Patents
Literature
184 results about "Dichloroacetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
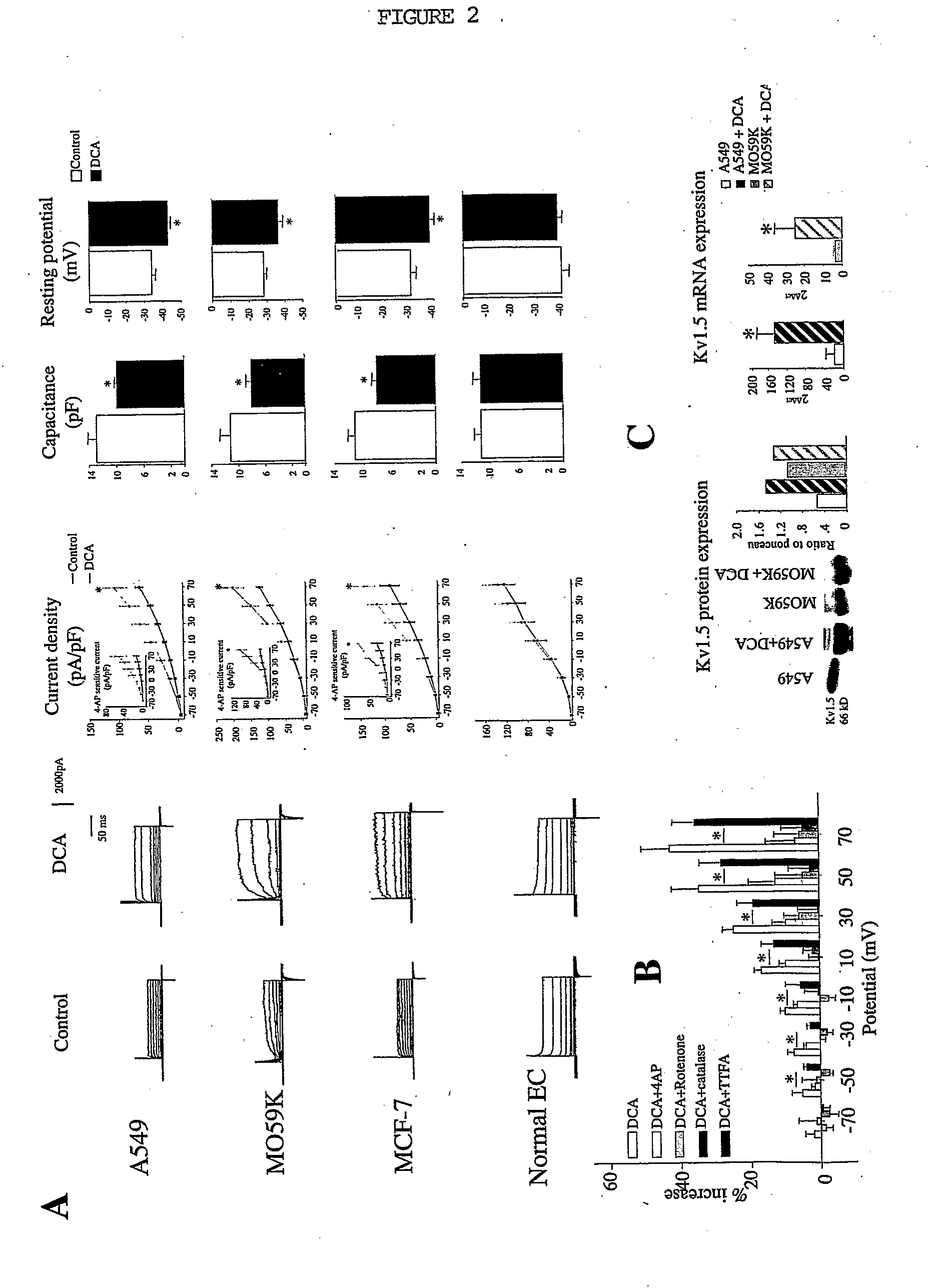
Dichloroacetic acid (DCA), sometimes called bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is the chemical compound with formula CHCl₂COOH. It is an acid, an analogue of acetic acid, in which 2 of the 3 hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have been replaced by chlorine atoms. Like the other chloroacetic acids, it has various practical applications. The salts and esters of dichloroacetic acid are called dichloroacetates. Salts of DCA have been studied as potential drugs because they inhibit the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.
Manufacture of substantially pure monochloroacetic acid
ActiveCN101528657AHigh selectivityMeet general industrial requirementsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationAcetic acidHydrogen
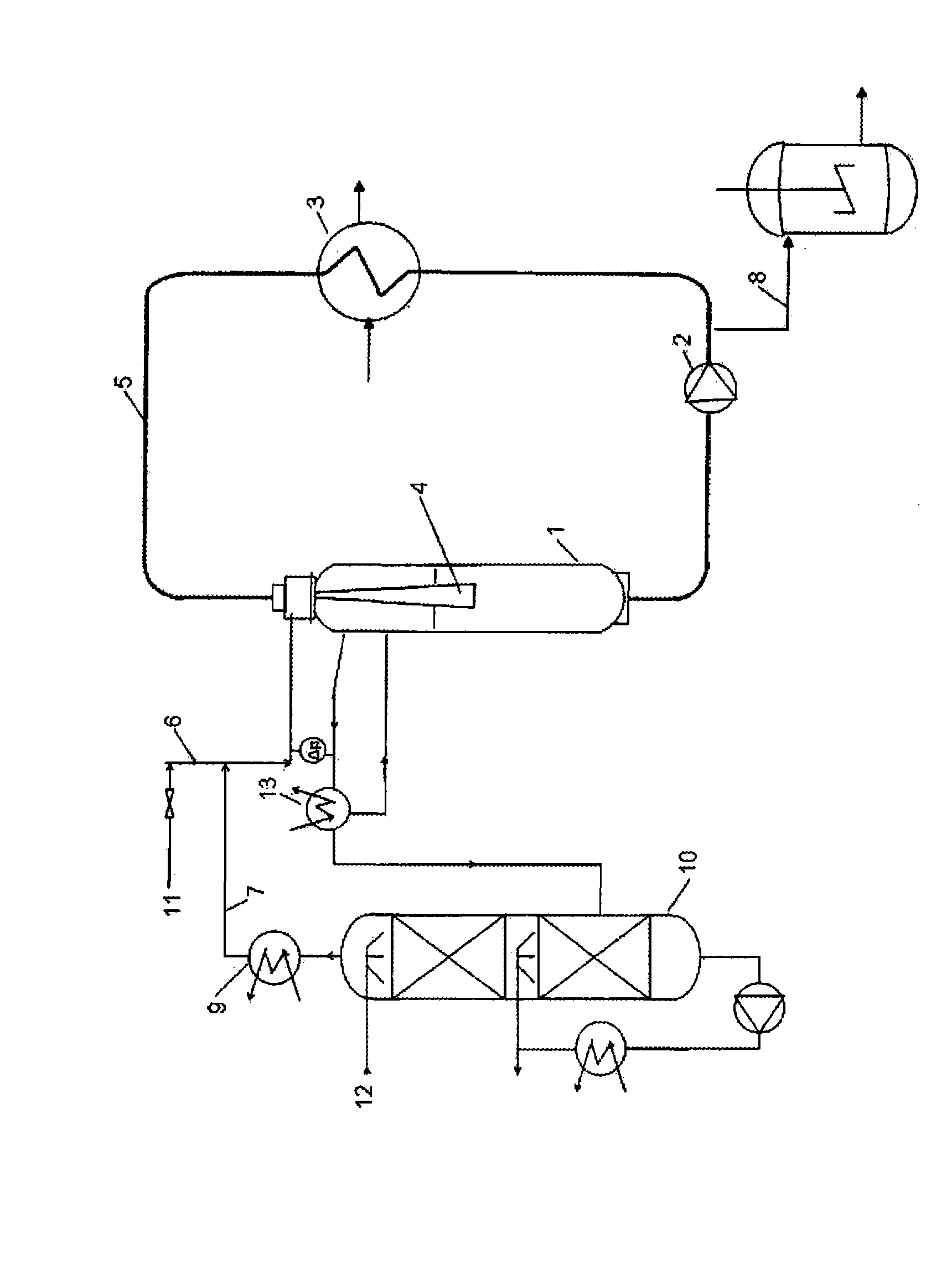
The present invention describes a process for the manufacture of substantially pure monochloroacetic acid from a liquid chloroacetic acid mixture comprising monochloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid, in particular in an amount of 2 to 40 percent by weight, wherein said mixture, further mixed with a suspended hydrogenation catalyst, is mixed with hydrogen gas and the resulting mixture is brought to reaction in a reactor, which is characterized in that the reactor is a loop reactor comprising a gas and liquid recirculation system coupled via an ejector mixing nozzle, in which reactor the gas and liquid are circulated in co-current flow, and the mixing intensity introduced to the liquid phase is at least 50 W / l of liquid phase.
