Use of TGF-beta antagonists to treat infants at risk of developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia
A technology of dysplasia and antagonists, which can be used in medical preparations containing active ingredients, anti-animal/human immunoglobulins, and antibody medical ingredients, etc., which can solve problems such as reduction of morbidity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
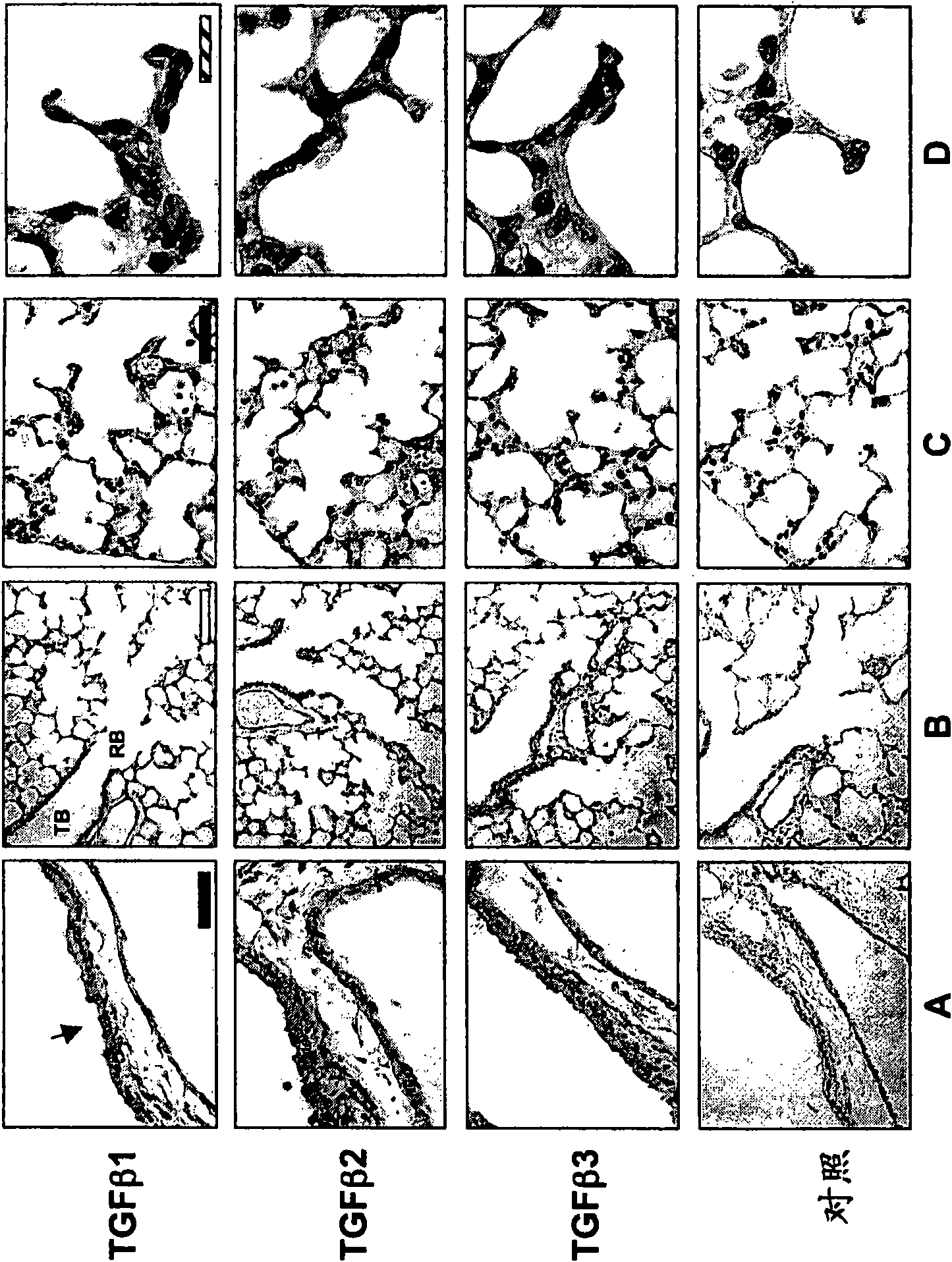
[0096] Example 1: Expression of TGF-β in the developing lung, and modulation of TGF-β signaling with anti-TGF-β antibodies
[0097] Although increased RNA levels of TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 were observed in postnatal rat lung (Zhao et al., Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 278: L1231-1239 (2000)), TGF The expression pattern of the -β isoform in the developing lung periphery is poorly understood. Such as figure 1 As indicated, TGF-β1-3 immunoreactivity was detected in the lungs of 10-day-old mouse pups. Similar levels of TGF-β isoforms were observed in large conducting airways, as well as in terminal and respiratory bronchioles. Although TGF-β1 showed the highest immunoreactivity in the peripheral lung, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 were also detected there. Since it was desired to determine whether inhibition of TGF-β activity in the distal developing lung suppressed the effects of lung injury on alveolar development, we first tested whether a pan-specific TGF-β neutralizing antibody re...
