Pulsating heat pipe heat-transfer device for low grade heat energy utilization
A pulsating heat pipe, low-grade technology, applied in tubular elements, heat exchange equipment, indirect heat exchangers, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient use of heat pipes, difficulty in adding fins, large heat transfer resistance, etc., and achieve compact structure , light weight, good heat transfer effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
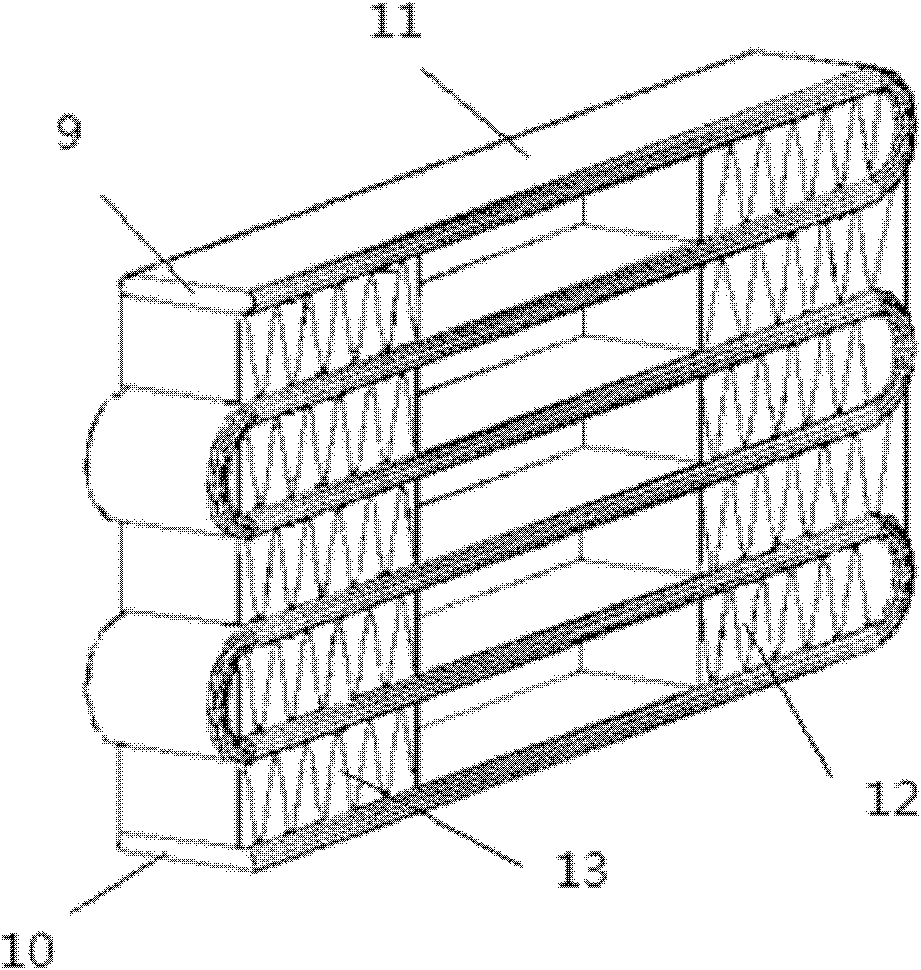
[0026] The single row of porous flat tubes 11, which are made of aluminum, are divided into many channels by a grille 14 in the middle and closed at both ends, and are bent into multiple layers, forming a heating section 17 and a cooling section 15, and the middle section is an adiabatic section 16. The channels are all square holes, which are more conducive to the heat transfer of the pulsating heat pipes. Each serpentine pipe in the single row of porous flat tubes 11 forms an open serpentine pipe respectively, thus forming several open-circuit pulsating heat pipes connected in parallel. The inside of the serpentine pipe is evacuated and filled with 30% ammonia by volume. Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of the channel connection of this kind of pulsating heat pipe. Between the heating section 17 and the cooling section 15, two adjacent layers of single-row porous flat tubes 11 are brazed with corrugated fins 13 in the heating section and corrugated fins 12 in the cooling s...