Owner:BUSS CHEMTECH
Process for preparation of alpha-ketoglutaric acid
InactiveCN102584568APreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationSodium methoxideGlutaric acid
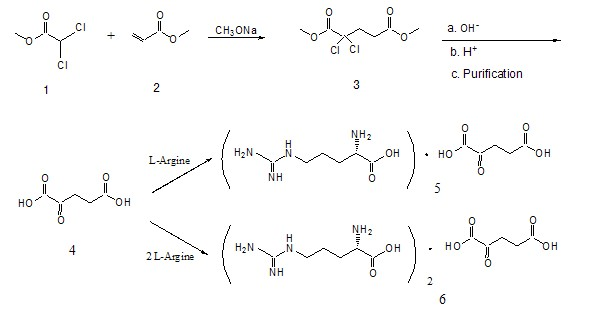
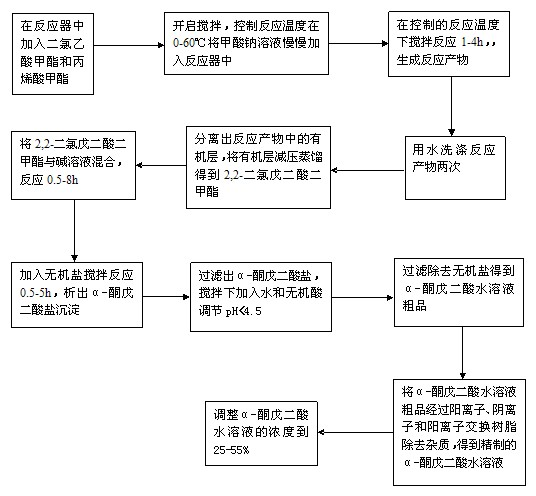
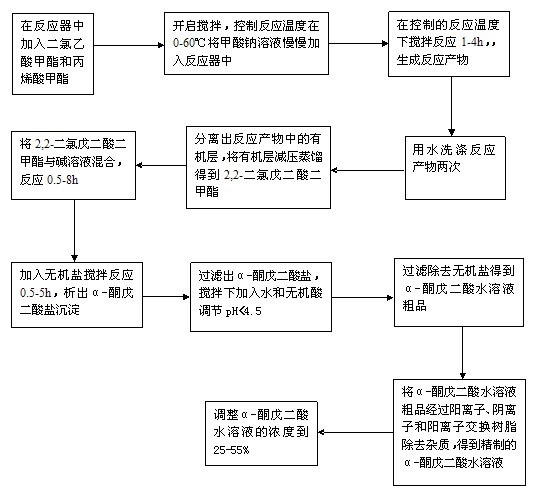
A process for preparation of [alpha]-ketoglutaric acid, comprising the steps of: (a) reacting methyl dichloroacetate and acrylic acid methyl ester with sodium methoxide to obtain dimethyl 2,2-dichloroglutarate; (b) reacting the dimethyl 2,2-dichloroglutarate from step (a) with hydroxide solution to obtain crude [alpha]-ketoglutaratic acid aqueous solution; (c) purifying the crude [alpha]-ketoglutaratic acid aqueous solution to obtain purified [alpha]-ketoglutaratic acid aqueous solution; and (d) adjusting a concentration of the purified [alpha]-ketoglutaratic acid aqueous solution by adding water, thereby a yield of the purified [alpha]-ketoglutaratic acid aqueous solution is approximately 75%. While avoiding the use of massive organic solvents, the process of the present invention has a remarkable high yield to realize mass production with low manufacturing cost and shortened production time.
Owner:张国基
Composite membrane with polymer coating and preparation method of composite membrane
ActiveCN105576175AHigh densityImprove product qualityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersWater basedSlurry
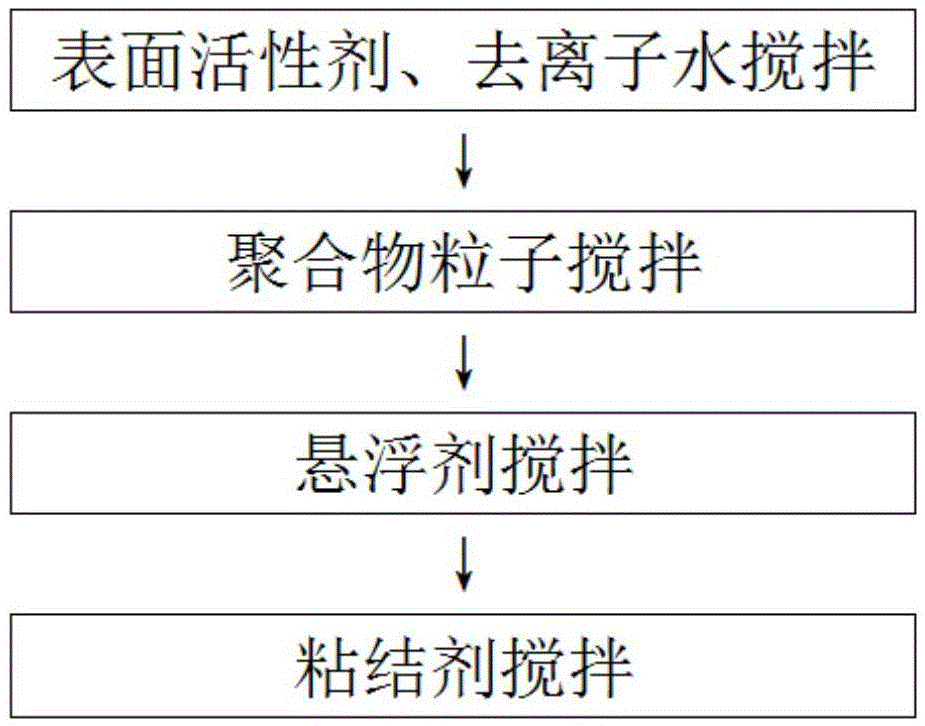
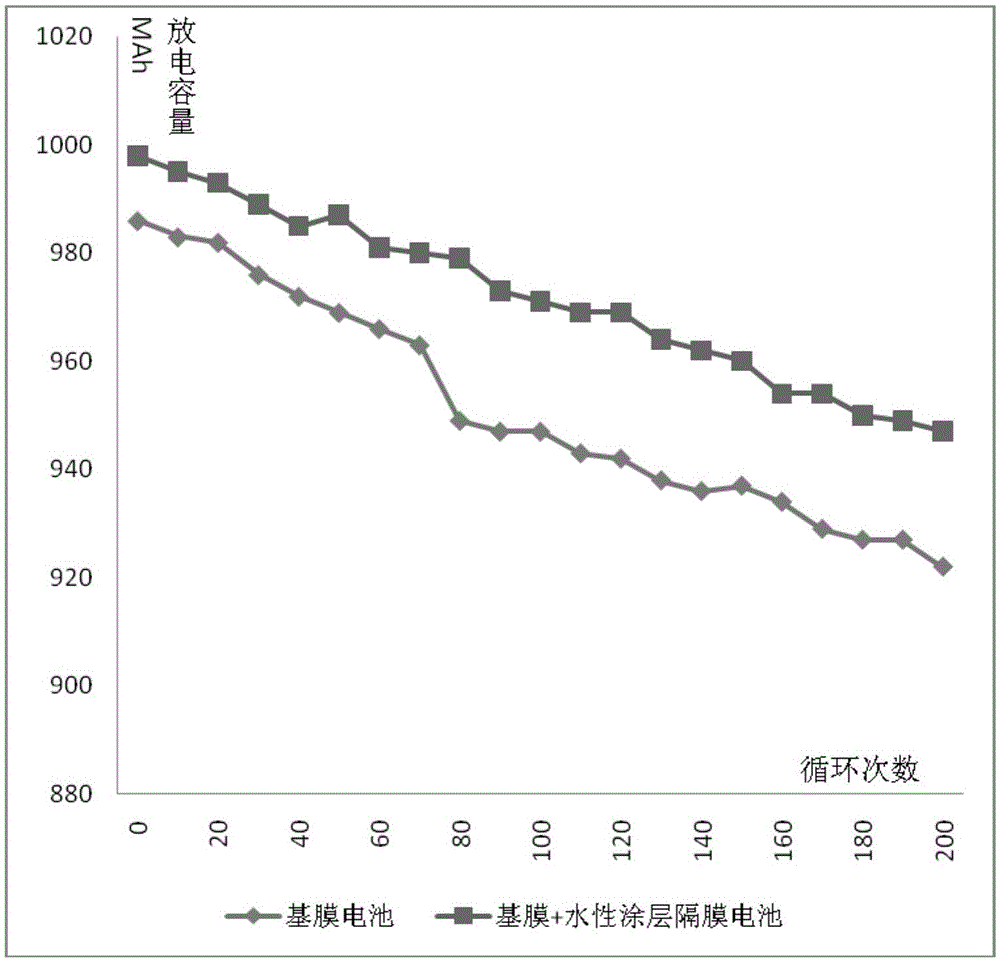
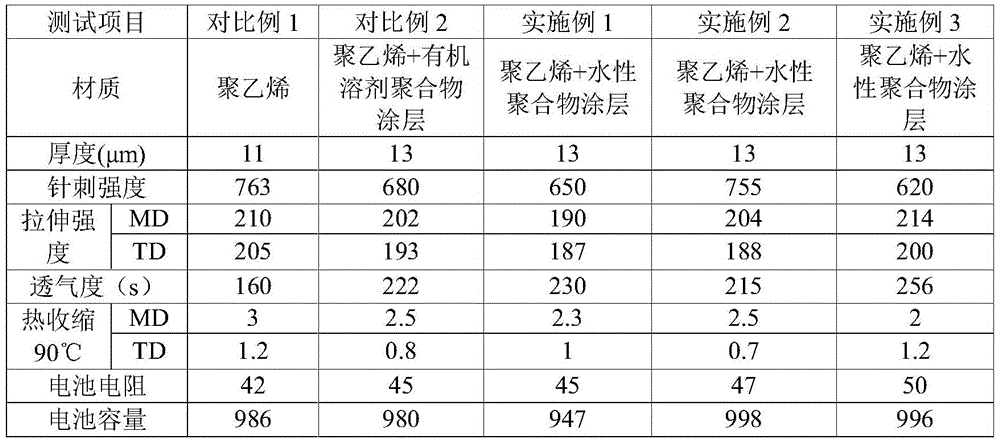
The invention discloses a composite membrane with a polymer coating and a preparation method of the composite membrane. According to the preparation method, water-based slurry coats one or two surfaces of a base membrane to form the polymer coating; with deionized water as a solvent, polymer particles, a surfactant and an aqueous adhesive are dispersed into the deionized water to form the water-based slurry; the water-based slurry also contains a suspending agent; the amount of the suspending agent is 3%-25% of total weight of the water-based slurry; and the suspending agent is at least one of potassium chloride, sodium chloride, dichloroacetic acid, ethylene dibromide, 3-bromopyridine, 4,5-dichloro 1,3-dioxolame-2-ketone, dichloroethane, dichloroethylene and 1,3-butanediol sulfite. According to the preparation method, the suspending agent is added to the water-based slurry; the solvent density is improved; and the polymer particles can be evenly dispersed into the deionized water to form the stable water-based slurry, so that the production quality of the composite membrane with the polymer coating is improved; and a basis is laid for preparation of a high-quality lithium-ion battery.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGXING NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Hydrodechlorination method for producing high-purity monochloro acetic acid
InactiveCN105503574AMass content reductionHigh activityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationDistillationFixed bed
The invention discloses a hydrodechlorination method for producing high-purity monochloro acetic acid. The Hydrodechlorination method comprises the following steps: 1, filling a fixed bed reactor with a catalyst bed; 2, uniformly mixing hydrogen and a reaction mixed solution in a gas-liquid mixer, and injecting the obtained mixture into a heat exchanger to be pre-heated so as to obtain a reaction raw material; 3, discharging air in the fixed bed reactor by the nitrogen gas pump-in method, then discharging nitrogen gas in the fixed bed reactor by the hydrogen pump-in method, and injecting the reaction raw material into the fixed bed reactor for hydrodechlorination reaction so as to obtain an intermediate product; 4, performing distillation separation on the intermediate product to obtain monochloro acetic acid with the quality purity not less than 99.5%. The method continually and selectively conducts catalytic hydrogenation to remove dichloroacetic acid in the reaction mixed solution, inhibits formation of a by-product (acetic acid) in the intermediate product to be within an acceptable range, and reduces the mass content of dichloroacetic acid in the obtained by-products to be 0.5% or below.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Liposome-encapsulated organic-metal-framework nano medicine delivery system preparation method and application
InactiveCN109125266ALarge particle sizeLow costPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSolubilitySpherical shaped
The invention discloses a liposome-encapsulated organic-metal-framework nano medicine delivery system preparation method and application. An organic metal framework is MOF-Fe prepared from an iron compound and an organic ligand, is octahedral morphologically and has mimetic peroxidase catalytic activity. Water solubility can be improved by PEC modified liposome encapsulation, and dichloroacetic acid solution in pH of 4.0 is loaded into liposome to provide acidic catalytic reaction conditions for MOF-Fe, so that the liposome-encapsulated organic-metal-framework nano medicine delivery system isfinally formed. The medicine delivery system is characterized in that the particle size is about 150nm, spherical shape, high stability, high catalytic activity and slowness in release are realized, and hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions are continuously generated through reaction with H2O2. Internal oxidative stress level of tumor cells can be raised, tumor cell apoptosis is induced, and remarkable suppression effects on tumor tissues are achieved. Therefore, a novel scheme is provided for antitumor treatment such as tumor non-chemotherapeutic pharmaceutical treatment and multi-drug resistance of tumors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Microetching and roughening liquid for copper surface and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a microetching and roughening liquid for a copper surface. The microetching and roughening liquid comprises the following components by mass concentration: 5-50 g / L bivalent copper ions from a copper ion source, 20-150 g / L organic acid, 3-105 g / L chloride ions from a chloride ion source, a 0.0005-2 g / L water-soluble polymer and a 0.001-10 g / L pyridine derivative; a solventis water; the organic acid is at least one of formic acid, acetic acid, malic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid, edetic acid, iminodisuccinic acid, monochloro acetic acid, dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid; and the water-soluble polymer is a polymer of which a molecular chain contains a Imidazole or ammonium salt structure. The microetching and roughening liquid can form uniform roughening on the copper surface, is not affected by the crystal structure of the copper surface, and in the follow-up processes, can effectively increase the adhesive force of a solder-resist coating with which the copper surface is coated.
