QTLs for mastitis resistance in cattle
A technology of inflammation resistance and bovine udder, which is applied in the field of determination of test bovine mastitis resistance, can solve problems such as low quality and pollution, and achieve the effect of avoiding economic losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
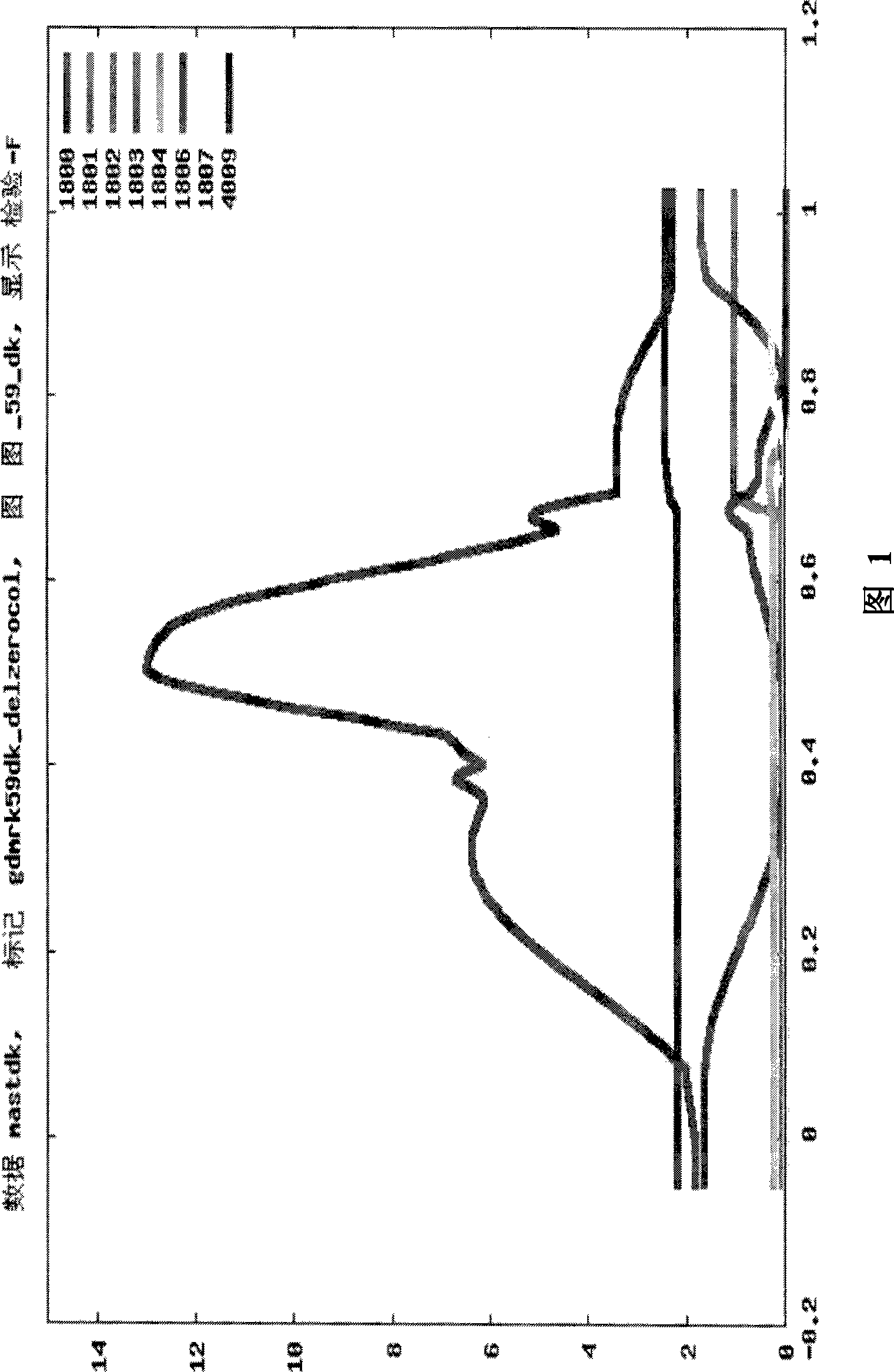
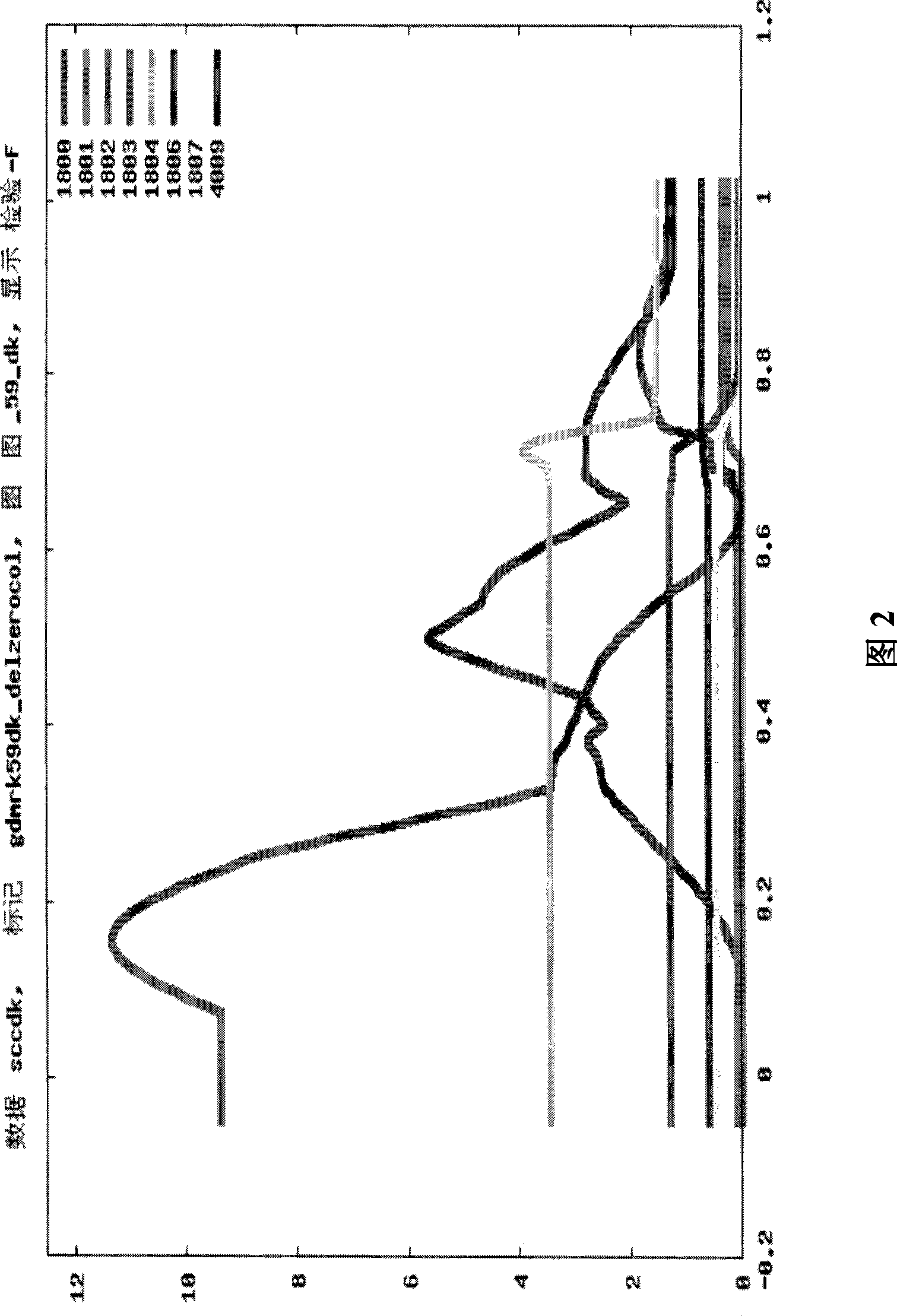
[0319] BTA9
[0320] Statistical Analysis
[0321] Several statistical methods described below were used to identify genetic markers associated with or associated with mastitis and thus mastitis resistance.
[0322] QTL analysis
[0323] Linkage analysis (LA) is used to identify QTLs by mapping genetic markers in families to chromosomal regions that are associated with disease or trait values within the pedigree that are higher than probabilistically expected. Such linked regions are more likely to contain causal genetic variants. Analyze data with series models. Initially, individual trait models using a multipoint regression approach for all traits were analyzed within families. Chromosomes with significant effects within families were analyzed with the variance components method to confirm QTLs found across families and characterization of QTLs.
[0324] regression analysis
[0325] Group allele frequencies at markers were estimated using the EM algorithm. Allele f...
