Manufacture of substantially pure monochloroacetic acid
A technology of chloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid, applied in the preparation of carboxylate, the preparation of organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as uneconomical, and achieve the effect of improving selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
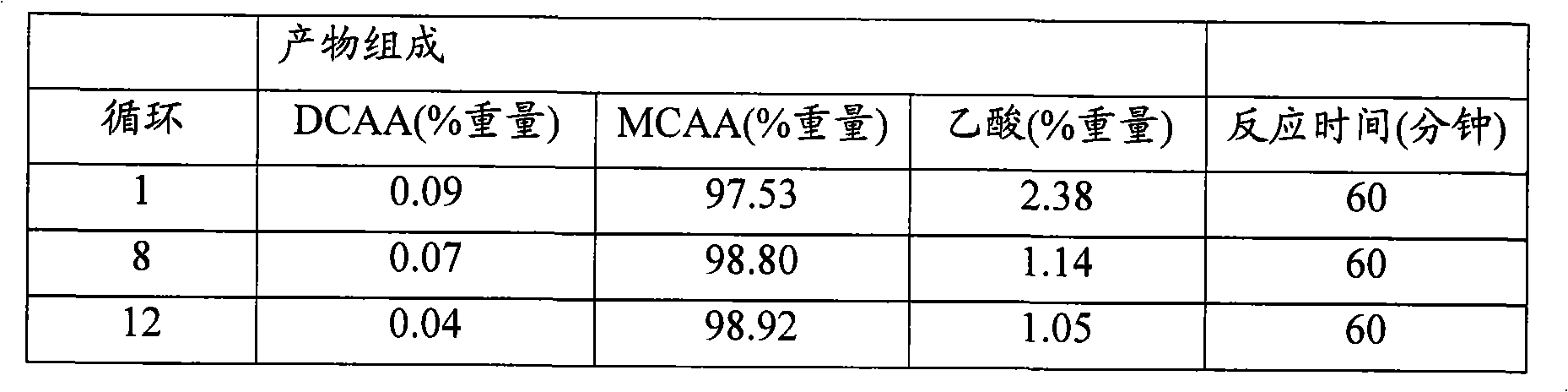
[0032] Hydrogenation of a mixture containing 35.0% by weight dichloroacetic acid
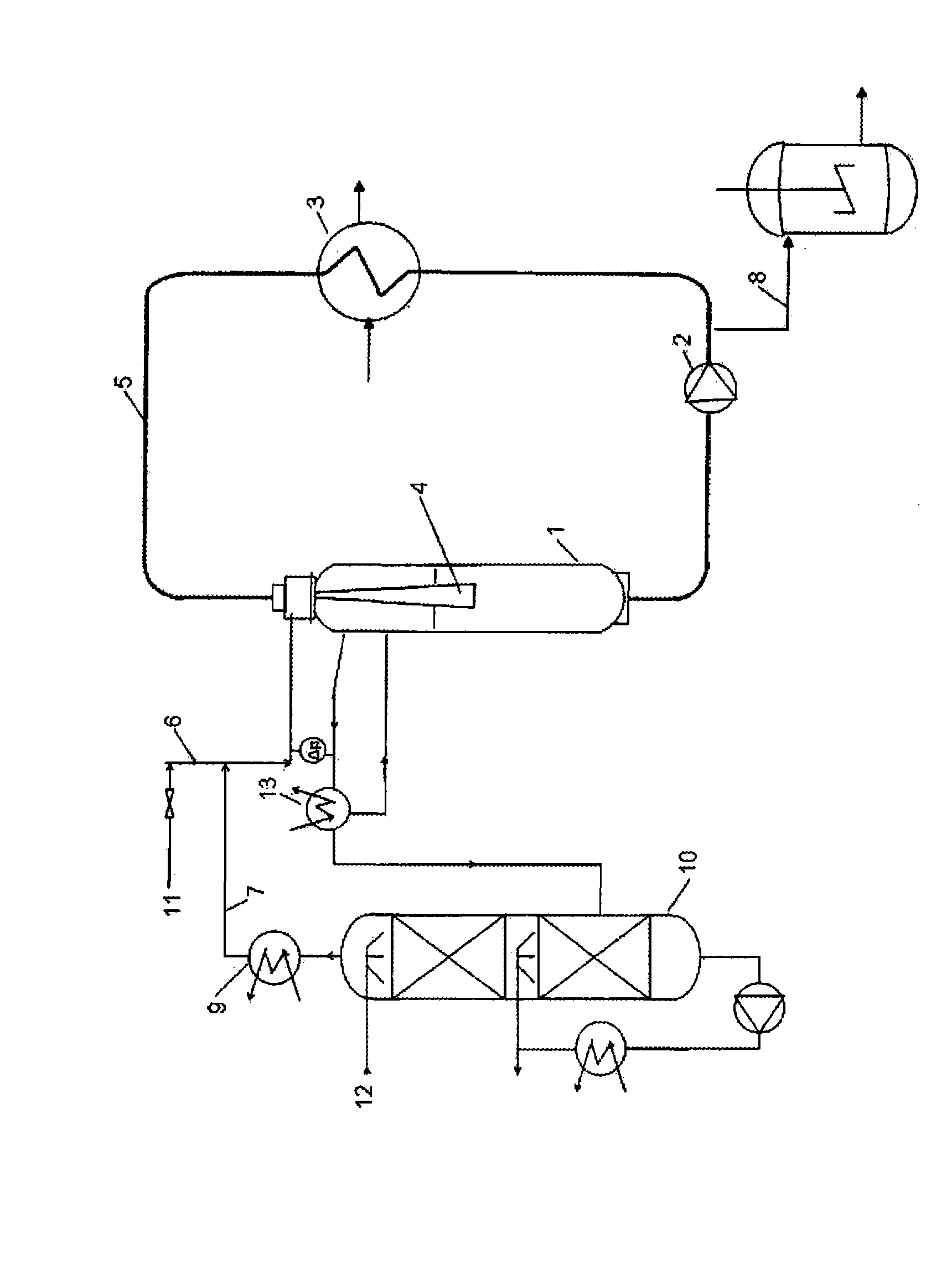
[0033] A tubular reactor with a Venturi mixer and equipped with a condenser and an absorption column integrated in the internal gas circuit as shown in the drawing was used. Into a passivated tubular reactor with a working volume of 15 liters was introduced 19 kg of a molten mixture comprising 35% by weight of DCAA and 65% by weight of MCAA. The reaction pump was started and 0.032 kg of a commercially available palladium on carbon catalyst (5% Pd on carbon) was added through the catalyst launder. Start the combined HCl absorption system filled with water. The reactor was flushed with hydrogen and the reaction mixture was heated to 155°C. The tubular reactor was pressurized with hydrogen to 3 bar and the hydrogenation was started by supplying hydrogen at a controlled pressure. During the reaction, the reactor headspace gas, consisting mainly of hydrogen chloride and hydrogen gas, is continuous...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Hydrogenation of a mixture containing 3.0% by weight dichloroacetic acid