Owner:KUNSHAN CITY BANMING ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH
Method of treating cancer using dichloroacetate
The invention relates to the use of dichloroacetate and chemical equivalents thereof for the treatment of cancer by inducing apoptosis or reversing apoptosis-resistance in a cell Preferably, the dosage is 10-100 mg / kg Preferably, sodium dichloroacetate is used. The dichloroacetate may optionally be given in combination with a pro-apoptotic agent and / or a chemotherapeutic agent Preferably, the cancers treated are non-small cell lung cancer, glioblastoma and breast carcinoma.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
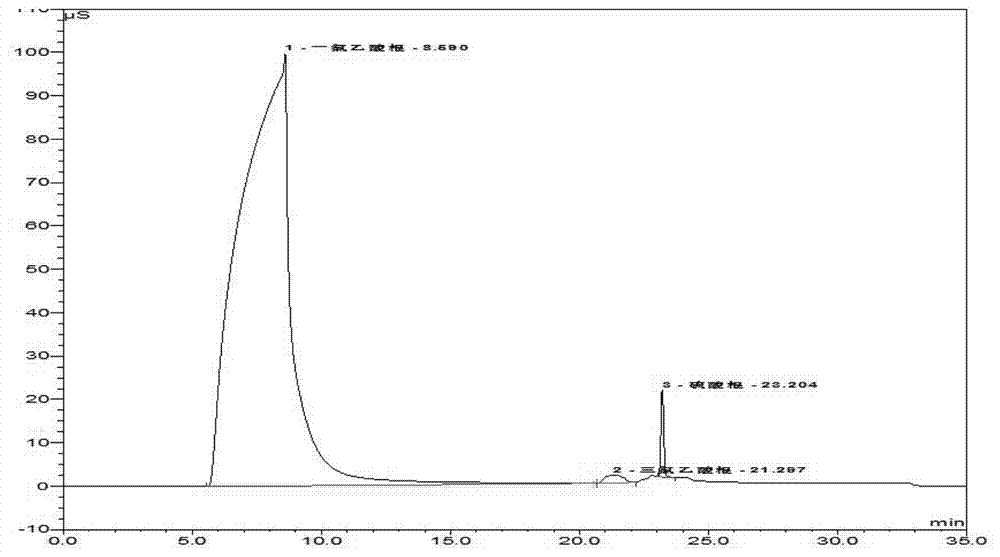
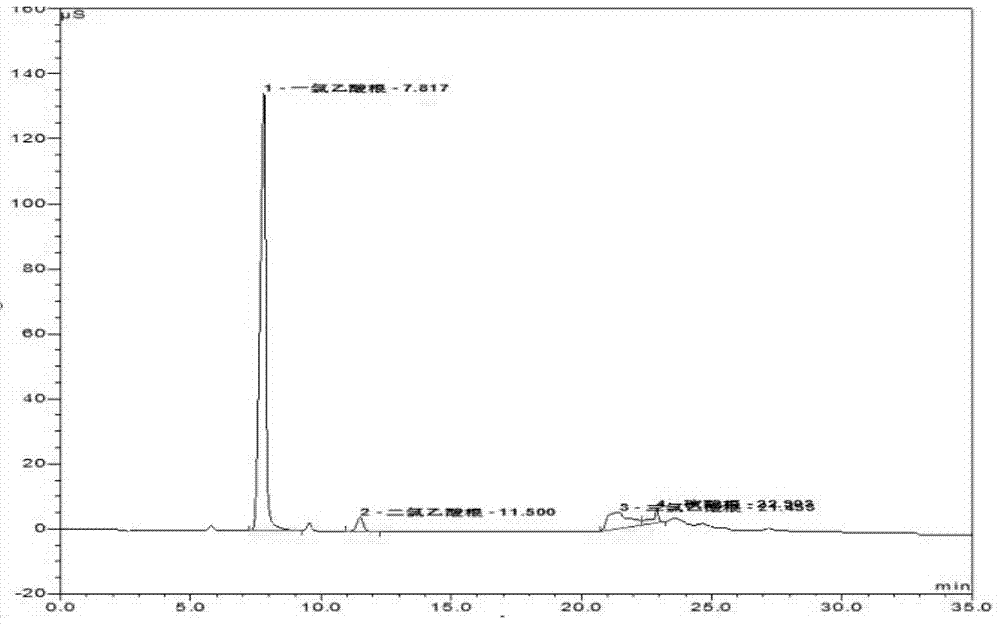
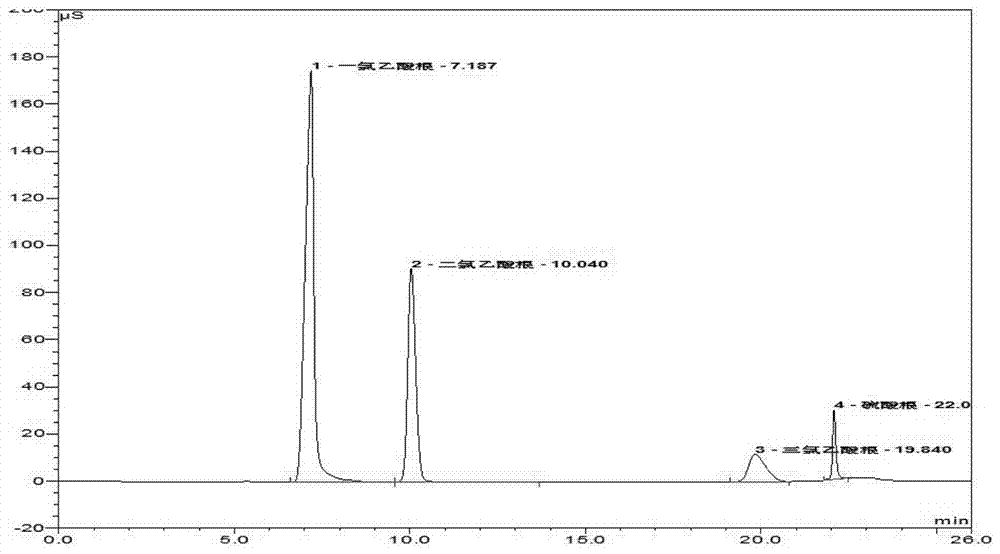
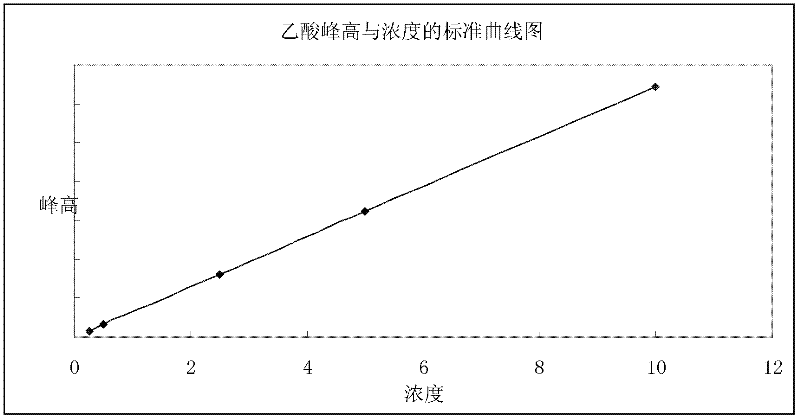
Method for detecting monochloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid and sulfate radical in chloroacetic acid by ion chromatography
ActiveCN108008061AEasy to operateSave manpower and timeComponent separationIon chromatographySulfate radicals
The invention discloses a method for detecting monochloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid and sulfate radical in chloroacetic acid by ion chromatography, which comprises the following steps: preparing a mixed standard solution of four anions including monochloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid and sulfate radical, feeding the mixed standard solution intoan ion chromatography detection system to perform gradient leaching by using an AS19-HC analytical column and KOH leacheate, thus obtaining a linear equation of concentration and peak area, and calculating the contents of all components in chloroacetic acid through the linear equation. The invention has the advantages that the whole analysis process is simple and convenient, the pollution and loss is smaller, the blank and marked sample recovery rate is 96 to 99.75 percent and the method is suitable for content detection of monochloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid andsulfate radical in chloroacetic acid.
