Light distribution lens design method aiming at point light source
A light distribution lens and design method technology, applied in optics, optical components, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems that are not well solved, have many formulas, and have high mathematical requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
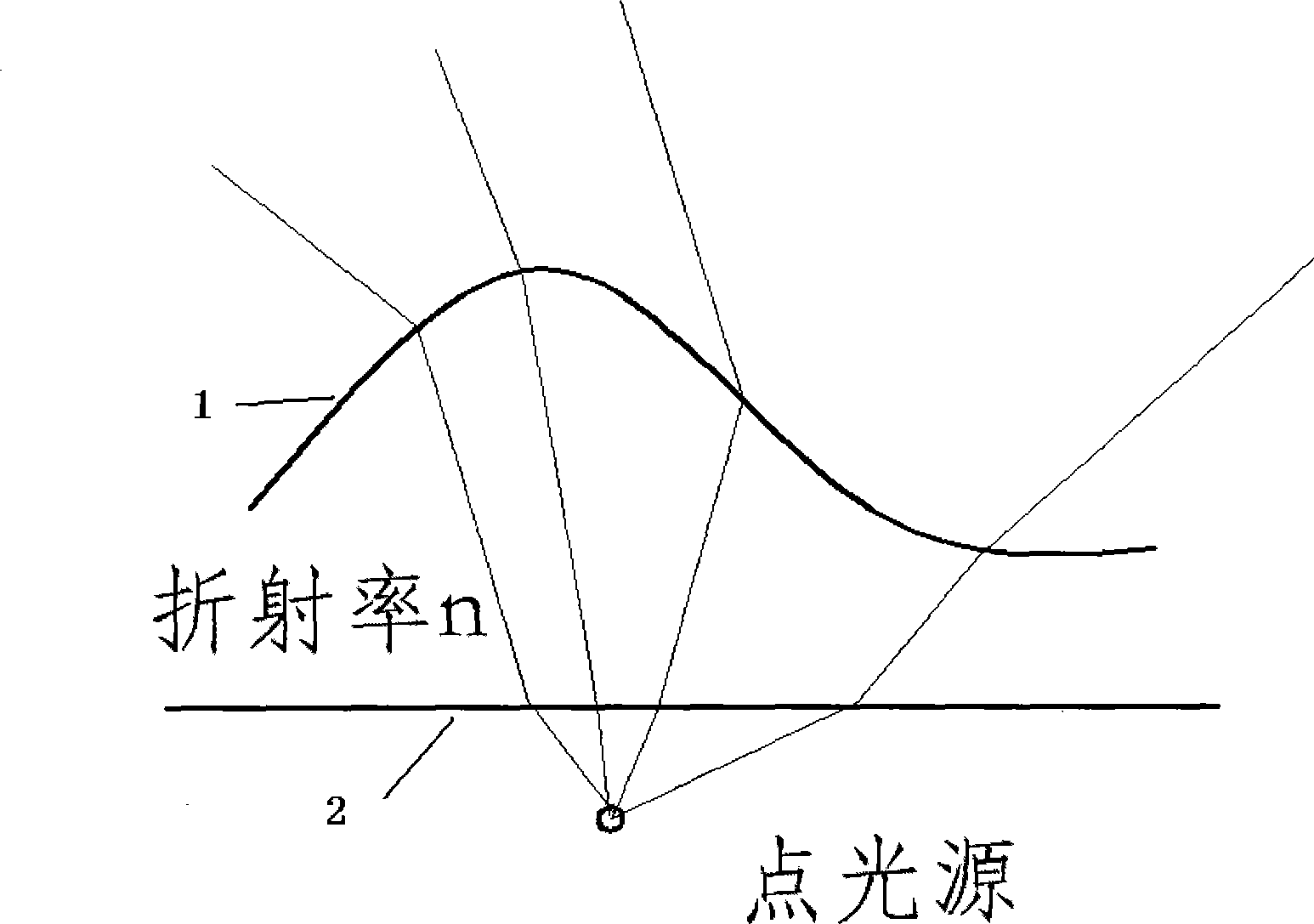
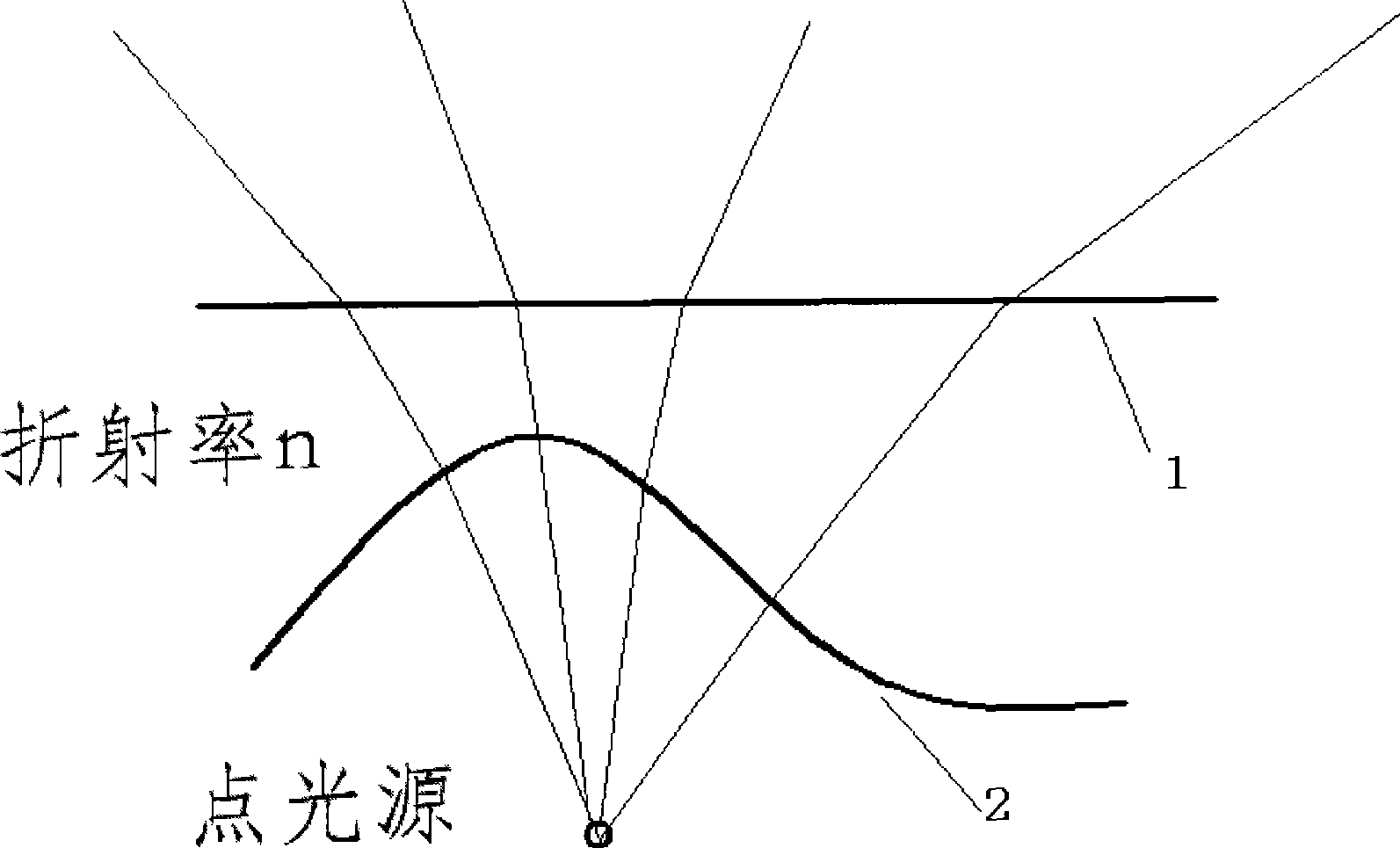
[0074] Embodiment 1: the initial structure that the lens is intended to take is as attached figure 2 As shown, the inner surface 2 adopts a spherical surface, and the outer surface 1 is a free-form surface. Therefore, the focus of this design is how to design the outer surface of the lens. The energy of the incident light and the energy of the outgoing light correspond to the longitude and latitude, such as Image 6 . The light source adopts Lambertian LED, that is, I(α)=I cos(α), and I is the central light intensity. The center point of the lens is required to be P(10mm, 0, 0). The observation surface is placed 10 meters away, and it is required to form a rectangular uniform spot with a length of 30 meters and a width of 10 meters, and its center is on the y-axis.
[0075] First, place the LED at the origin of the coordinate system so that its central axis coincides with the y-axis. The light intensity distribution of the known LED is I(α)=I cos(α), expressed in the coo...