Embodiment 2
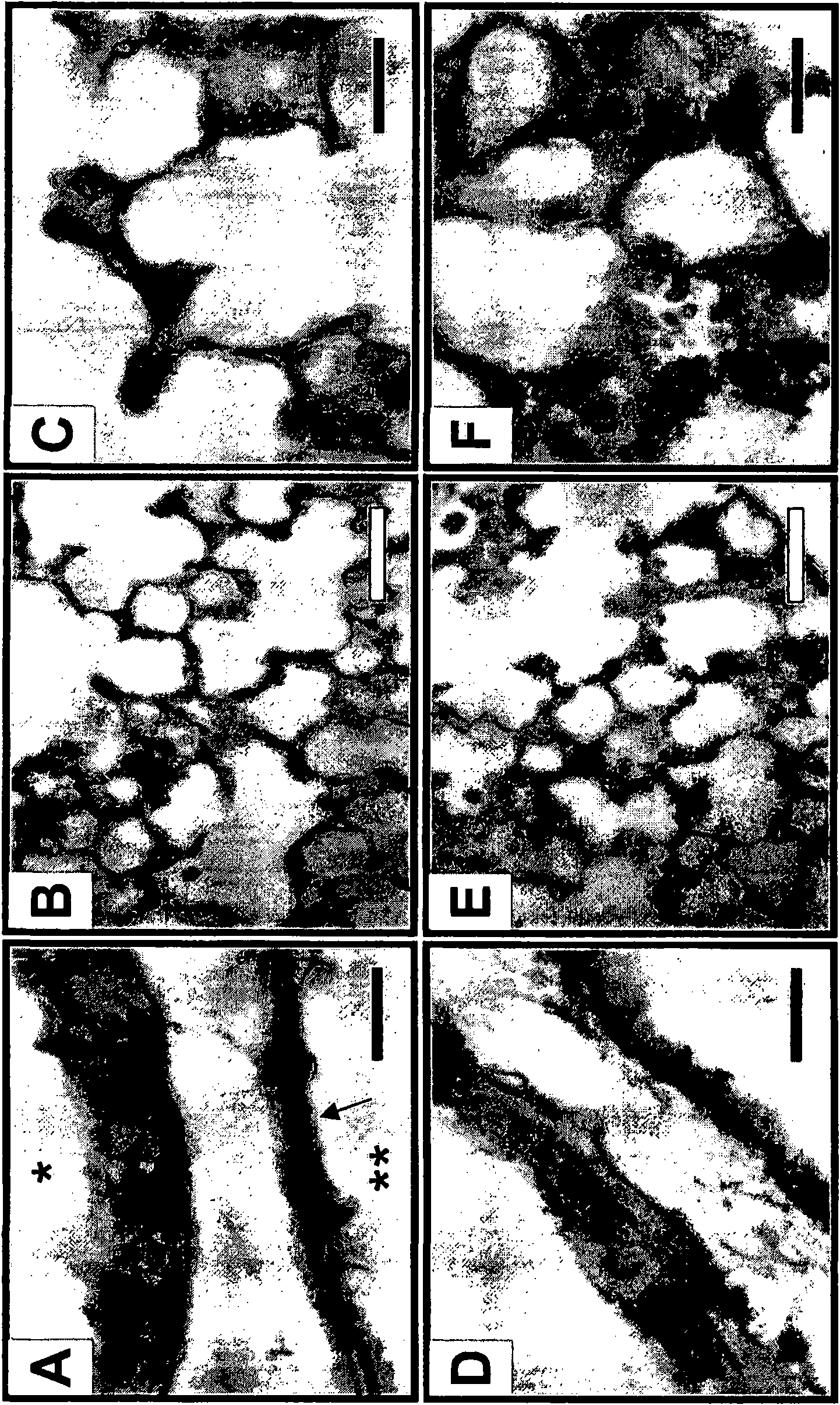
[0099] Example 2: Anti-TGF-β antibody treatment improves alveolar production in damaged neonatal lung
[0100] Chronic inhalation of high levels of oxygen in newborn rodents results in lung injury and inhibits terminal lung development in a manner similar to that observed in infants with BPD (Bonikos et al., Lab Invest. 32:619-635 (1975); Frank et al., J. Appl. Physiol. 45: 699-704 (1978); Pappas et al., Lab Invest. 48: 735-748 (1983); Bonikos, Am. J. Pathol. 85: 623-650 (1976) ; Warner et al., Am. J. Physiol. 275:L110-117 (1998)). Therefore, a model of lung injury in hyperoxic mouse pups was used to examine whether treatment with TGF-β neutralizing antibodies improved alveolar development. Neonatal mouse pups were continuously exposed to 85% O 2 10 days, as this level of exposure was observed in preliminary studies to result in reduced alveolar production with concomitant >80% survival. Such as Figure 4 As shown, chronic exposure to 85% O 2 Associated with hypoplasia o...