Owner:湖北省兴发磷化工研究院有限公司
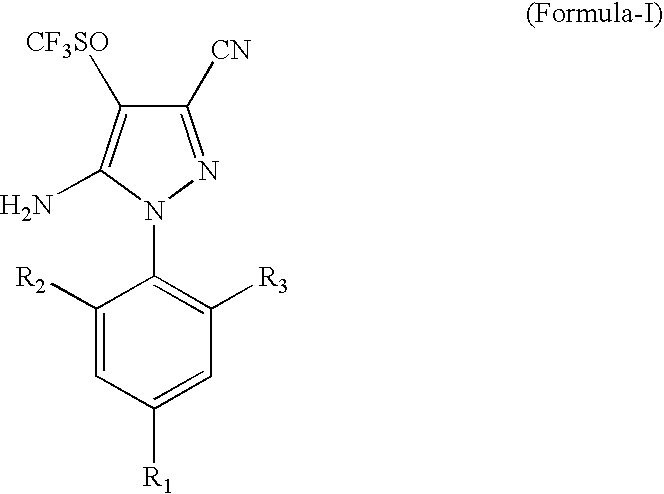
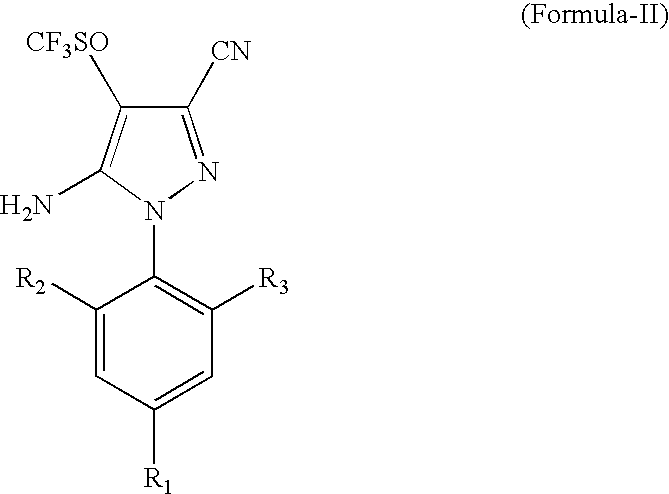
Process for the preparation of Fipronil, an insecticide, and related pyrazoles
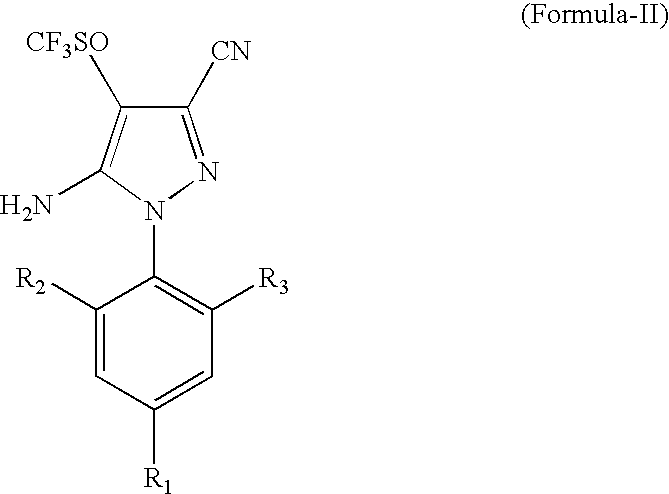
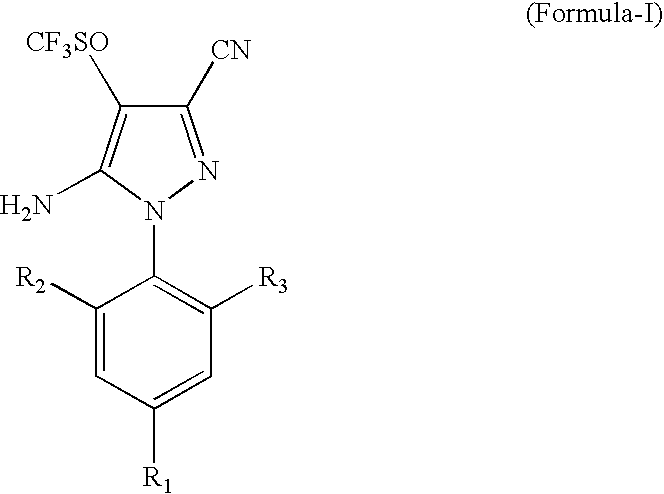
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of 5-amino-1-phenyl-3-cyano-4-trifluoromethyl sulphinyl pyrazoles as defined by Formula-I,wherein: R1=trifluoromethyl or trifluoromethoxy, and R2, R3=individually hydrogen, chlorine or bromine, the process comprising the step of oxidizing a compound of Formula-II,wherein: R1=trifluoromethyl or trifluoromethoxy, and R2, R3=individually hydrogen, chlorine or bromine, in a medium comprising at least one oxidizing agent and trichloro acetic acid, and / or the reactions product (s) of the at least one oxidizing agent and trichloro acetic acid, and at least one melting point depressant. The preferred pyrazole is Fipronil, preferably prepared using hydrogen peroxide and dichloro acetic acid at room temperature.
Owner:GHARDA CHEM LTD
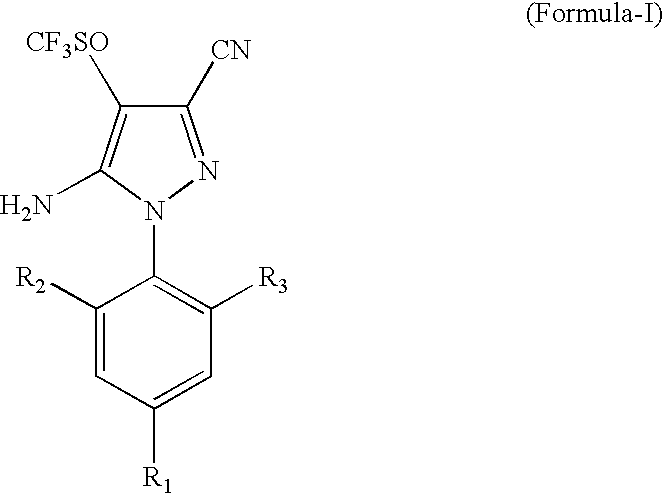
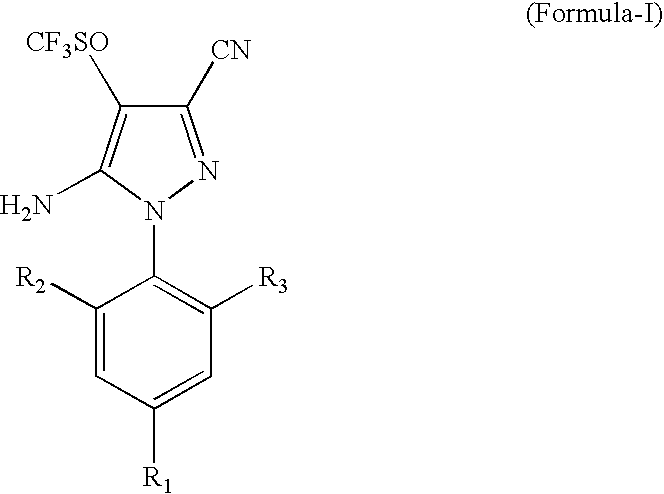
Process for the Preparation of Fipronil, an Insecticide, and Related Pyrazoles
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of 5-amino-1-phenyl-3-cyano-4-trifluoromethyl sulphinyl pyrazoles as defined by Formula-I,wherein: R1=trifluoromethyl or trifluoromethoxy, and R2, R3=individually hydrogen, chlorine or bromine, the process comprising the step of oxidizing a compound of Formula-II,wherein: R1=trifluoromethyl or trifluoromethoxy, and R2, R3=individually hydrogen, chlorine or bromine, in a medium comprising at least one oxidizing agent and trichloro acetic acid, and / or the reactions product (s) of the at least one oxidizing agent and trichloro acetic acid, and at least one melting point depressant. The preferred pyrazole is Fipronil, preferably prepared using hydrogen peroxide and dichloro acetic acid at room temperature.
