Multiphase transverse magnetic field permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
A permanent magnet linear synchronous and transverse magnetic field technology, which is applied to synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc. Simple, high control characteristics, high force density results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
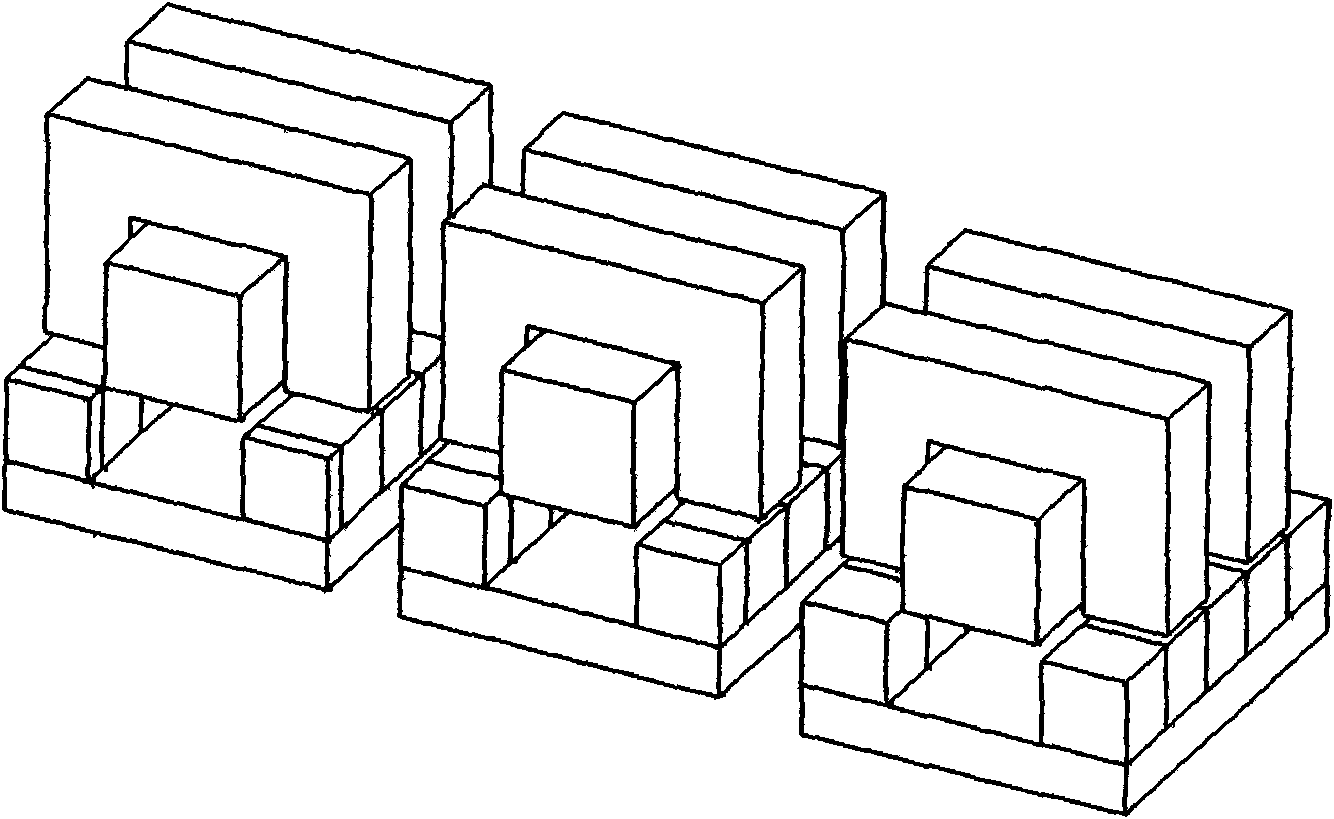
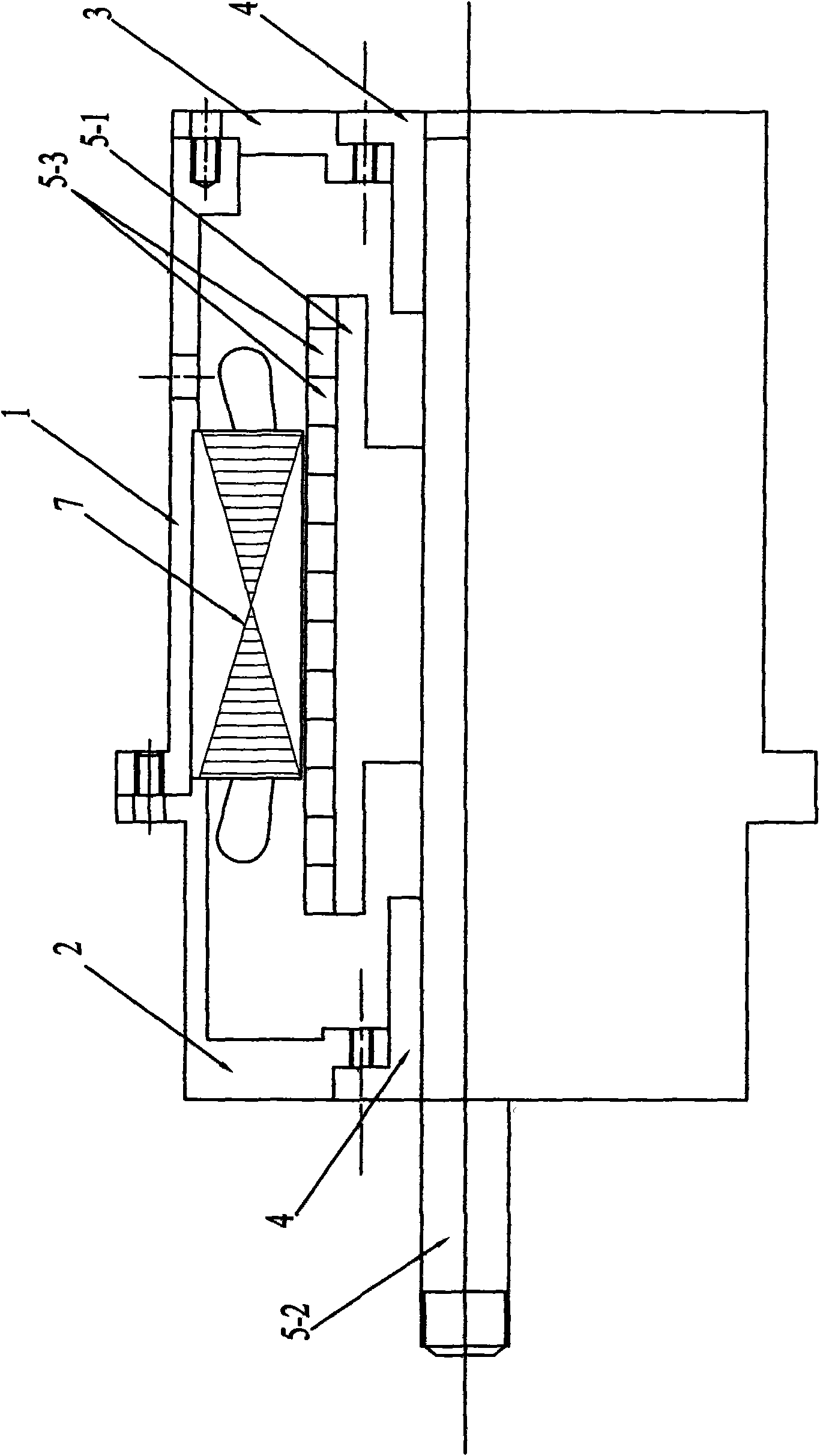
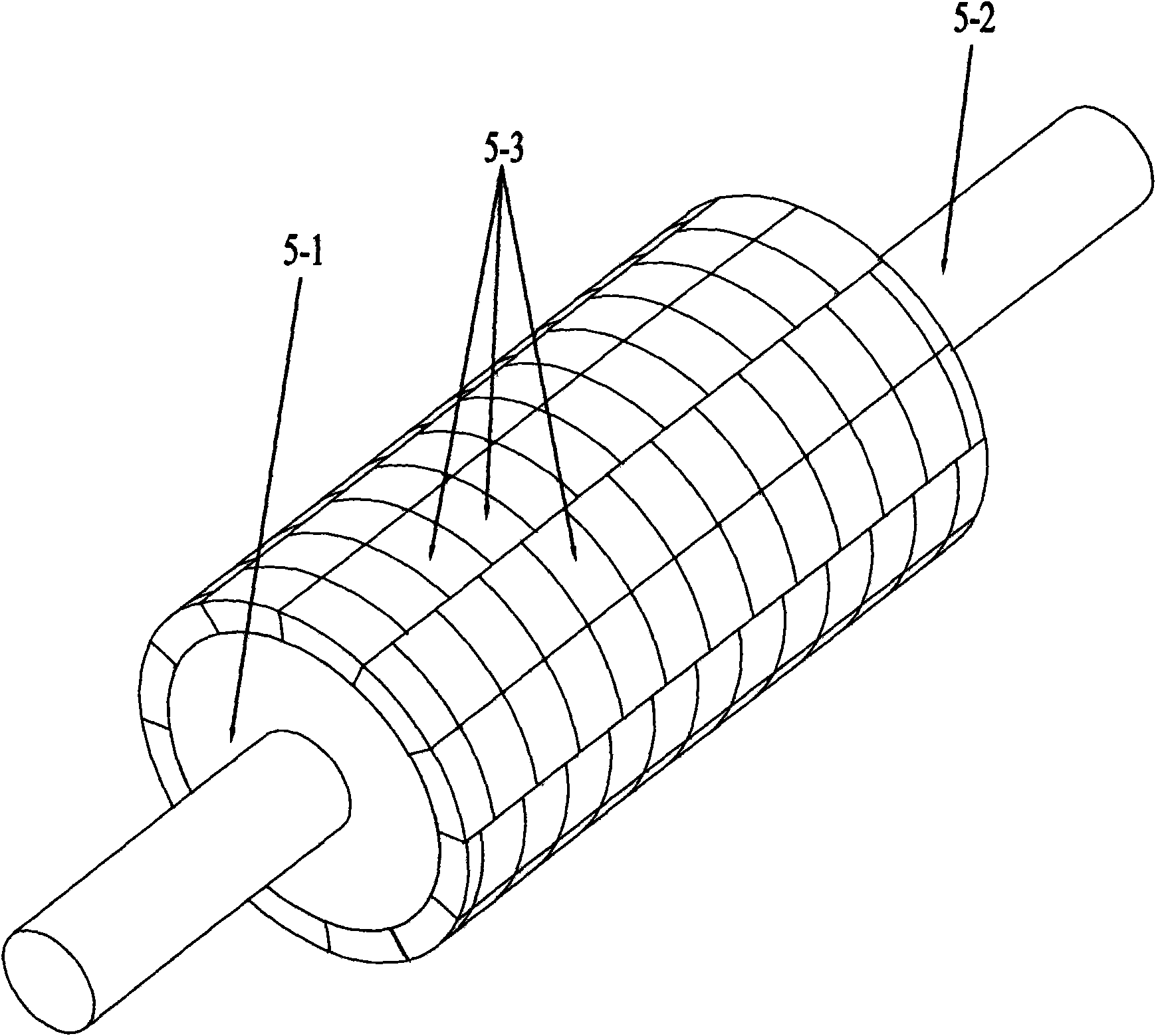
[0008] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 9 , Figure 10 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment is composed of a casing 1, a front end cover 2, a rear end cover 3, two linear bearings 4, a mover assembly and a stator assembly; the front end cover 2 and the rear end cover 3 are respectively connected to the casing by bolts The two ends of 1 are fixedly connected; the stator assembly is installed inside the casing 1 by means of mechanical tight fit, and the mover assembly is