Hydrodechlorination method for producing high-purity monochloro acetic acid
A technology for catalytic hydrogenation and chloroacetic acid, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, catalysts for physical/chemical processes, etc., can solve problems such as low selectivity, limited processing capacity, unrealizable separation and removal, etc., to achieve High reaction efficiency, high activity and selectivity, and the effect of suppressing by-product acetic acid and other polymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
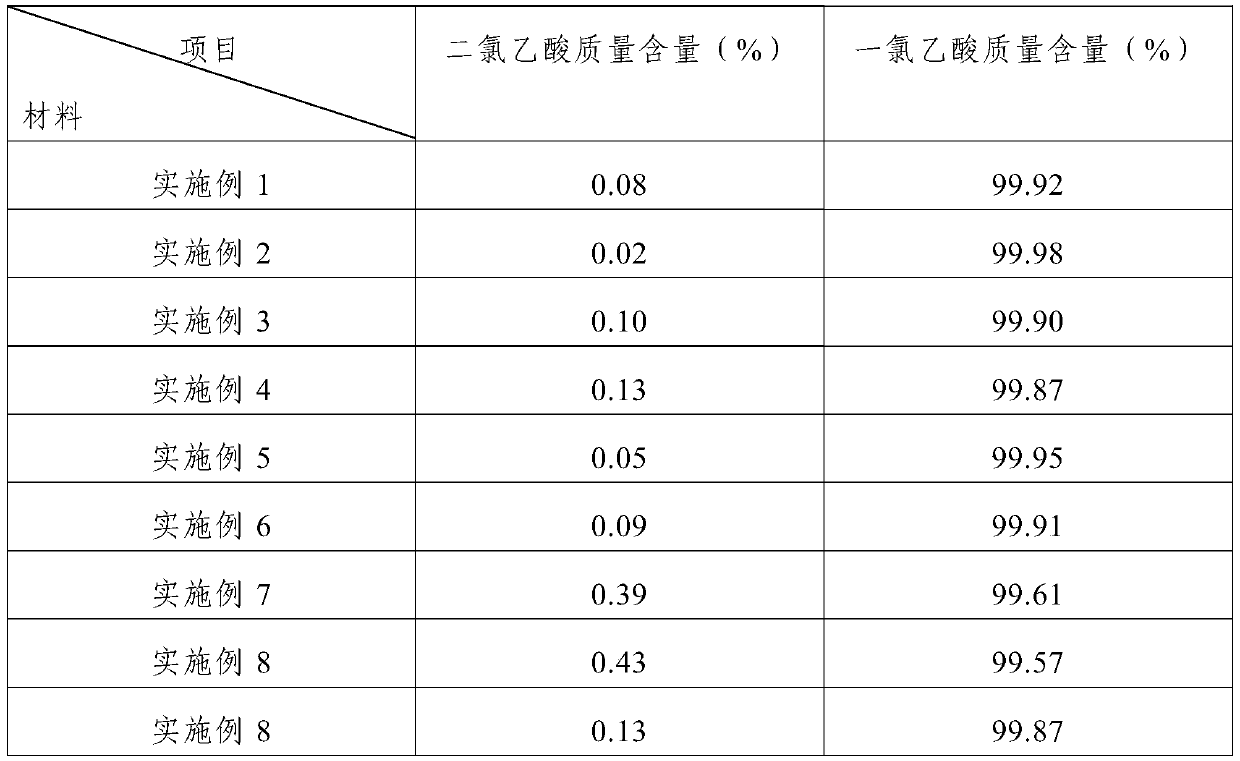
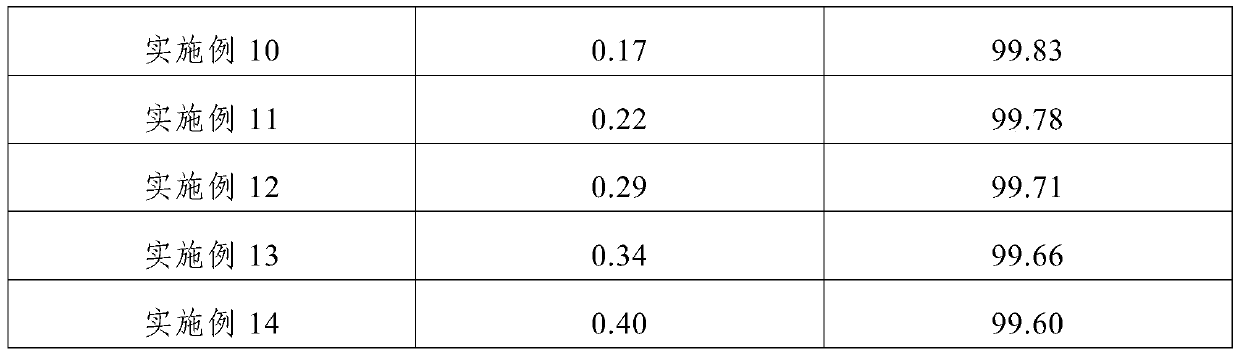
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This embodiment includes the following steps:
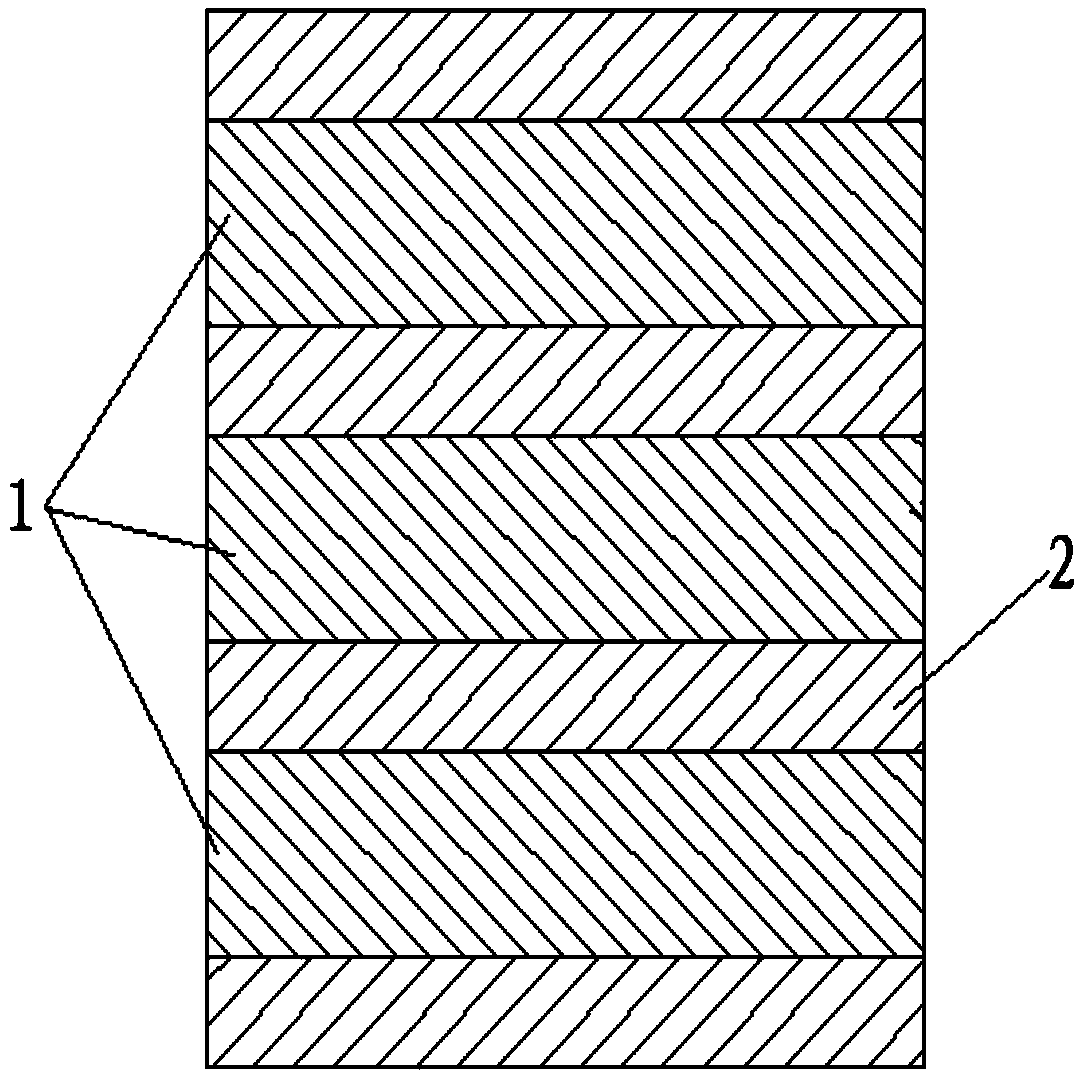
[0031] Step 1. The fixed-bed reactor is filled with a catalyst bed in a staged packing method. The catalyst bed is composed of a palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 and an inert material layer 2 that are overlapped (such as figure 1 (Shown), the height of each palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 in the catalyst bed is 1.0 times the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor, and the height of each inert material layer 2 in the catalyst bed is 0.5 times the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor, the uppermost layer and the lowermost layer of the catalyst bed are both inert material layer 2, the number of layers of the palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 is not less than 3; the palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 Consists of the following components by mass percentage: 1.0% active component, 0.1% metal promoter, the balance being a carrier, the active component is Pd, the metal promoter is Mg, and the carrier is activated carbon; The a...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The method for producing high-purity monochloroacetic acid by catalytic hydrodechlorination in this embodiment is the same as that of embodiment 1, except that the metal promoter in step 1 is Ba, Ce, La, Fe or Al, or Ba A mixture of at least two of, Ce, La, Fe, Mg and Al.
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1. The fixed-bed reactor is filled with a catalyst bed in a staged packing method. The catalyst bed is composed of a palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 and an inert material layer 2 that are overlapped (such as figure 1 (Shown), the height of each palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 in the catalyst bed is 1.0 times the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor, and the height of each inert material layer 2 in the catalyst bed is 0.5 times the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor, the uppermost layer and the lowermost layer of the catalyst bed are both inert material layer 2, the number of layers of the palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 is not less than 3; the palladium-carbon catalyst layer 1 Consists of the following components by mass percentage: 0.8% of the active component, 0.3% of the metal auxiliary agent, the balance being the carrier, the active component is Pd, and the metal auxiliary agent is a mixture of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cross section diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com