Owner:GHARDA CHEM LTD
Method for simultaneous determination of dichloroacetic acid, gluconic acid and acetic acid in compound diisopropylamine dichloroacetate tablets by ion chromatography
ActiveCN102565212ASolve productivitySolve the problem of determining the content of impuritiesComponent separationSodium acetateAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous determination of dichloroacetic acid, gluconic acid and acetic acid in compound diisopropylamine dichloroacetate tablets by ion chromatography. The contents of dichloroacetic acid, gluconic acid and acetic acid in compound diisopropylamine dichloroacetate tablets aqueous solution are measured by ion chromatography, and then are converted to the contents of diisopropylamine dichloroacetate, sodium gluconate and sodium acetate by formulas. The method disclosed by the invention is used for monitoring a production process of compound diisopropylamine dichloroacetate tablets, has the characteristics of rapidness, simplicity, no interference, high accuracy and simplicity and feasibility in operation, and has strong practicability in improvement of pharmaceutical synthesis process and product quality control.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
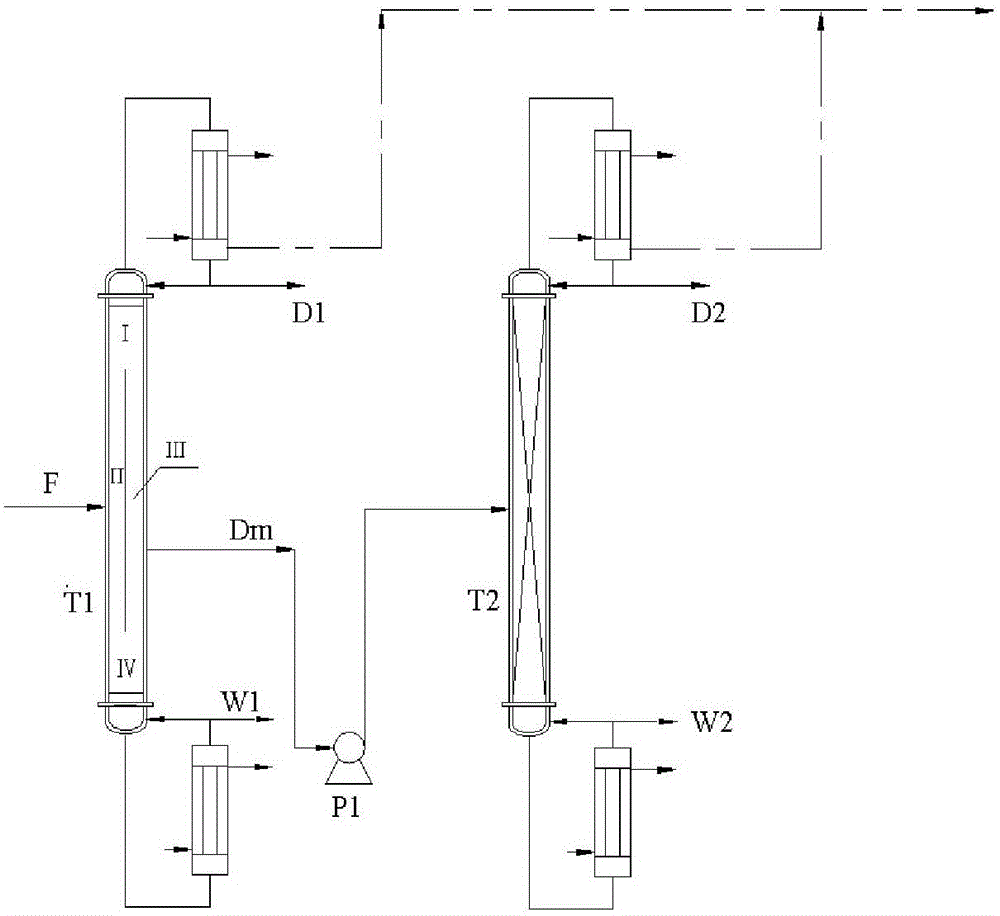
Treatment method of chloroacetic acid by-product crystallization mother liquid
InactiveCN106554270AEfficient separationContinuous productionCarboxylic compound separation/purificationDistillationChloroacetic acids
The invention relates to a treatment method of chloroacetic acid by-product crystallization mother liquid. The treatment method includes the steps of: (1) performing pressure reducing distillation to the crystallization mother liquid obtained from production of chloroacetic acid in a dividing wall rectifying column T1, withdrawing low boiling point impurities from the column top and high boiling point impurities from the column bottom, and withdrawing a monochloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid mixture from a side-withdrawing point in the middle of the column; (2) feeding the monochloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid mixture withdrawn from the side-withdrawing point of the dividing wall rectifying column T1 to a pressure reducing rectifying column T2 to perform pressure reducing rectification, and obtaining a high-purity monochloroacetic acid product on the top of the column and a high-purity dichloroacetic acid product in the bottom of the column. Compared with the prior art, the rectification is carried out with two sets of rectifying columns, so that effective separation of the chloroacetic acid crystallization mother liquid is achieved. The method greatly reduces equipment cost and energy consumption during separation and can continuously and stably produce the high-purity monochloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid products simultaneously. Purities of the products are both more than 99%.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
Prepn of dissolved liquid crystal of chitosan grafted polylactic acid
The preparation of dissolved liquid crystal of chitosan grafted polylactic acid includes vacuum deairing of chitosan for 1 hr, charging nitrogen, adding toluene as dispersant, dripping toluene solution of aluminium ethide as catalyst in 1-3 molar times of chitosan, ring opening polymerization of lactide inside solution to produce grafted copolymer of chitosan and polylactic acid. The copolymer is dissolved in trifluoro acetic acid, acetic acid, dichluoro acetic acid or water, and when the solution concentration is greater than 1%, the liquid crystal behavior may be observed in polarizing microscope. The grafted copolymer of the present invention has special performance, and may be used as interface coupling agent for polymer blend of chitin, chitosan and polylactic acid as well as medicine delayed releasing material and other human body implanting biological material and various biological fibrous material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for purifying chloroacetic acid by catalytic hydrogenolysis in chloroacetic acid production and application thereof
ActiveCN102001930AReduce consumptionImprove removal effectChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationHydrogen separationGas phaseFixed bed
The invention discloses a method for purifying chloroacetic acid by catalytic hydrogenolysis in chloroacetic acid production and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging a VIII-group metal serving as a hydrogenolysis catalyst bed layer in a catalytic reactor with a lining made from polytetrafluoroethylene or a zirconium material; making the solution of chloride flow through a fixed bed layer and making a hydrogen-nitrogen mixed gas and a liquid phase flow in parallel to enter the bed layer at the gage pressure of 100 to 800 kPa and the temperature of 100 and 200 DEG C; performing hydrogenolysis on all or most of polychlorinated acid in the solution of the chloride; taking a material out of the reactor; performing gas-liquid separation; crystallizing the liquid phase of the solution of the chloride; washing to obtain a chloroacetic acid product; and condensing, absorbing and separating a gas phase for recovering hydrogen, chlorine hydride and acetic acid. The method can improve the removal effect and the treatment efficiency of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid and product purity, reduce the deactivation trend and the activity descent speed of a catalyst, shorten reaction time, reduce hydrogen consumption, improve raw material utilization rate and product yield, and further improve economic benefits.
Owner:CHINA TIANCHEN ENG +2
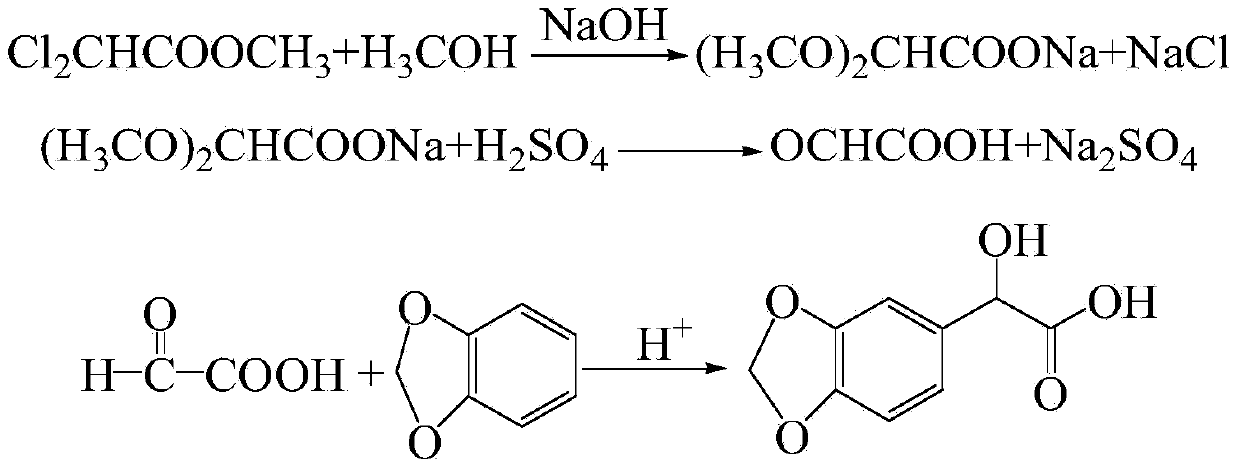
Preparation method for 3,4-methylene dioxy mandelic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method for a heliotropin midbody such as 3,4-methylene dioxy mandelic acid through microwave radiation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking methyl dichloroacetate as a raw material, and reacting with sodium hydroxide or methanol solution of potassium hydroxide under microwave radiation to obtain glyoxylic acid water solution; then reacting the obtained glyoxylic acid water solution with 1,2-methylenedioxybenxene under microwave radiation to prepare 3,4-methylene dioxy mandelic acid finally. Through the application of microwave, under the condition that the reaction time is greatly reduced, the yield of 3,4-methylene dioxy mandelic acid is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Chloroactic acid method for treating wastewater of glycine, and comprehensive utilization method
InactiveCN1958481ASolve pollutionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by heatingDecompositionEvaporation
This invention is aimed to treating toxic wastewater from glycine production by chloroacetic acid method and recovering valuable resources from the wastewater. This invention utilizes evaporation, concentration, cooling and crystallization to remove amine, conversion to remove chloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid, alcohol-precipitation to remove glycine and iminodiacetic acid, extraction to remove acetic acid, monochloroacetic acid and dichloroacetic acid, and oxidative decomposition to completely decompose toxic substances in the wastewater. This invention provides a good method for environmental protection engineering and resource recycling.
