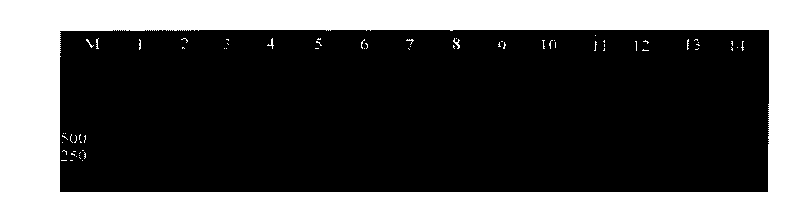Nested PCR detection method of oak wilt
A detection method, the technology of Quercus wilt, which is applied in the detection of Quercus fusarium wilt and the nested PCR detection of Quercus fusarium wilt, can solve the problems that have not been reported, and achieve the effects of strong reliability, simple procedure, and shortened quarantine period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The nested (Nested) PCR detection of embodiment 1 oak wilt
[0033] Follow these steps:
[0034] 1. Sample DNA Extraction
[0035] 1.1 DNA extraction from mycelium samples
[0036] 1.1-1 Test strain culture and mycelium collection
[0037] The tested strains were inoculated on PDA medium, cultured in the dark at 20-25°C for 10 days, the mycelium was gently scraped off with an inoculation needle, placed in a centrifuge tube, freeze-dried, and stored at -20°C for future use.
[0038] 1.1-2 Use the CTAB method to extract mycelial DNA, the specific operation is as follows:
[0039] 1) Take 0.5g of frozen mycelium, put it in a 2.0ml flat-bottomed centrifuge tube, add 2 steel balls with a diameter of 3mm, close the cap, put it on the Oscillating Mill MM400 grinder, 30f / min, and grind for 3 minutes;
[0040]2) Take out the steel ball, add 500 μl CTAB, freeze in liquid nitrogen for 2 minutes, then bath in 75°C water bath for 2 minutes, repeat twice, and finally melt in 75°C...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2 Specific Amplification Sensitivity Test
[0071] Dilute the DNA of strain Ceratocystisfagacearum ATCC 200423 into different concentration gradients, 1×10 2 pg / μl, 10pg / μl, 1pg / μl, 1×10 -1 pg / μl, 1×10 -2 pg / μl, take 1μl of DNA of each concentration as a template, and use only specific primers CF01 / CF02 for PCR amplification once, and the electrophoresis results after amplification are shown in figure 2 . The same results were obtained by repeating the amplification three times.
[0072] figure 2 Among them, M is a 2000-bp DNA marker; 1-5 represent the amplification products with DNA concentrations of 100pg, 10pg, 1pg, 0.1pg, and 0.01pg in the 25μl reaction system; 6 is the negative control. figure 2 It was shown that the minimum detectable bacterial DNA concentration was 10 pg / μl when the specific primers CF01 / CF02 were used only for one PCR amplification.
Embodiment 3
[0073] The sensitivity test of embodiment 3Nested PCR
[0074] Same as Example 2, the DNA of bacterial strain Ceratocystisfagacearum ATCC 200423 was diluted into different concentration gradients, respectively 1 × 10 2 pg / μl, 10pg / μl, 1pg / μl, 1×10 -1 pg / μl, 1×10 -2 pg / μl, take 1 μl as a template, and perform two rounds of amplification, the first round and the second round, in sequence according to step 2 and step 3 of Example 1.
[0075] The electrophoresis results of the products obtained after two rounds of amplification are shown in image 3 , in the figure, M is a 2000-bp DNA marker; 1-5 are amplification products in 25μl reaction system with DNA concentrations of 100pg, 10pg, 1pg, 0.1pg, and 0.01pg; 6 is a negative control. From image 3 It was shown that after two rounds of PCR amplification, the lowest detectable bacterial DNA concentration was 1pg / μl.
[0076] with Example 2 figure 2 In comparison, it can be seen that the Nested PCR of the present invention use...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com