[0036] The same reactor as in Example 1 was used to hydrogenate a mixture comprising 3.0% by weight DCAA, 95.4% by weight MCAA and 1.2% by weight acetic acid. 19 kg of the molten mixture having the abovementioned composition were introduced into the passivated tubular reactor. The reaction pump was started and 0.019 kg of a commercially available palladium on carbon catalyst (5% Pd on carbon) was added through the catalyst launder. Start the combined HCl absorption system filled with water. The reactor was flushed with hydrogen, then the reaction mixture was heated to 150°C. The tubular reactor was pressurized with hydrogen to 3 bar and the hydrogenation was started by supplying hydrogen at a controlled pressure. During the reaction, the reactor headspace gas, consisting mainly of hydrogen chloride and hydrogen gas, is continuously passed through an internal absorption system where hydrogen ch...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Hydrogenation of a mixture containing 4.0% by weight dichloroacetic acid at ambient conditions
[0039] The same reactor as in Example 1 was used to hydrogenate a mixture comprising 4.0% by weight DCAA, 93.1% by weight MCAA, 2.5% by weight acetic acid and 0.4% by weight water. 19 kg of the molten mixture having the abovementioned composition were introduced into the passivated tubular reactor. The reaction pump was started and 0.076 kg of a commercially available palladium on carbon catalyst (5% Pd on carbon) was added through the catalyst launder. Start the combined HCl absorption system filled with water. The reactor was flushed with hydrogen, then the reaction mixture was heated to 145°C. The hydrogenation was started by supplying hydrogen at a controlled pressure. Keep the pressure constant at 0-0.2 bar. During the reaction, the reactor headspace gas, consisting mainly of hydrogen chloride and hydrogen gas, is continuously passed through an internal absorption s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com