Owner:ZHONGKEQUAN WUYING ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION BEIJING
Synthetic method for stable isotope labeled thiamphenicol
ActiveCN107827791AIncrease usageThe synthesis steps are simpleOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsStable Isotope LabelingBenzaldehyde
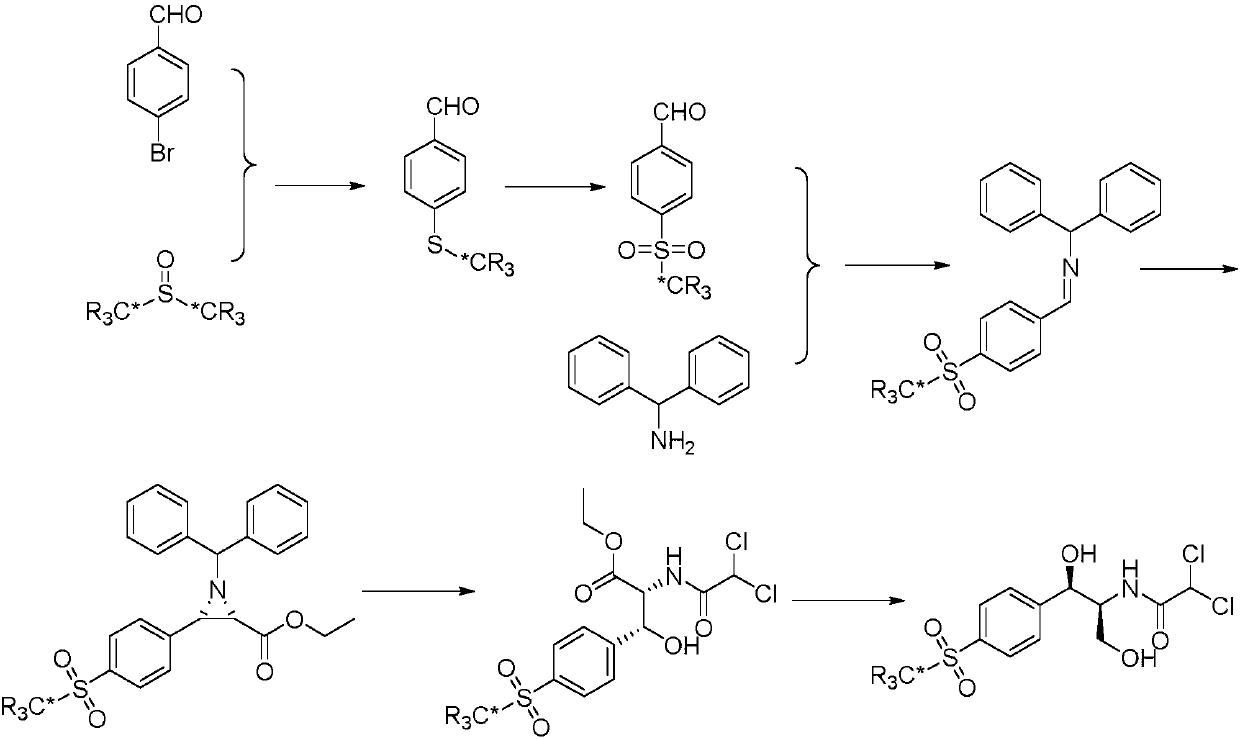
The invention relates to a synthesis method for stable isotope labeled thiamphenicol and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The synthesis method for stable isotope labeled thiamphenicol is characterized in that p-bromobenzaldehyde and stable isotope labeled dimethylsulfoxide are taken as raw materials, the raw materials are synthesized to obtain stable isotope labeled p-methylthiobenzaldehyde, oxidization is performed to obtain stable isotope labeled 4-methylsulfonyl benzaldehyde, next, condensation is performed on stable isotope labeled 4-methylsulfonyl benzaldehyde and benzhydrylamine to obtain imine, then imine further reacts with ethyl diazoacetate under the action of (R)-VAPOL and triphenyl borate to build an ethylene imine structure fragment, at last, ring opening is performed on ethylene imine under a dichloroacetic acid condition, an ester group is reduced to synthesize stable isotope labeled thiamphenicol. The raw materials required for synthesis and an intermediate are simple and easily accessible, and the target product (stable isotope labeled thiamphenicol) is high in purity and stable isotope abundance, can be used for internal standard substances for veterinary drug residue test in the food safety field and study of the thiamphenicol metabolic mechanism, and has an important practical application value.
Owner:山东辉璟生物医药科技有限公司
Microcrystalline Cellulose-Chitosan Fiber
InactiveCN102277650AImprove the statusLow viscosityConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsAcetic acidZinc Acetate Dihydrate
The invention relates to a microcrystalline cellulose-chitosan fiber, which is characterized in that the components contained in the stock solution and the mass ratio ranges of each component are as follows: chitosan 2wt%-5wt%, glycerin 0.1wt%-1.0wt %, zinc acetate 1wt%-5wt%, microcrystalline cellulose 1wt%-10wt%, and water. It is prepared by wet and dry method. Because of the addition of microcrystalline cellulose, the charged state of chitosan molecules is improved, the viscosity of chitosan acidic solution is reduced, and the generation of jelly is prevented, which replaces the traditional method of adding urea, isopropanol, dichloroacetic acid, etc. The raw materials produced by the jelly, as well as reagents such as acetic acid that act as viscosifiers and defoamers, save raw materials and reduce costs.
Owner:WUJIANG RUIFENG WEAVING
Environment disinfectant for livestock cultivation
InactiveCN102870811ASimple preparation processLow costBiocideDisinfectantsDisinfectantPotassium permanganate
The invention discloses an environment disinfectant for livestock cultivation, which comprising the following components according to part by weight: 5 to 10 parts of potassium permanganate, 1 to 3 parts of dichloroacetic acid, 1 to 4 parts of phthalic dicarboxaldehyde and 90 parts of water. The environment disinfectant for livestock cultivation has the advantages of simple preparation technology, low cost and obvious effect.
Owner:QINGDAO SANDING SANITARY PROD
Disinfectant for poultry and livestock breeding houses
InactiveCN104041516AEffective ingredientsComposition is stableBiocideDisinfectantsDisinfectantFatty alcohol
A disclosed disinfectant for poultry and livestock breeding houses is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 7-10 parts of kaolinum, 8-16 parts of o-phthalaldehyde, 10-20 parts of silicon dioxide, 5-10 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 10-18 parts of potassium permanganate, 9-15 parts of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, 3-6 parts of dichloroacetic acid, 11-21 parts of calcium peroxide, 15-25 parts of polyaluminum chloride, 16-26 parts of polyferric sulfate and 5-10 parts of gypsum. The provided disinfectant for poultry and livestock breeding houses is scientific and reasonable in formula compositions, substantial in disinfection effect, free of drug residue and free of toxic and side effects, is capable of effectively improving the immunity of livestock and poultry, and has relatively high killing rate on bacteria and virus pathogenic organisms.
Owner:QINGDAO BOHONG MARINE BIOTECH
Imitated silk fabric dyeing and finishing process
InactiveCN105386310AExcellent mothproofImprove mildew resistanceHeat resistant fibresGrip property fibresPolymer scienceHexamethylenetetramine
