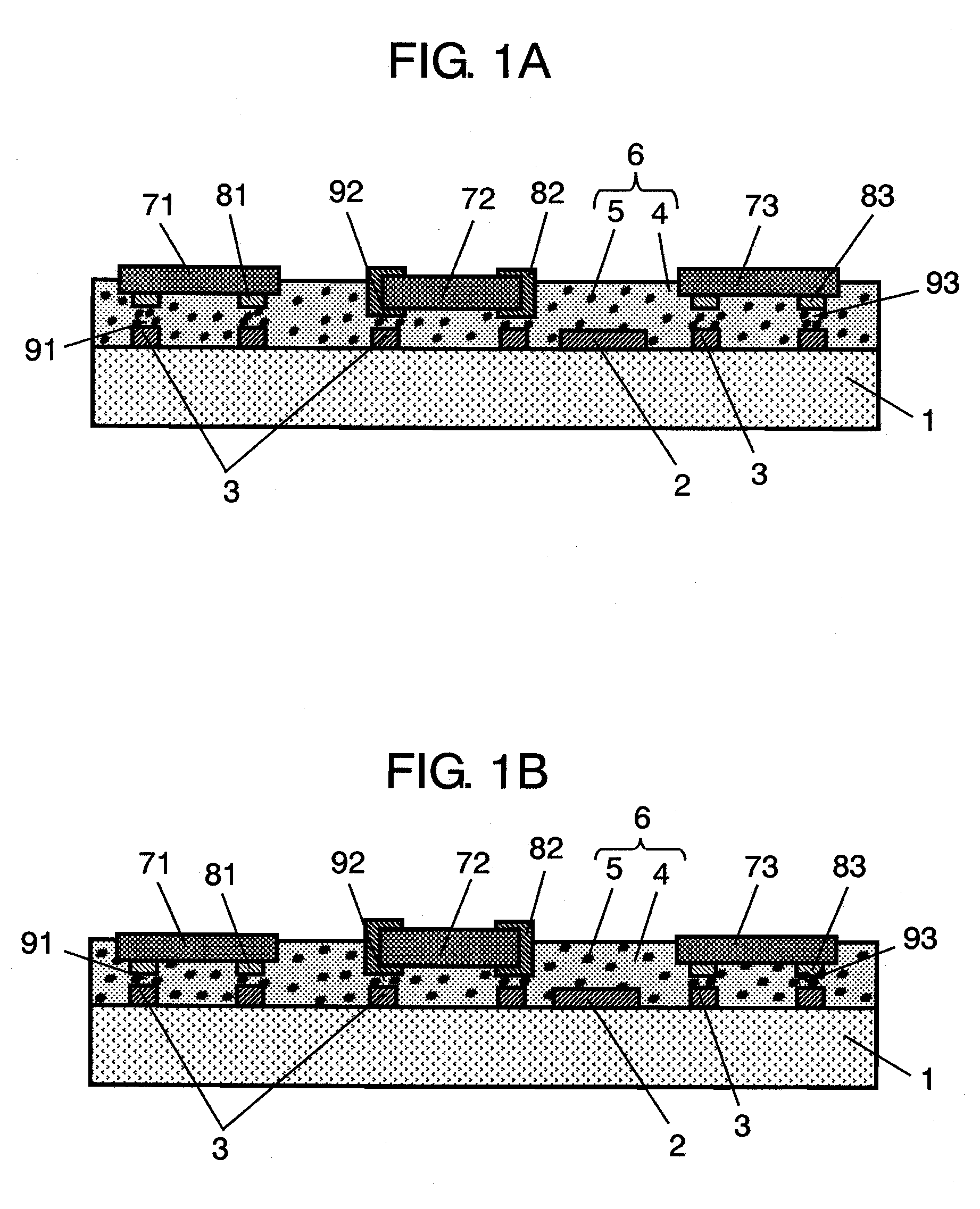
InactiveUS20090133900A1Simplify manufacturing stepsLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFiberElectrical conductor
Circuit board having conductor wiring and connection terminal; anisotropic conductive resin layer provided on one surface of circuit board; and plurality of electronic components respectively provided with electrode terminals in positions facing the connection terminal are included. The anisotropic conductive resin layer includes at least one kind of conductive particles selected from coiled conductive particles, fiber fluff conductive particles and conductive particles provided with a plurality of conductive protrusions, and resin binder; electrically couples electrode terminals of plurality of electronic components to connection terminals to each other with conductive particles; mechanically fixes electronic components and circuit board to each other; and protects conductor wiring.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com