Strain of gluconacetobacter and application thereof
A technology of gluconacetobacter and strains, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, application limitation, low bacterial cellulose production, etc., and achieve good water absorption and high reliability Regulatory, suitable for the effect of large-scale industrial fermentation production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
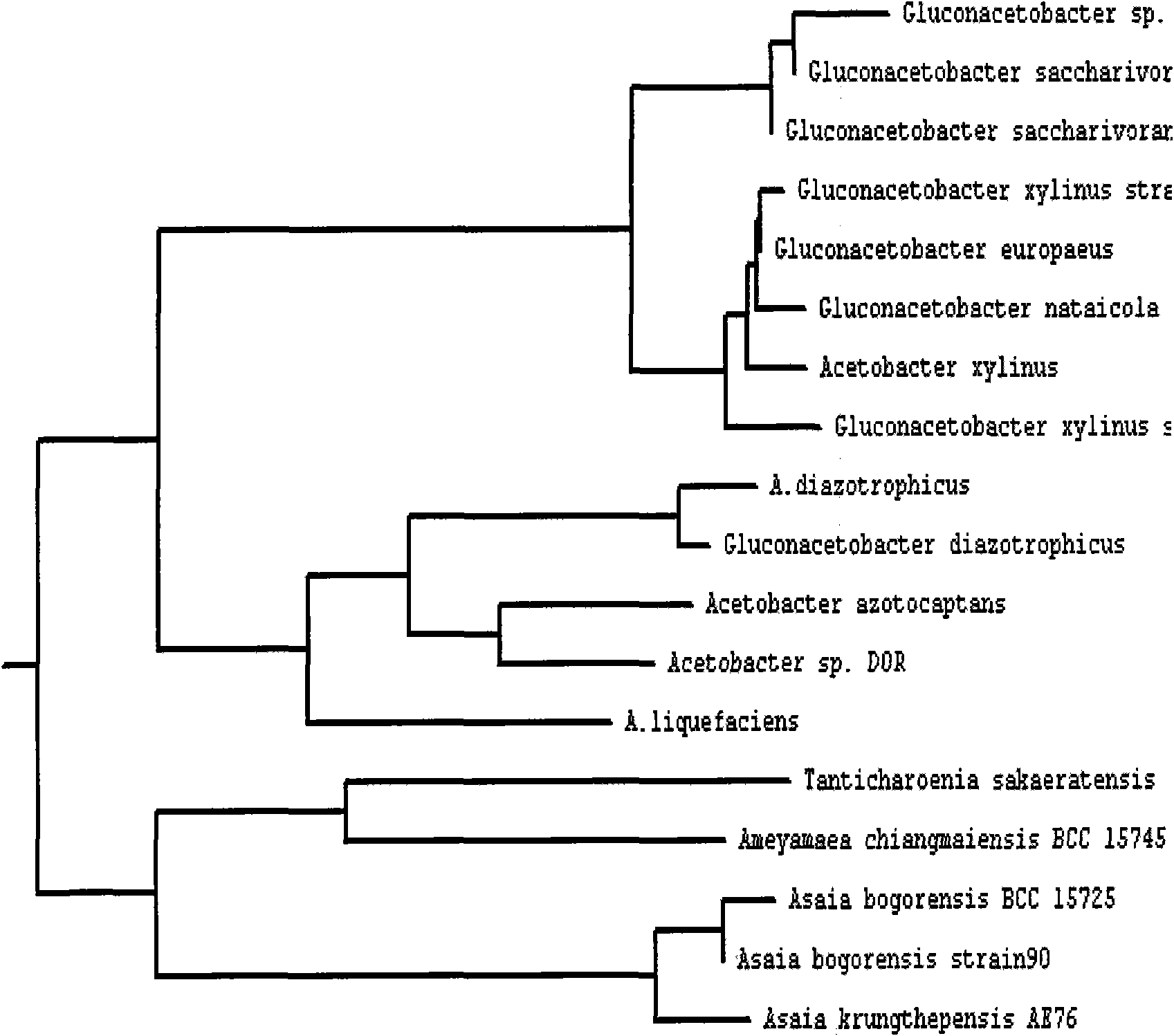
[0030] Example 1. Isolation of Gluconacetobacter sp.SC-01 (Gluconacetobacter sp.SC-01)
[0031] The experimental materials come from rotten persimmons produced in Ji County, Tianjin.
[0032] The specific steps are as follows: take the rotten persimmon juice, filter it with a 100-mesh sieve, and dilute it in a 10-fold gradient with sterile normal saline, and dilute it to 10 1 -10 6 , take 10 3 -10 5 Spread it on a solid GYC medium plate, culture at 25-35°C for 4 days, observe the growth of the colony, pick the colony with transparent spots and transfer it to the liquid HS medium for 10 days, and there is a film on the surface of the culture medium After the membrane is treated, it is detected as a bacterial cellulose membrane, and it is preliminarily judged that the bacteria is a bacteria that produces bacterial cellulose. After Gram staining, physiological and biochemical experiments, 16S rDNA gene sequence analysis and BIOLOG identification, it was determined that the st...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2, fermentation of Gluconacetobacter sp.SC-01 (Gluconacetobacter sp.SC-01)
[0034] Fermentation medium 1 was used. The specific steps are as follows: first inoculate the strains into the seed culture medium, shake the shaker at 25-35°C, and the rotation speed is 135rpm. After 24 hours of cultivation, insert the fermentation medium at an inoculum size of 10%, and shake fully during inoculation, so that The cells are evenly dispersed, and cultured at a constant temperature of 25-35°C for 10 days. Take out the cellulose membrane, rinse with deionized water several times to remove the medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane, immerse the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH, boil at 100°C for 1 hour, remove the bacterial cells and residual medium in the membrane, Milky white and translucent, soak in deionized water overnight, then rinse with deionized water several times until the pH is about 7.2, then centrifuge in a 250ml centrifuge tube at 4000rpm for 40min...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3, adopt fermentation medium 2. The specific steps are as follows: first inoculate the strains into the seed culture medium, shake the shaker at 25-35°C, and the rotation speed is 135rpm. After 24 hours of cultivation, insert the fermentation medium at an inoculum size of 10%, and shake fully during inoculation, so that The cells are evenly dispersed and cultured with constant temperature shaking at 25-35°C for 5 days. The following steps are the same as in Example 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com