Stairs climbing control method for crawler moving robot with guide arm
A mobile robot and crawler technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as the reliability of the autonomous algorithm needs to be improved, the inability to work for a long time, and wrong control commands
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
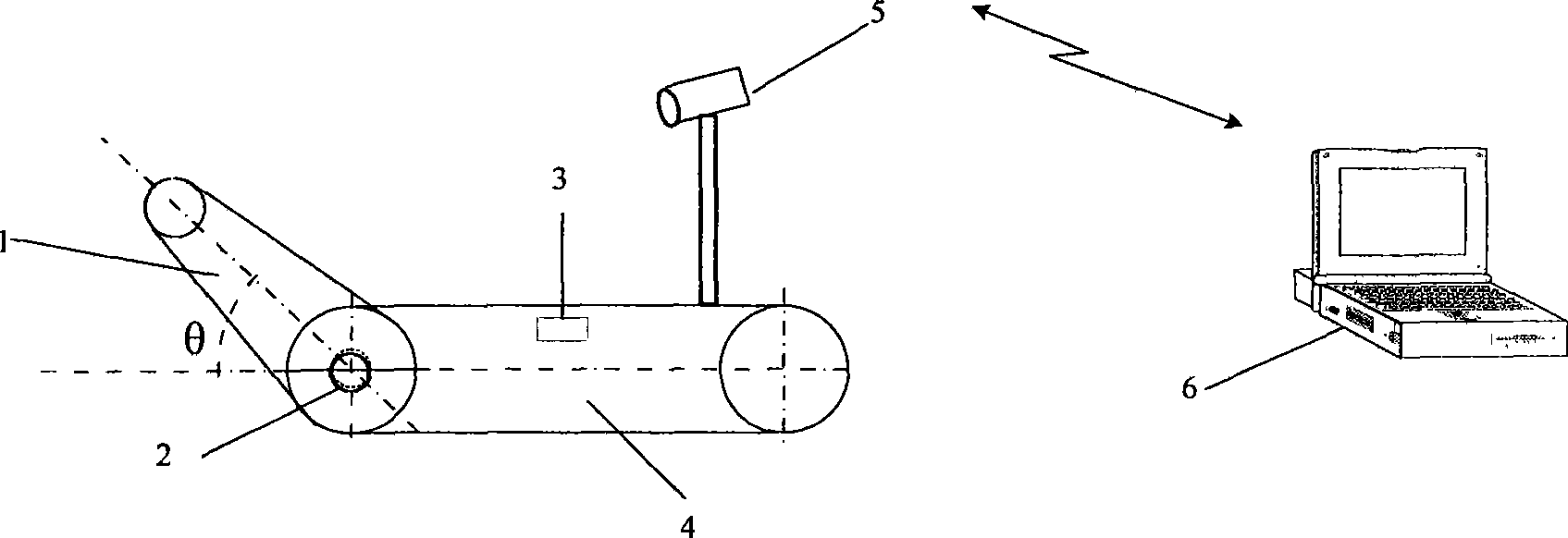
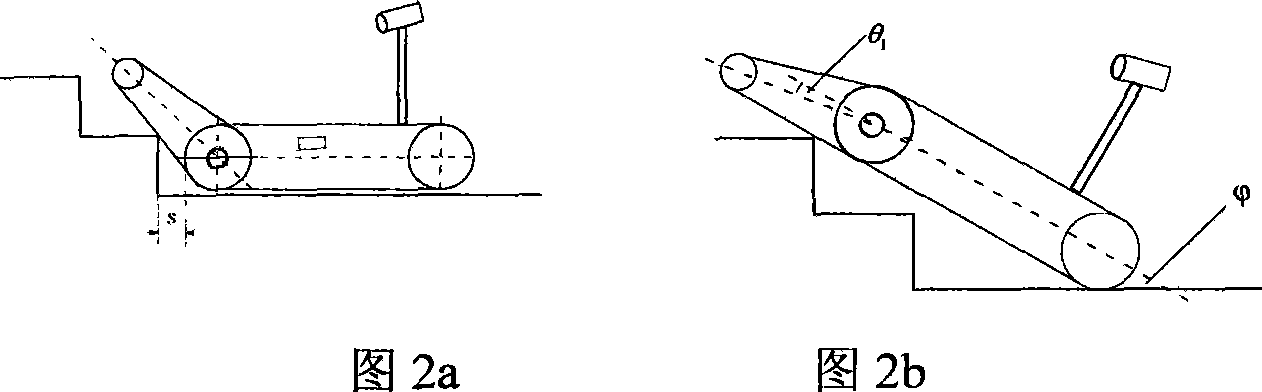
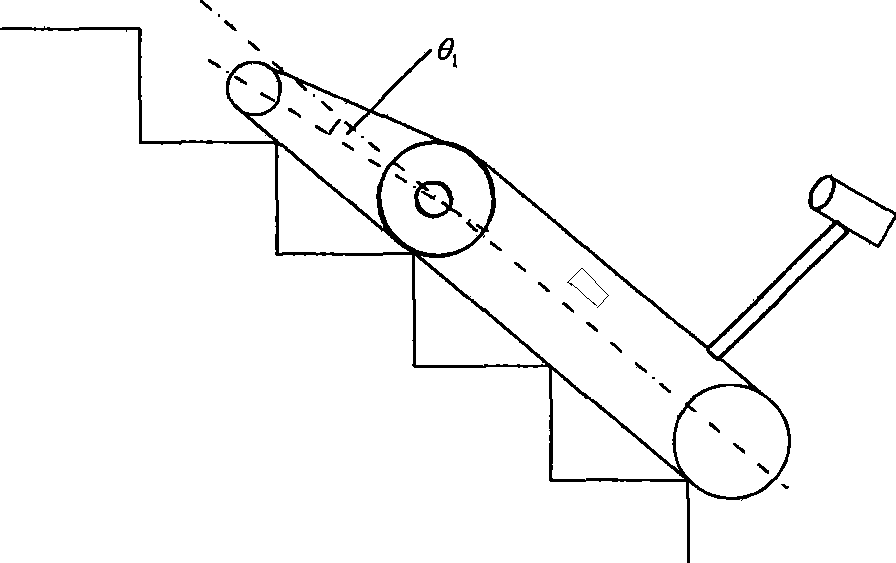
[0018] A method for climbing stairs of a crawler-type mobile robot with a guide arm. The crawler-type mobile robot with a guide arm includes a front wheel and a rear wheel. The front wheel is a driving wheel, and the rear wheel is a follower wheel. The front and rear wheels of the robot are respectively covered by two crawlers to form the robot's traveling mechanism. A crawler-type guide arm mechanism is installed coaxially with the front wheel of the robot, and the front wheel shaft is used as the rotation center to make a 360-degree circular rotation along the direction of the robot's travel. An ultrasonic ranging sensor and an infrared ranging sensor are installed in front of the robot to measure the distance between the teleoperated small mobile robot and the obstacle in front, and a torque sensor is installed on the front wheel shaft of the robot to measure the alignment of the guide arm to the front wheel shaft For the moment generated, a two-dimensional attitude sensor i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com