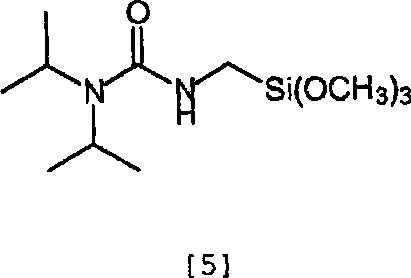
Compositions containing phosphonate-functional particles
A technology of composition and particles, applied in coatings, adhesives, filling slurries, etc., which can solve the problems of not achieving the best results and limited choices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0108] In the case of another preferred method of preparing particles (P), said particles (P) are prepared via cohydrolysis of organosilanes (S) with other silanes (S4) or compounds (L). It is possible here to use all hydrolyzable silanes and silanes containing hydroxysilyl groups as silanes (S4). Siloxanes or silazanes may also be used. Typical examples of suitable silanes (S4) are tetraethoxysilane, tetramethoxysilane, methyltrimethoxysilane, phenyltrimethoxysilane, methyltriethoxysilane, phenyltriethoxysilane Silane, Dimethyldimethoxysilane, Dimethyldiethoxysilane, Trimethylmethoxysilane or Trimethylethoxysilane. It is of course also possible to use different mixtures of different silanes (S4). It is thus not only possible to use mixtures containing only silanes (S4) without further organofunctional groups in addition to silane (S), but also silanes (S4) which contain no further organofunctional groups in addition to silane (S) and Silanes (S4) with additional organofunc...
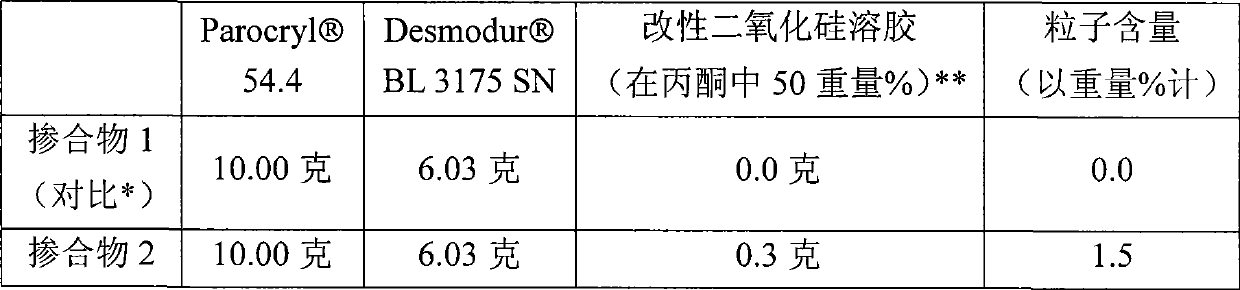
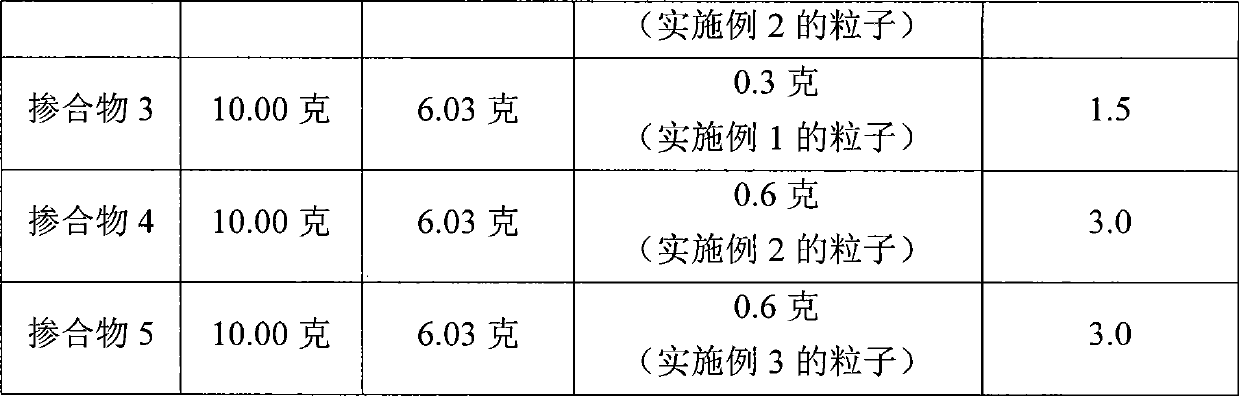
Embodiment 1
[0137] Example 1: Synthesis of Phosphonate Functionalized Particles from Silica Hydrosol.
[0138] A solution of 1.96 g of diethylphosphonomethyldimethylmethoxysilane in 40 mL of methoxypropyl acetate was added dropwise to 14.0 g of silica water over the course of 10 minutes under vigorous stirring. Sol (from GRACE DAVISON's AS 40, 24 nm, 40% by weight), the mixture was heated at 60° C. for 4 hours. The resulting milky white emulsion was then concentrated under reduced pressure until a transparent silica sol was obtained. The average particle size of the modified silica sol measured by dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer Nano from Malvem) was 32 nm. After distilling off the solvent, 7.16 g of a colorless solid are obtained, which are redispersed in isopropanol by stirring incorporation. The average particle size of the silica sol in isopropanol was 44 nm.
Embodiment 2
[0139] Example 2: Synthesis of phosphonate functionalized particles from silica organosols.
[0140] A mixture of 480 g of silica sol in isopropanol (IPA-ST from NISSAN CHEMICAL, 12 nm, 30% by weight) and 48.0 g of diethylphosphonomethyldimethylmethoxysilane was prepared in Heat at 60°C for 6 hours. The average particle size of the modified silica sol measured by dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer Nano from Malvem) was 13 nm. After distillative removal of the solvent, 191 g of a colorless solid are obtained, which are redispersed in acetone and isopropanol by stirring incorporation. The silica sol in isopropanol had an average particle size of 14.5 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average particle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com