Embodiment 2
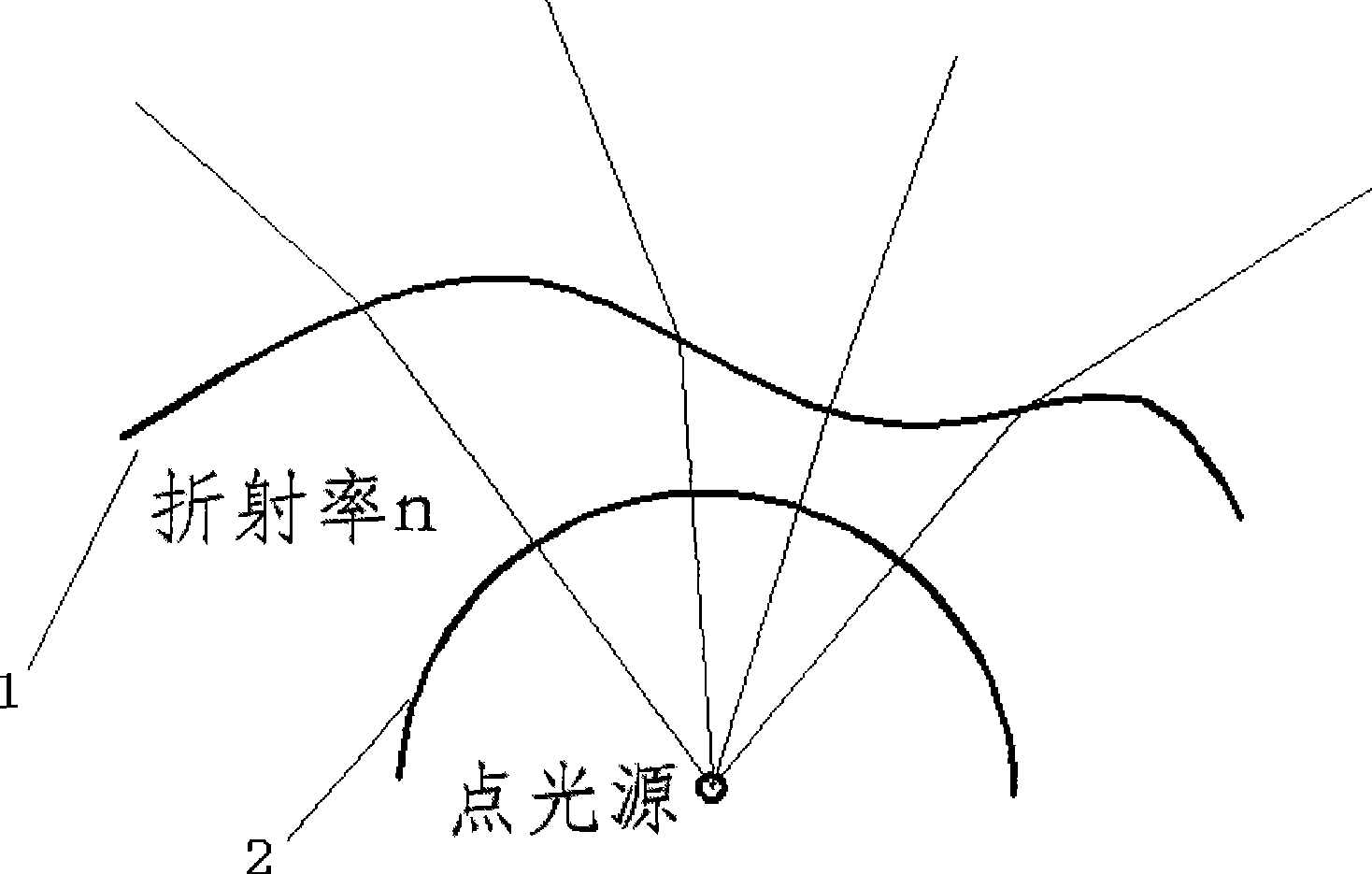
[0093] Embodiment 2: the initial structure that lens adopts is as attached image 3 shown. The outer surface adopts a plane, and the inner surface adopts a free-form surface. This initial structure is relatively complex. Because the ray is deflected twice, the index of refraction formula is used twice. The corresponding relationship between the incident light and the outgoing light is Image 6 The radiating annulus shown corresponds to . After two iterations of the refraction index vector formula, the formula is listed for simplified numerical solution, and the surface is drawn to form a solid diagram, as shown in the attached Figure 13 shown. The outer surface of the lens is flat, and the inner surface is formed by splicing four discontinuous fan-like shapes.
Embodiment 3
[0094] Embodiment 3: the initial structure that lens adopts is as attached image 3 shown. The outer surface adopts a plane, and the inner surface adopts a free-form surface. The corresponding relationship between the incident light and the outgoing light is Figure 5 The latitude and longitude grids shown correspond. After two iterations of the refractive index vector formula, the formula is listed for simplified numerical solution, and the surface diagram is drawn as attached Figure 14 shown. The outer surface of the lens is plane, and the inner surface is a curved surface similar to a saddle.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com