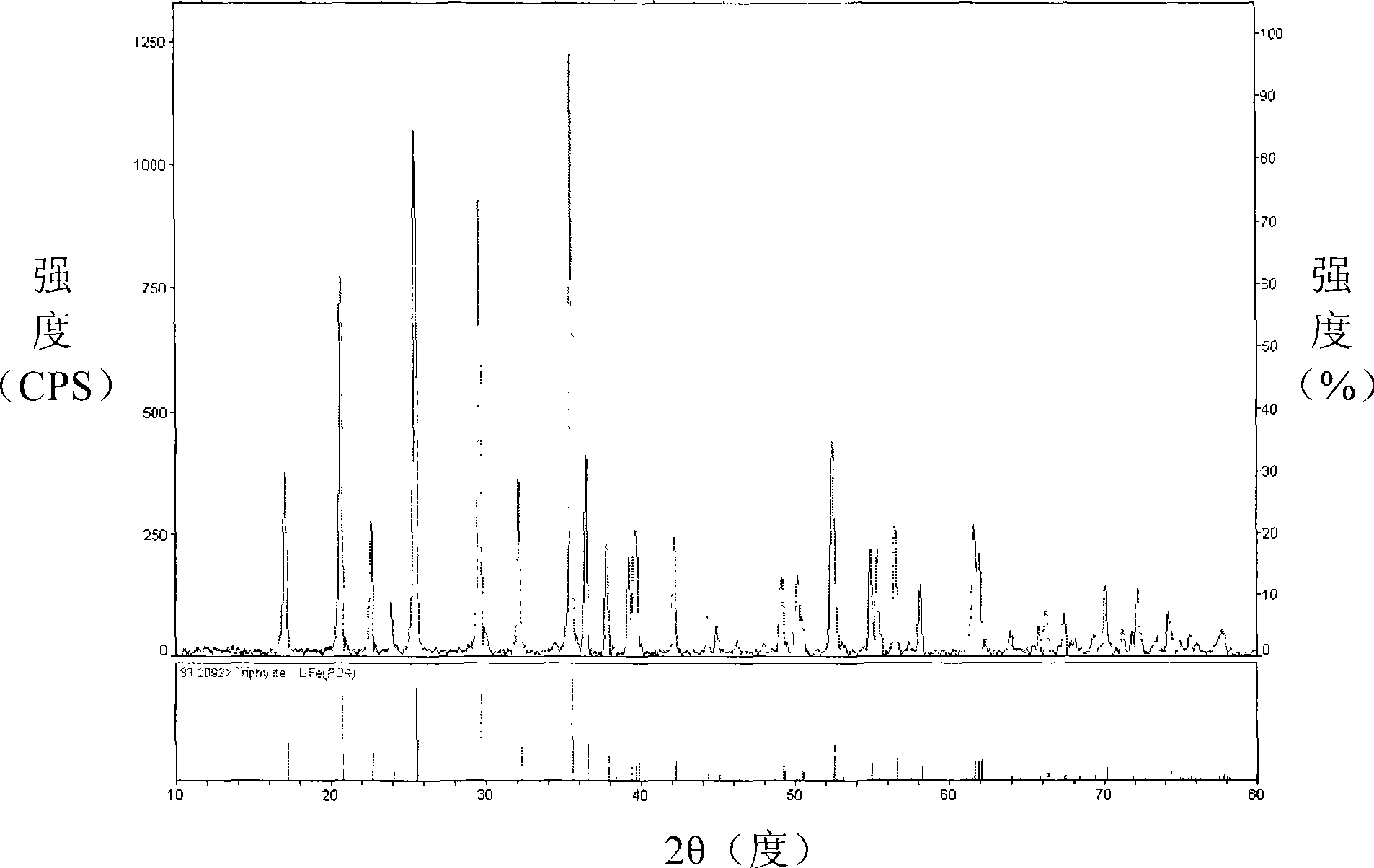
Method for preparing active substance lithium iron phosphate for lithium ion secondary battery anode
A positive electrode active material, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in the direction of electrode manufacturing, battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of good cycle performance, low production cost, high initial discharge specific capacity, etc., and achieve high discharge specific capacity , cycle performance improvement, cycle performance significant effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] This example illustrates the preparation method of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the present invention.
[0025] 43.3 g LiOH·H 2 O (Shanghai Zhongli Industrial Co., Ltd., special grade for batteries, LiOH·H 2 O content 97.01%), 80.4 grams median particle size D 50 0.37 microns, D 95 2.50 µm Fe 2 o 3 (ELEMENTIS, Fe 2 o 3 Content 99.3%), 115.0 g H 3 PO 4 (Guangdong Guanghua Chemical Factory Co., Ltd., analytically pure, H 3 PO 4 content is 85.2%), 38.2 grams of sucrose (Guangdong Guanghua Chemical Factory Co., Ltd., analytically pure) and 200 milliliters of deionized water are placed in the reactor, stirred at a rate of 200 rpm for 1.5 hours, then dried at 120 ° C After 8 hours, the precursor was obtained. The precursor was sintered at a constant temperature of 690° C. for 8 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosp...
Embodiment 2-6
[0028] Prepare the positive electrode active material lithium ferrous phosphate according to the method of Example 1, the difference lies in the lithium source and its amount, the amount and particle size of ferric oxide, the amount of phosphoric acid, the carbon source and its amount, and the amount of deionized water , drying temperature and drying time, sintering temperature and sintering time, the specific differences are shown in Table 1.
[0029] Table 1
[0030] Example Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Example 6 Lithium source LiOH·H 2 o LiOH·H 2 o Li2CO 3 Li 2 CO 3 Li 2 CO 3 The amount of lithium source (g) 42 45 39 39 38 The amount of ferric oxide (grams) 80 85 80 80 80 Particle size D of ferric oxide 50 (microns) 0.42 0.66 0.31 0.37 0.50 Particle size D of ferric oxide 95 (microns) 2.53 4.89 1.97 2.50 3.64 Amount of phosphoric acid (g) 115 118 115 114 115 carbon s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com