The present invention discloses an imitated silk fabric dyeing and finishing process comprising the following steps: 1) pre-treatment; 2) dyeing; and 3) finishing, to be more specific, sequentially pouring 1 to 2 parts by weight of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 2.1 parts by weight of sodium benzoate, 1.5 parts by weight of peppermint extract and 0.7 part by weight of dichloroacetic acid into 26 parts by mass of deionized water, stirring well; and then simultaneously pouring 0.4 part by weight of Toosendan, 0.2 part by weight of boron phosphate, 0.7 part by weight of hexamethylenetetramine and 0.9 part by weight of polyethylene glycol stearate, continuing stirring until full mixing to prepare a finishing solution; then padding a fabric in the finishing solution, then taking out, and drying at constant temperature. The fabric dyed and finished by the imitated silk fabric dyeing and finishing process has excellent moth-proofing, mouldproof, antibacterial, flame retardant and antistatic performances, and is strong in washability and soft to touch.
Owner:常熟市华威服饰厂
Preparation method of methyl difluoroacetate
InactiveCN102531895APhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventDifluoroacetic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing difluoromethyl acetate. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: mixing methyl dichloroacetate with potassium fluoride serving as a catalyst; reacting at a high temperature; slowly adding an organic solvent; cooling a system to be below zero DEG C and preserving heat; stirring; distilling under reduced pressure; filtering; washing a precipitate with methylbenzene; continually drying a filtrate with anhydrous sodium sulfate; and driving a filter cake away to obtain difluoromethyl acetate serving as a product.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOFLUORO SCI
Novel synthesis method of Istaroxime
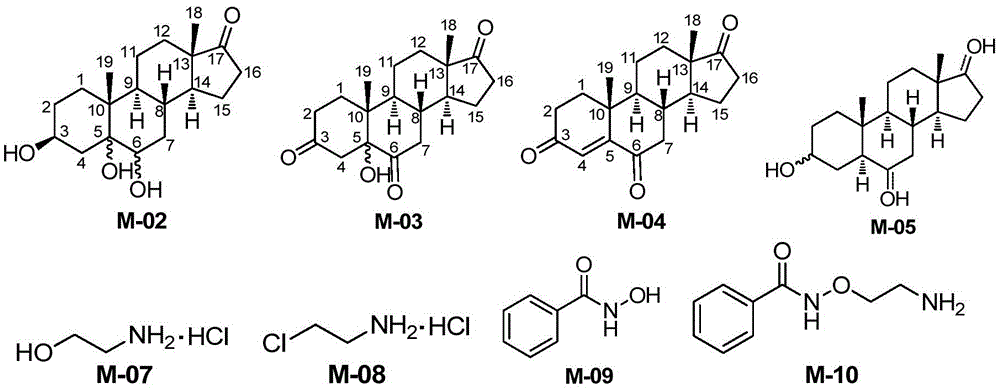
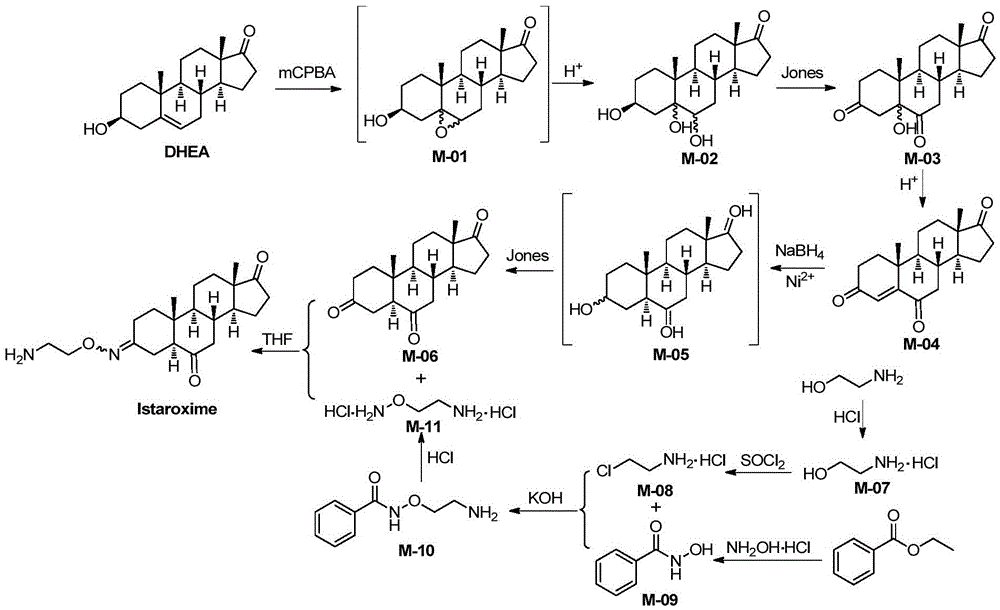
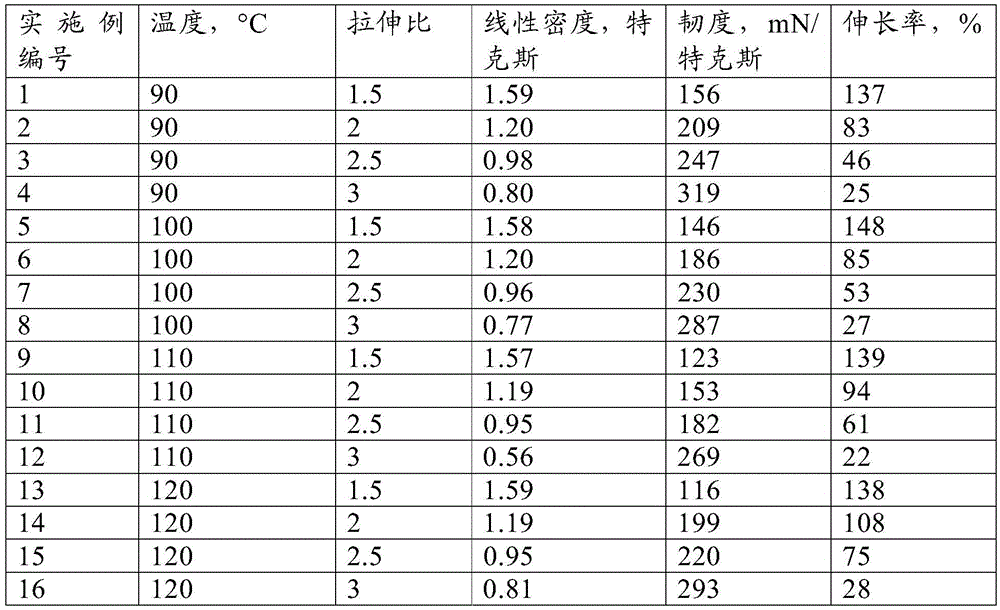
InactiveCN105585607AEasy to operateRaw materials are easy to getSteroidsBenzoic acidChemical reaction
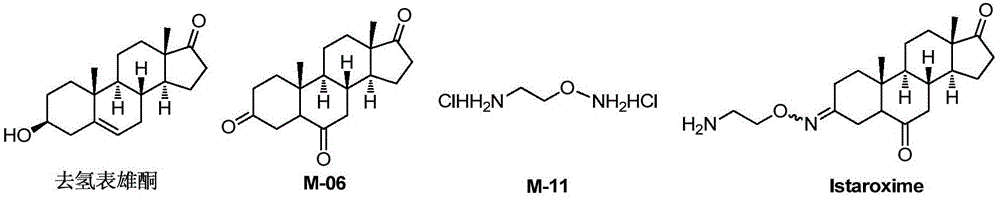
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and discloses a novel synthesis method of Istaroxime. The method comprises the following steps: by using dehydrogenated epiandrosterone as an initial raw material, carrying out epoxidation, ring opening, reduction, oxidation and other reactions to prepare an intermediate M-06; by using ethyl benzoate as an initial raw material, reacting the ethyl benzoate with hydroxylamine hydrochloride to obtain phenyl hydroximic acid, carrying out hydrochlorination and chlorination by using ethanolamine as a raw material to obtain dichloroacetate, and carrying out substitution, hydrolysis and other reactions on the dichloroacetate and the phenyl hydroximic acid to obtain an intermediate M-11; and finally, reacting the M-06 with the M-11 to obtain the end product Istaroxime. According to the method, in the intermediate M-06 synthesis process, the polarity of all the intermediates has great differences from that of the impurities and reaction reagents; and in the intermediate 11 synthesis process, the active spots capable of participating in the chemical reaction in the reaction substrate are simple. Therefore, the method can achieve the requirements without carrying out column chromatography purification, thereby simplifying the synthesis after-treatment process.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Dichloroacetic acid diisopropylamine oral preparation and its preparation process-treatment of liver function injury
InactiveCN1439363AStable and controllable qualityPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemEffervescent tabletCoated tablets
An orally applied disotat for treating hepatic dysfunction is prepared from disotat as active component and proper auxiliaries. It may be tablet, coated tablet, effervescent tablet, enteric tablet, chewing tabet, capsule, softgel, pill, etc.
Owner:HONGYI SCI & TECH CO LTD NANCHANG
Process for the preparation of a fiber, a fiber and a yarn made from such a fiber
A fiber comprising polyethylene-2,5-furan-dicarboxylate, is prepared by melt spinning in a process wherein a molten composition comprising polyethylene-2,5-furan-dicarboxylate having an intrinsic viscosity of at least0.55 dl / g, determined in dichloroacetic acid at 25 DEG C, is passed through one or more spinning openings to yield molten threads; wherein the molten threads are cooled to below the melting temperature of the composition to yield spun fibers; and wherein the spun fibers are drawn to a linear density in the range of 0.05 to 2.0 tex per fiber. The invention also proves a fiber comprising polyethylene-2,5-furan-dicarboxylate having a linear density of 0.05 to 2.0 tex, wherein the polyethylene-2,5-furan-dicarboxylate has an intrinsic viscosity of at least0.45 dl / g, determined in dichloroacetic acid at 25 DEG C.
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
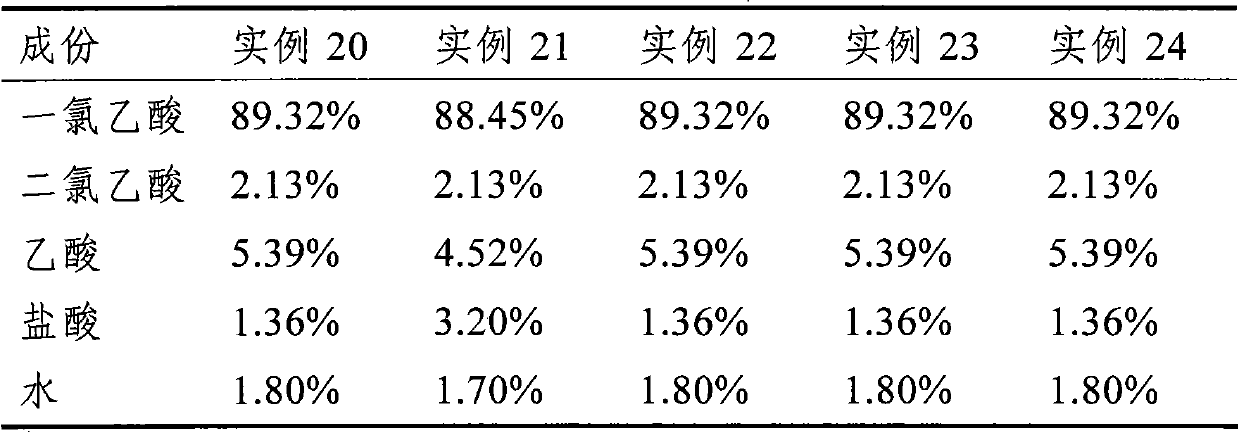
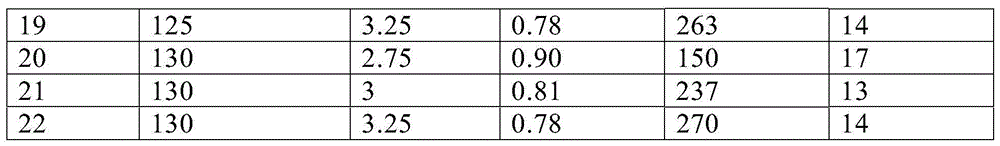
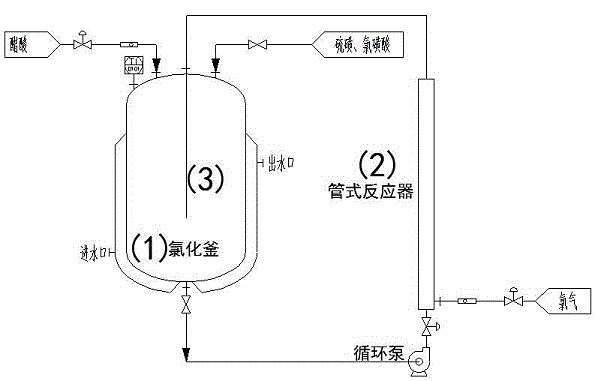
Method for preparing chloroacetic acid by using intermittent chlorination process