Embodiment 2
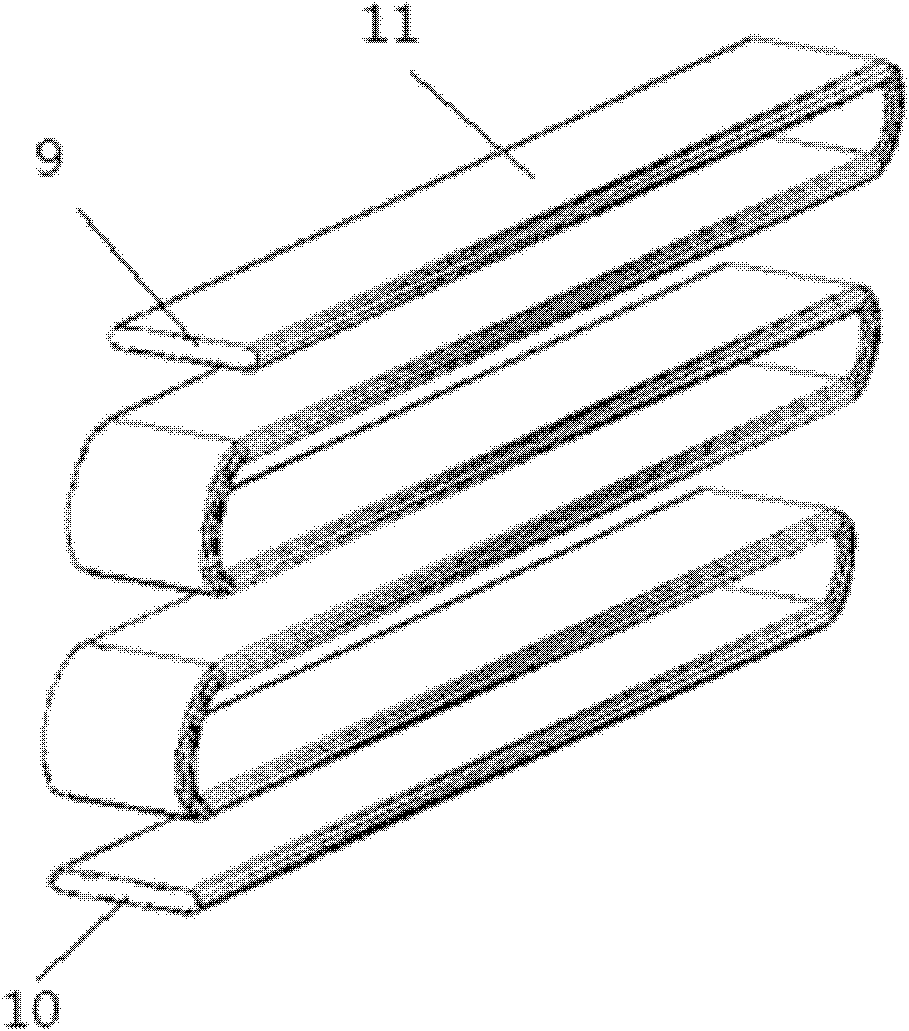
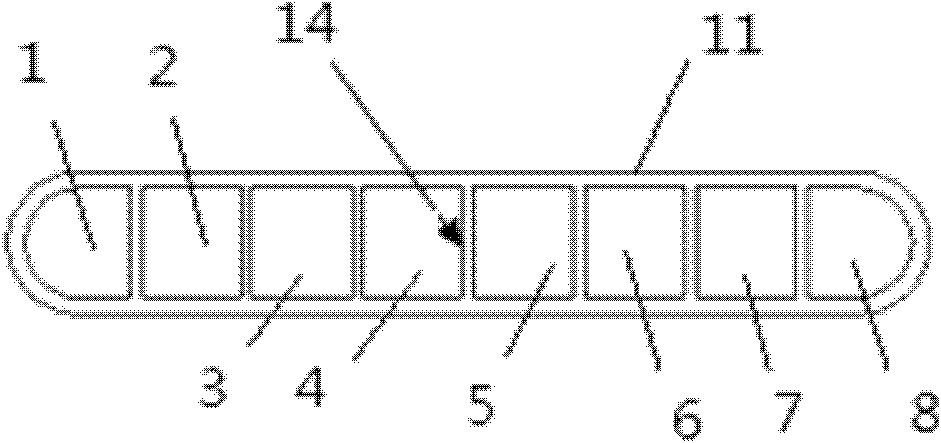
[0029] A single row of porous flat tubes made of copper is divided into many channels by a grid in the middle and closed at both ends, and is bent into multiple layers to form a heating section and a cooling section. The middle section is an adiabatic section 16, and all channels are square. holes, which are more conducive to the heat transfer of the pulsating heat pipe, and each passage in the single row of porous flat tubes 11 forms a serpentine pipe respectively, and then through further processing (taking 8 passages as an example, see figure 1 ): the first serpentine duct 1 and the second serpentine duct 2, the third serpentine duct 3 and the fourth serpentine duct 4, the fifth serpentine duct 5 and the sixth serpentine duct 6, the seventh serpentine duct 7 and the eighth serpentine duct 8 cut off a part of the grille 14 at the front end 9; at the same time, the second serpentine duct 2 and the third serpentine duct 3, the fourth serpentine duct 4 and the fifth serpentine d...
Embodiment 3
[0032] A single row of porous flat tubes 11 made of copper, divided into many channels by a grid 14 in the middle and closed at both ends, is bent into multiple layers, forming a heating section 17 and a cooling section 15, and the middle section is an adiabatic section 16. The passages are all square holes, which are more conducive to the heat transfer of the pulsating heat pipes. Each passage in the single row of porous flat tubes 11 forms a serpentine pipe respectively, and then through further processing (taking 8 passages as an example, see figure 1 ): between the first serpentine duct 1 and the second serpentine duct 2, the third serpentine duct 3 and the fourth serpentine duct 4, the fifth serpentine duct 5 and the sixth serpentine duct 6, the seventh serpentine duct A part of the grille 14 between the serpentine duct 7 and the eighth serpentine duct 8 is cut off at the front end 9 and the tail end 10 simultaneously, like this, the first serpentine duct 1 and the second ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com