Low speed magnetic floating system F rail seaming structure and processing method thereof
A low-speed, maglev technology, applied in tracks, roads, buildings, etc., can solve the problems of increasing accident factors of joint structures, hidden dangers of unfavorable safe operation, and difficulty in centering adjustment, achieving simple and feasible structure, improving service life, and maintaining The effect of reduced work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
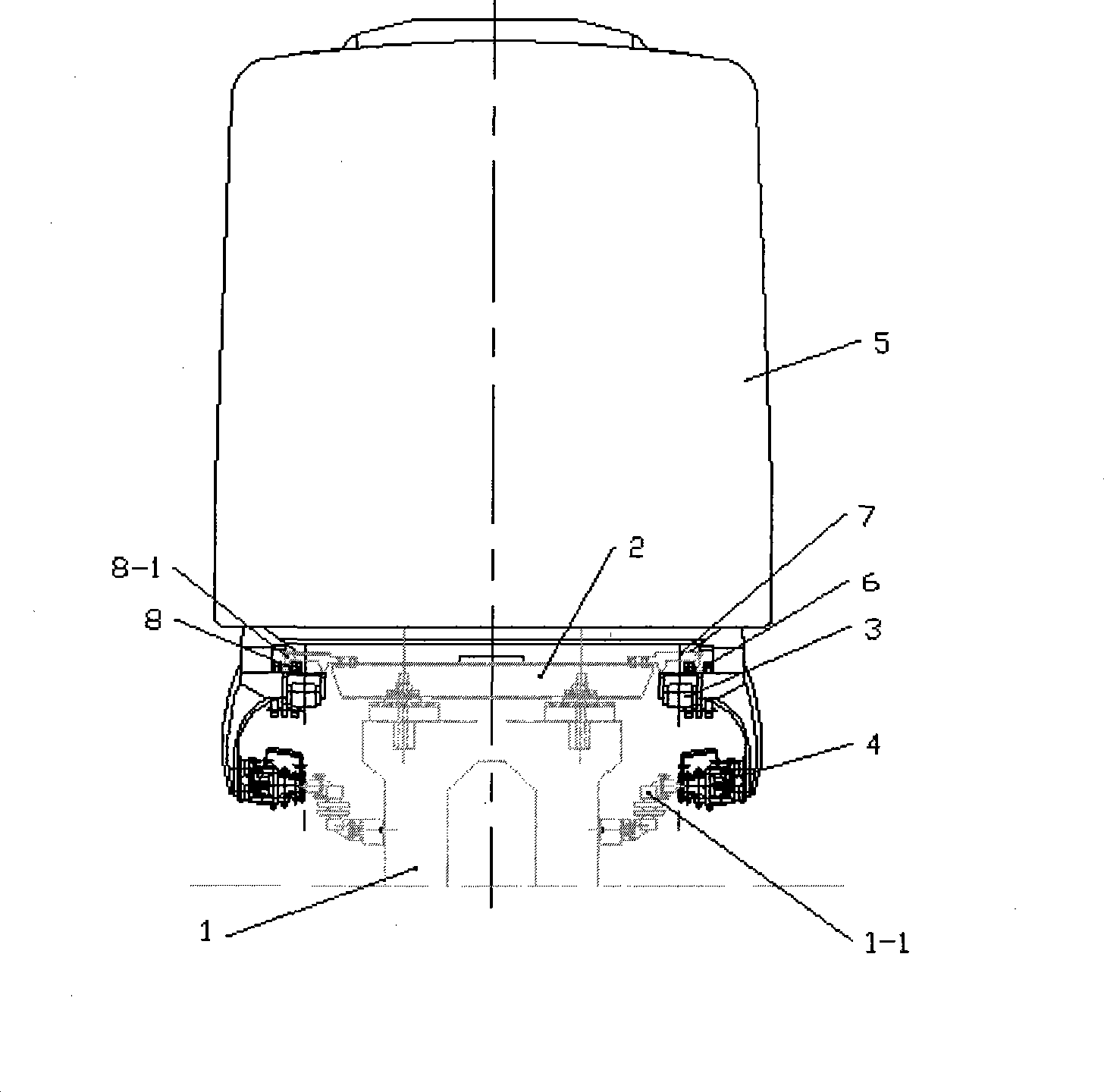
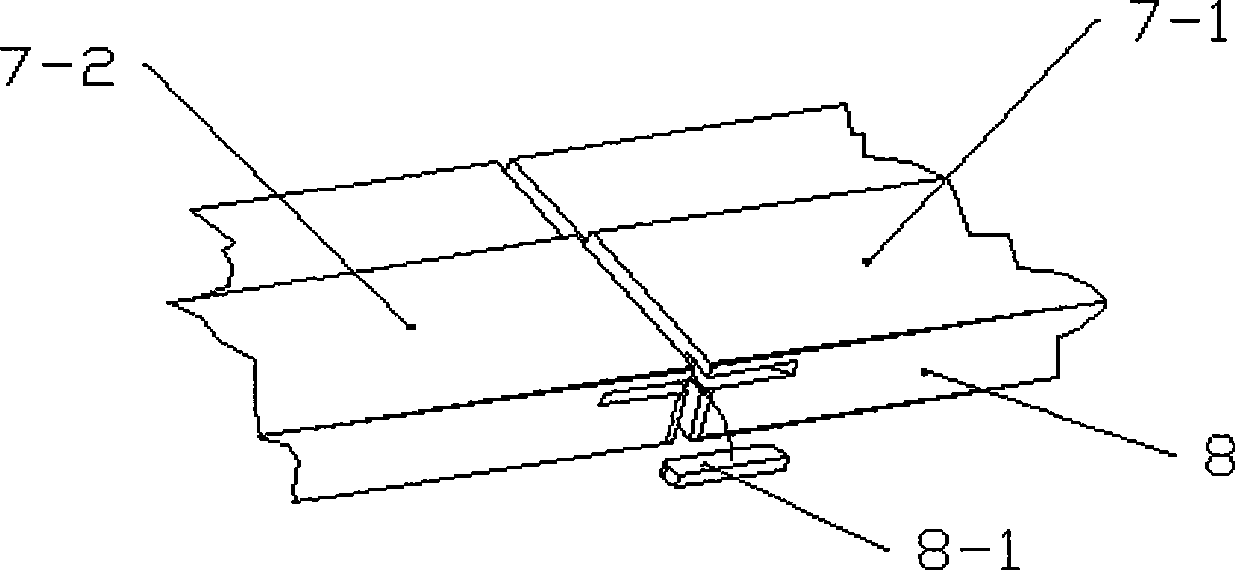
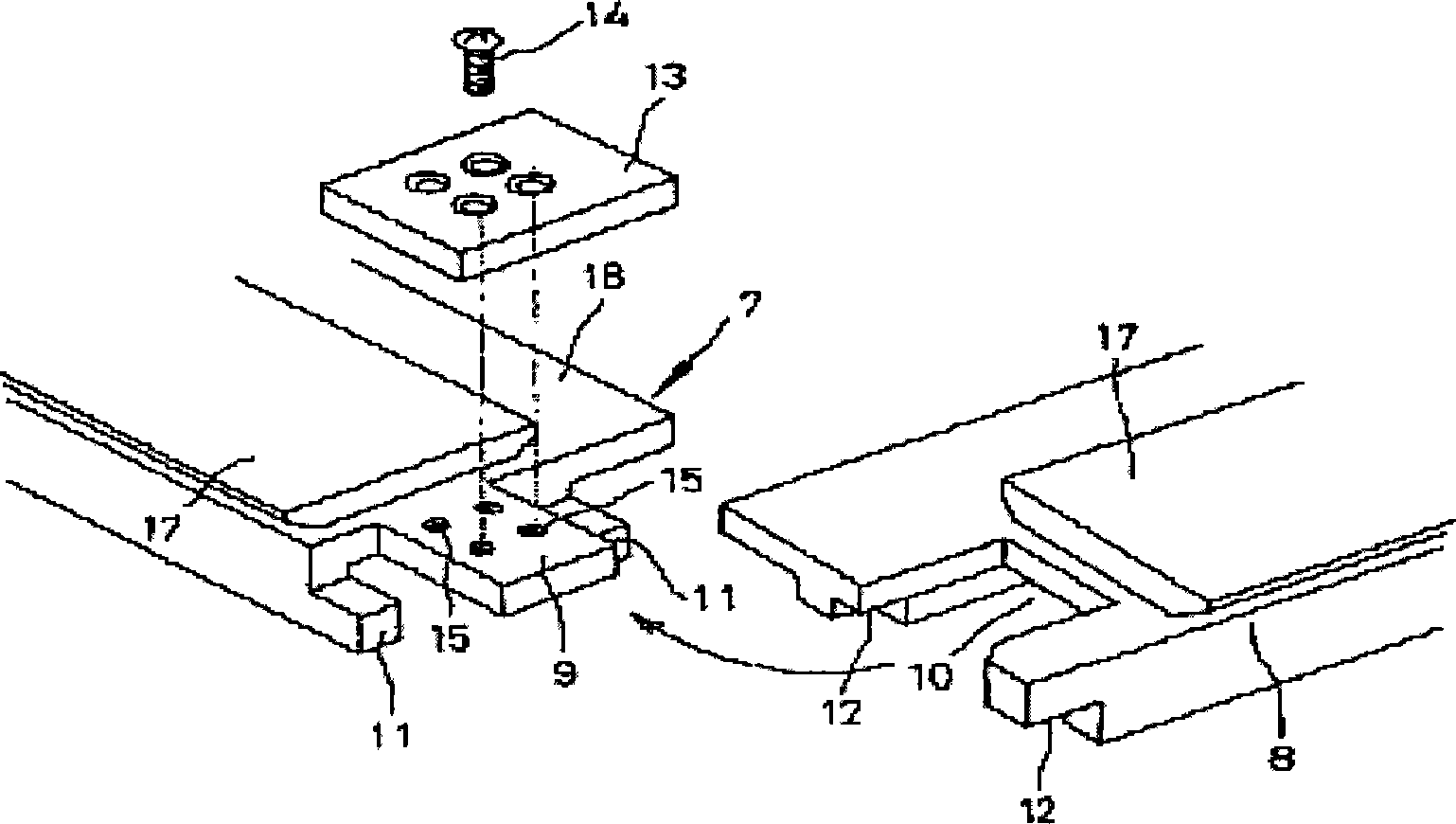
[0023] In the embodiment of the seam structure of the F rail of the low-speed maglev system of the present invention, the structure is simple and easy to process. Such as figure 1 As shown, the low-speed maglev vehicle 5 straddles the track so that the vehicle and the track have the following geometric positional relationship: the levitation magnet 3 and the F rail 7 maintain a suspension gap of 8.0mm in the vertical direction (Z direction) relative to each other, and in the horizontal direction (Y direction). ) does not have a strict guiding gap limitation, and only relies on the automatic restoring force of the suspension magnet 3 to guide. A necessary gap (about 12.0mm) that the hydraulic brake can complete the braking function is maintained between the on-board mechanical brake and the F rail 7 . The track (F track) of the low-speed maglev system cannot be produced as a continuous length, and it is impossible to elongate without considering the temperature difference. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com