InactiveCN104478697AReduce generationShort reaction timePhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidChloroacetic acids
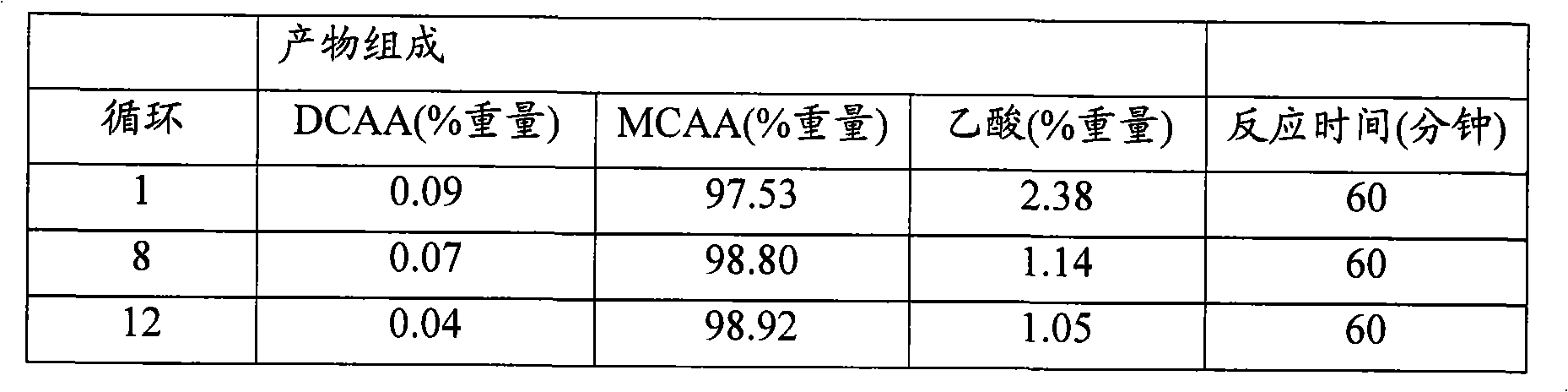
The invention discloses a method for preparing monochloro acetic acid based on an intermittent catalytic chlorination process of acetic acid. The method comprises the following steps: sequentially adding acetic acid, a main catalyst which is sulphur and a cocatalyst which is chlorosulfonic acid into a reaction kettle, increasing the temperature of the reaction kettle to 70-75 DEG C, reacting for 0.5-1 hour, then increasing the temperature of the reaction kettle to 95-100 DEG C, and continuously carrying out circulation reaction on a reaction solution and chlorine gas by virtue of a tubular reactor until reaction reaches the final point, wherein the constant temperature of the reaction kettle is retained by the circulation water in the reaction process. The method has the advantages that the production efficiency is high, and the generated dichloroacetic acid is low in content.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Drug sustained-release system for treating tumours and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102228424ASmooth releaseLarge specific surface areaPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectDrug carrier
The invention provides a drug sustained-release system for treating tumours, which comprises a drug carrier, a drug and a surface active agent. The drug carrier is a biodegradable polymer fibre. The drug is a dichloroacetic acid salt covered and loaded on the drug carrier. The surface active agent is covered and loaded on the drug carrier, wherein the drug accounts for 15-70 wt % of the drug sustained-release system and the surface active agent accounts for 0-15 wt % of the drug sustained-release system. The invention further provides a preparation method of the drug sustained-release system for treating the tumours. The drug sustained-release system can realize the sustained release of the local drug so that the concentration of the local drug around the tumours is in a scope of a therapeutic effect window; however, the drug concentration except the tumours and in body fluid is in a health scope, therefore, the utilization rate of the drugs is increased and the therapeutic effect is guaranteed as well as the usage amount of the drugs is reduced and the toxic side effects caused by large dosage of the drugs are reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
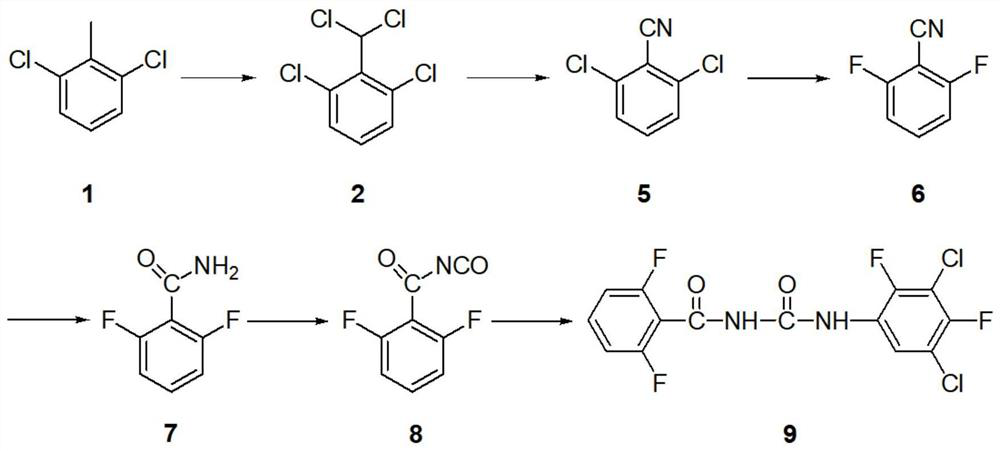
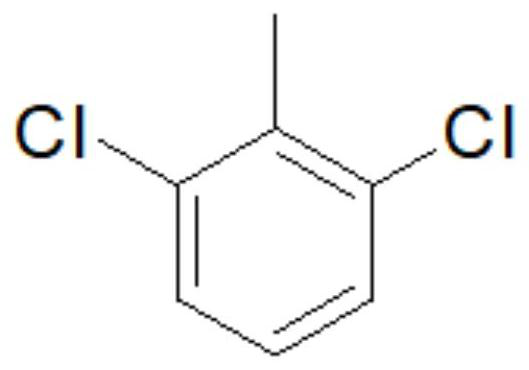
Synthesis method of insecticide teflubenzuron and intermediate 2,6-difluorobenzamide of insecticide teflubenzuron
ActiveCN111995538AShort reaction pathHigh yieldUrea derivatives preparationIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationSodium acetateHydroxylamine
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an insecticide teflubenzuron and an intermediate 2,6-difluorobenzamide of the insecticide teflubenzuron, belonging to the field of pesticides. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparation of 2,6-dichlorobenzylidene chloride: preparing turbid liquid of dichlorotoluene and phosphorus pentachloride, introducing chlorine gas, layering materials by utilizing a gas-liquid separator, collecting a crude product, and rectifying the crude product to obtain the 2,6-dichlorobenzylidene chloride; and 2, preparation of 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile: mixing 2,6-dichlorobenzylidene chloride, acetic acid, zinc chloride, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and sodium acetate, carrying out heating for a reflux reaction, conducting cooling, stirring,filtering and drying successively after the reaction is completed so as to obtain 2, 6-dichlorobenzonitrile. By adopting a one-pot method, a reaction route is shortened, total yield is increased to 67.3% from conventional 55.4%, and cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGYU JINTENG MEDICAL CHEM IND
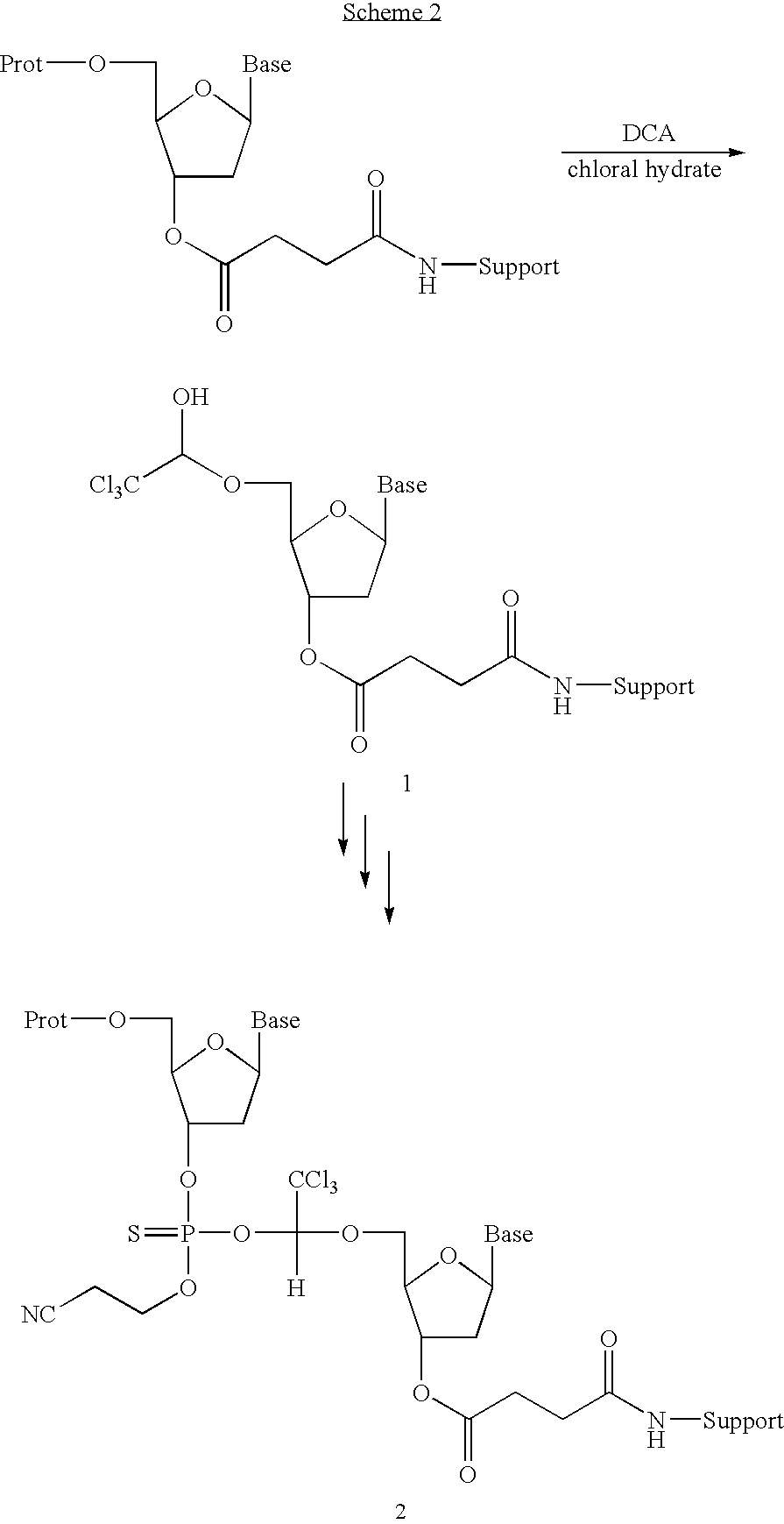
Methods for detection of chloral hydrate in dichloroacetic acid
InactiveUS7173123B2Accurate measurementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAcetic acidChloral hydrate
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Production process for chloroacetic acid
InactiveCN1566063AQuality improvementHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationAcetic acidChloroacetic acids
The invention discloses a process for preparing chloroacetic acid which comprises, conducting chlorination reaction to the chlorine and acetic acid at the presence of catalyst, adding mother liquid before the chlorination reaction, the weight ratio of acetic acid and mother liquid is 1:0.05-0.2, chlorine resisting agent can also be added before the chlorination reaction.
Owner:DONGFENG CHEM XINHUA MEDICINE GROUP ZIBO CITY SHANDONG PROV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com