Bioreactor for culturing tissue engineered esophageal stent
A bioreactor and tissue engineering technology, which is applied in the field of constructing and cultivating tissue engineered organs, can solve the problems of insignificant shear stress and functional impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
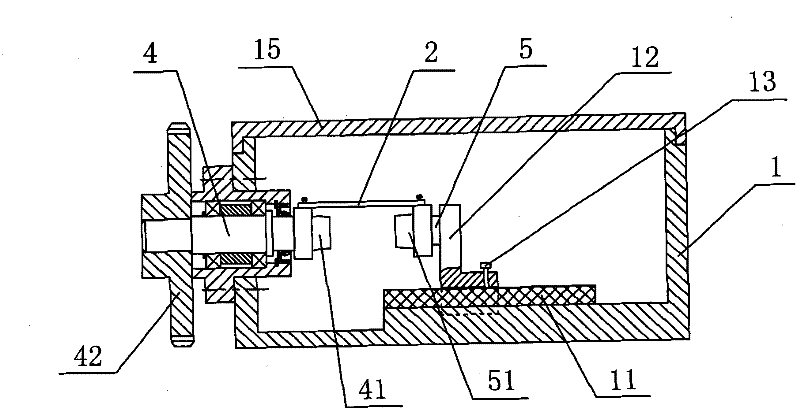
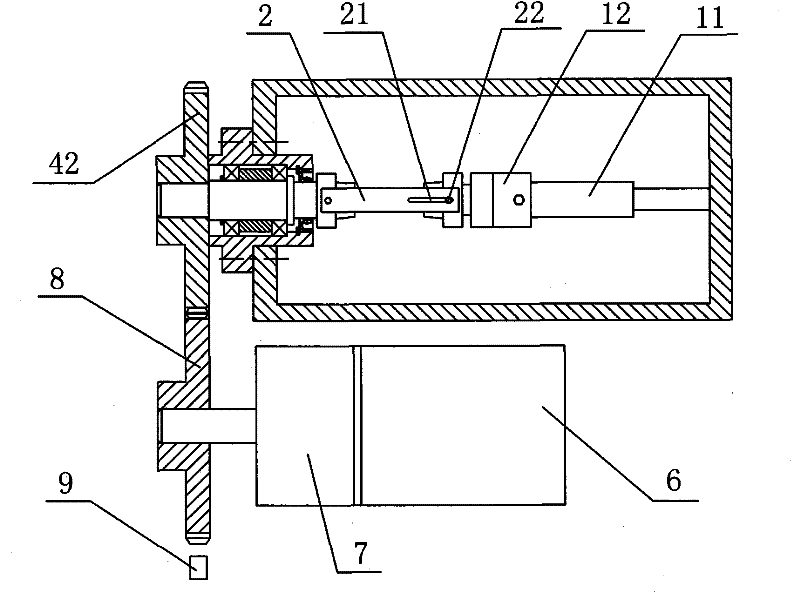
[0016] Embodiment 1: As shown in the figure, a bioreactor for cultivating an esophageal scaffold for tissue engineering includes a box body 1, a transmission connecting plate 2, a motor 6, a speedometer 9, a coaxial transmission shaft 4 and a The moving shaft 5 is fixed with a guide rail 11 on the inner bottom surface of the box body 1, and a shaft seat 12 is slidably arranged on the guide rail 11, and the shaft seat 12 is screwed with a first fixing screw 13 for fixing the shaft seat 12 on the guide rail 11 , the driven shaft 5 is axially connected to the shaft seat 12, the transmission shaft 4 is axially connected to one side of the box body 1, the first bracket joint 41 is fixedly arranged on the transmission shaft 4, and the second bracket joint 41 is fixedly arranged on the driven shaft 5. The bracket joint 51, one end of the transmission connecting plate 2 is fixedly arranged on the first bracket joint 41, the other end of the transmission connecting plate 2 is provided w...
Embodiment 2
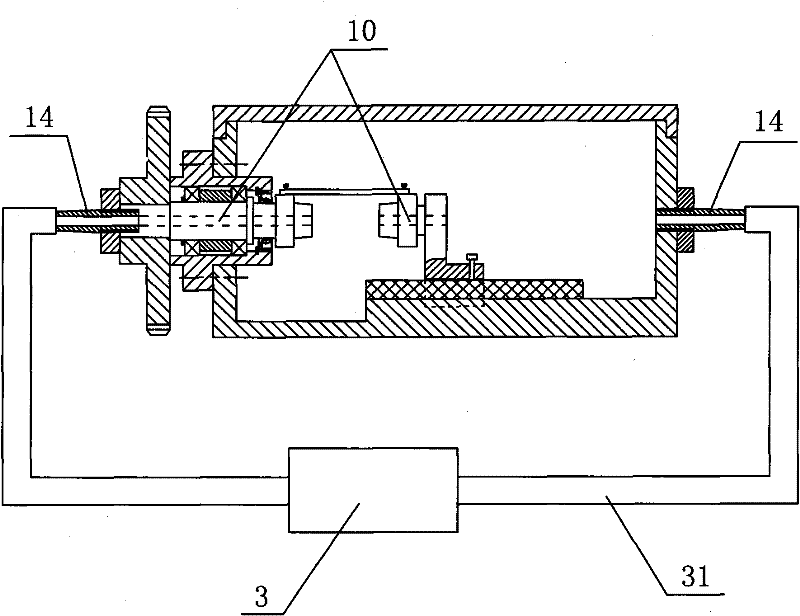
[0017] Embodiment 2: As shown in the figure, other structures are the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that it also includes a peristaltic pump 3, and the outer end of the transmission shaft 4 and the other side of the box body 1 are respectively provided with pipe joints 14, and the transmission shaft 4. The first support joint 41, the second support joint 51 and the driven shaft 5 are respectively provided with coaxial through holes 10, the through holes 10 communicate with the pipe joint 14, and the pipe joint 14 is connected with the peristaltic pump 3 through the pipe 31 .
[0018] In the above-described embodiment, when the motor 6 is working, the instant speed of the driving gear 8 can be measured by the tachometer 9, and then the output speed of the motor 6 can be adjusted according to the actual required speed, so as to obtain the actually required speed of the transmission shaft 4; In addition, when the motor 6 is not working (that is, the cultured esophageal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com