Embodiment 3
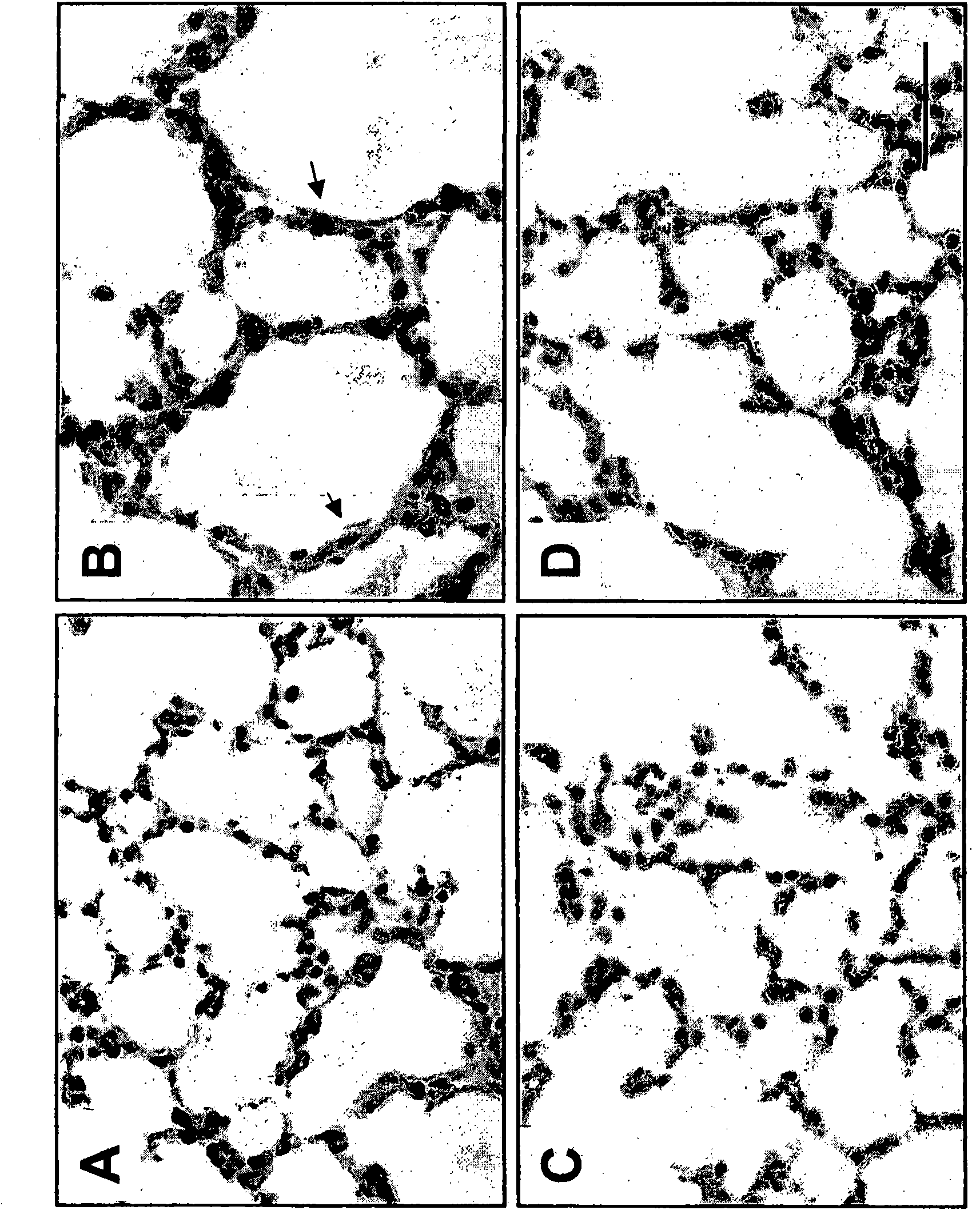
[0105] Example 3: Improvement of elastin structure of alveolar septa in damaged neonatal lungs by anti-TGF-β treatment
[0106] Elastin is an important component of the alveolar wall and pulmonary vasculature, and its biosynthesis and extracellular assembly are critical for normal lung development. In infant lungs with BPD, as in neonatal mice with lung injury (Veness-Meehan et al., Pediatr. Res. 48:434-444 (2002)), the normal structure of elastin is present at the top of the secondary cristae was disrupted, and instead elastin was observed in the distal airway wall. Since TGF-β regulates ECM proteins in mesenchymal cells (Leask et al., Faseb J.18:816-827 (2004)) and lung (Kucich et al., Am.J.Respir.Cell Mol.Biol.17:10 -16 (1997); Parks et al., Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 17:1-2 (1997)), the effect of treatment with 1D11 on extracellular matrix protein deposition was examined. Such as Figure 6 As shown, chronic respiratory high levels of O 2 Associated with changes in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com