Embodiment 2
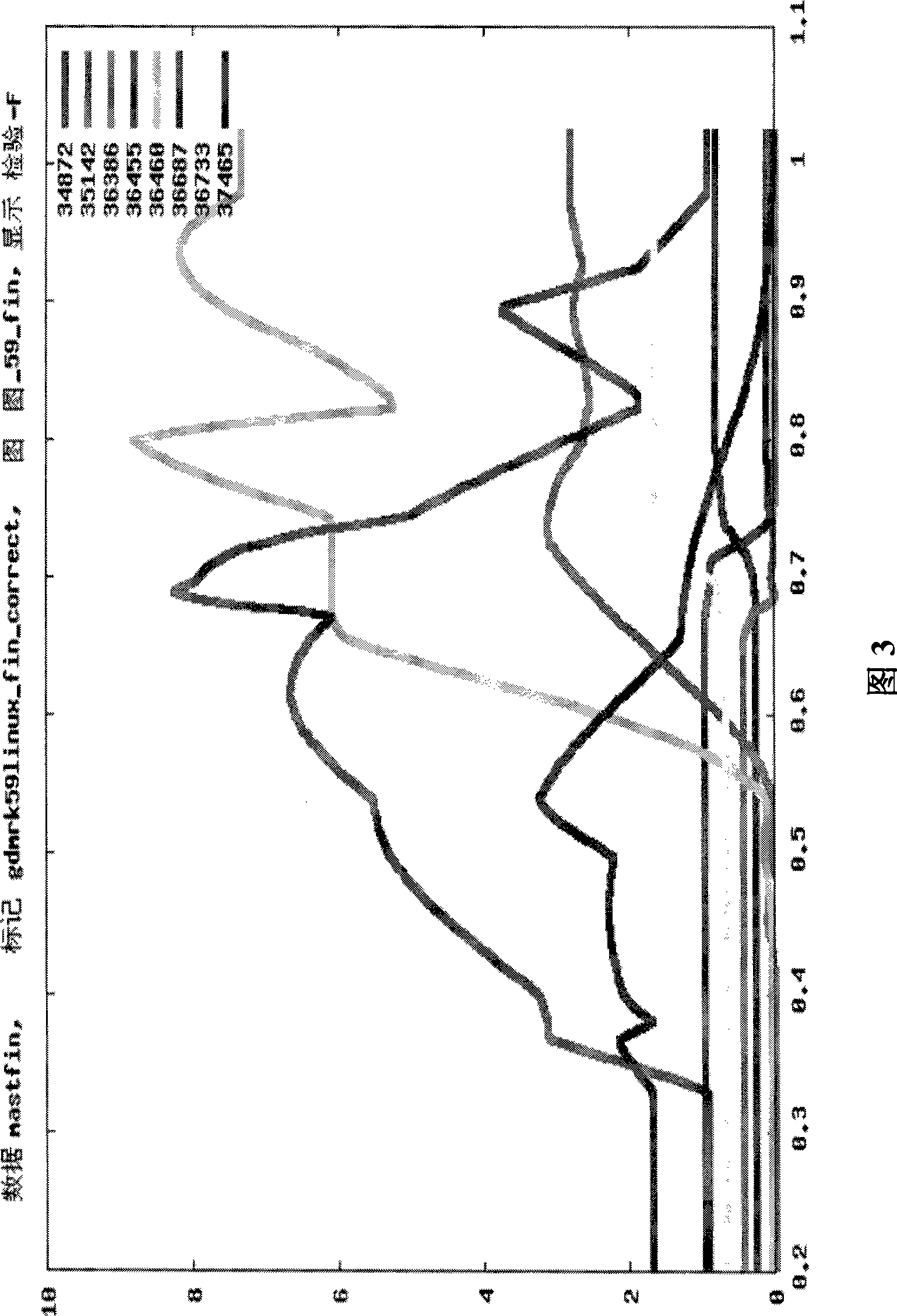
[0373] BTA11
[0374] Statistical Analysis
[0375] Several statistical methods described below were used to identify genetic markers associated with or associated with mastitis and thus mastitis resistance.
[0376] QTL analysis
[0377]Linkage analysis (LA) is used to identify QTLs by mapping genetic markers in families to chromosomal regions that are associated with disease or trait values within the pedigree that are higher than probabilistically expected. Such linked regions are more likely to contain causal genetic variants. Analyze data with series models. Three complementary methods were used: (i) half-sib family analysis (Haley and Knott, 1992) by regression-based method with GDQTL software (B. Guldbrandsten, 2005 personal communication); (ii) variance components method Cross-family linkage analysis, and (iii) combined linkage disequilibrium linkage analysis (LDLA) with variance components method. Each family was analyzed individually with GDQTL to determine th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com