connected to the front end cover 2 through two linear bearings 4 installed on the front end cover 2 and the rear end cover 3 It is slidingly connected with the rear end cover 3, and there is an air gap between the mover assembly and the stator assembly; the mover assembly is composed of a cylindrical mover core 5-1, a mover shaft 5-2 and a plurality of permanent magnets 5- 3 components; the mover shaft 5-2 is set through the center of the cylindrical mover core 5-1...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0009] Specific implementation mode two: combination Image 6 Describe this embodiment, the first difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that the magnetically conductive core ring 6-1 is a split type iron core with a polar arc coefficient equal to 1, that is, the magnetically conductive core ring 6-1 is the number and cylindrical A split iron core composed of I-shaped stator teeth 6-1-1 with the same number of permanent magnet bars on the outer circumferential surface of the mover iron core 5-1. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0010] Specific implementation mode three: combination Figure 8 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that the magnetically conductive core ring 6-1 is a split type iron core with a polar arc coefficient less than 1, that is, the magnetically conductive core ring 6-1 is a A split iron core composed of I-shaped stator teeth 6-1-1 with the same number of permanent magnet bars on the outer circumferential surface of the sub-iron core 5-1, and two I-shaped stator teeth 6-1-1 opposite to the permanent magnet bars of each phase 1-1 Integral structure, there is a gap between two stator teeth consisting of two I-shaped stator teeth 6-1-1 of an integral structure opposite to each adjacent two-phase permanent magnet strip. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in Embodiment 1. This structure can eliminate the coupling between the phases.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com